Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2022; 28(42): 6017-6033
Published online Nov 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i42.6017
Published online Nov 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i42.6017
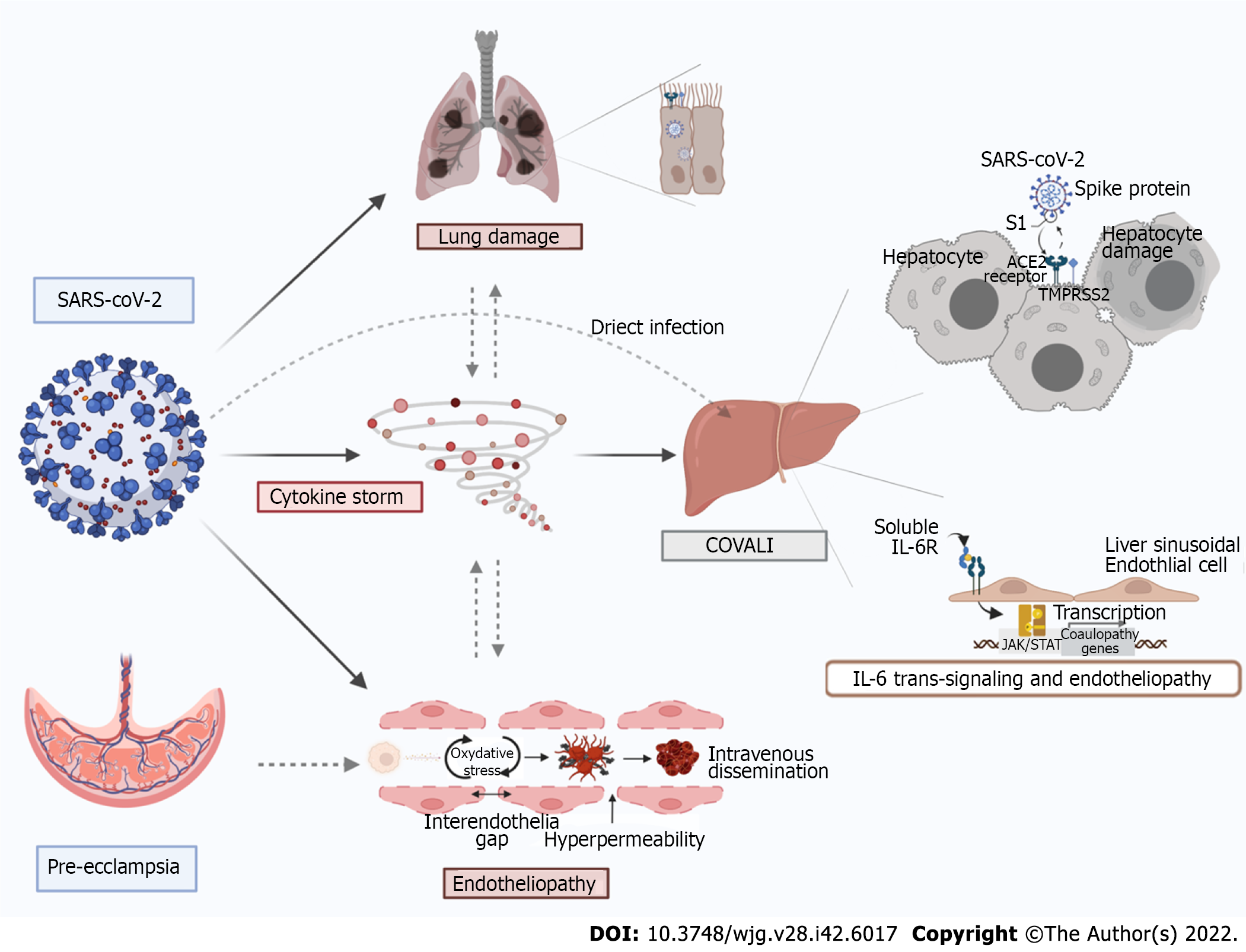
Figure 1 Mechanisms of COVID-19-associated liver injury: Inter-organ crosstalk.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) enters host cells via interaction of its spike protein with the receptor angiotensin converting enzyme 2 in the presence of TMPRSS2 in many tissues. Proposed mechanisms for SARS-CoV-2-mediaded liver injury include: (1) Direct viral cytopathic effect; (2) IL-6 trans-signaling in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells which leads to endotheliopathy; (3) cytokine storm-induced damage; and (4) hypoxemic injury. There is also a lung-gut crosstalk which promotes an increased inflammatory state as well as dysbiosis which increases intestinal permeability, thus facilitating viral entry. Furthermore, direct viral injury to the vascular endothelium leads to increased cytokine release, enhanced reactive oxygen species production and thrombo-embolic events involving both micro and macro circulation. In a similar fashion, pre-eclampsia spectrum syndromes cause inflammation and endotheliopathy that pre-disposes to liver injury and can be synergistic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and COVID-19 associated liver injury. Original figure was created with BioRender.com.
- Citation: Cooper KM, Colletta A, Asirwatham AM, Moore Simas TA, Devuni D. COVID-19 associated liver injury: A general review with special consideration of pregnancy and obstetric outcomes. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(42): 6017-6033
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i42/6017.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i42.6017