Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2022; 28(33): 4744-4761
Published online Sep 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i33.4744
Published online Sep 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i33.4744
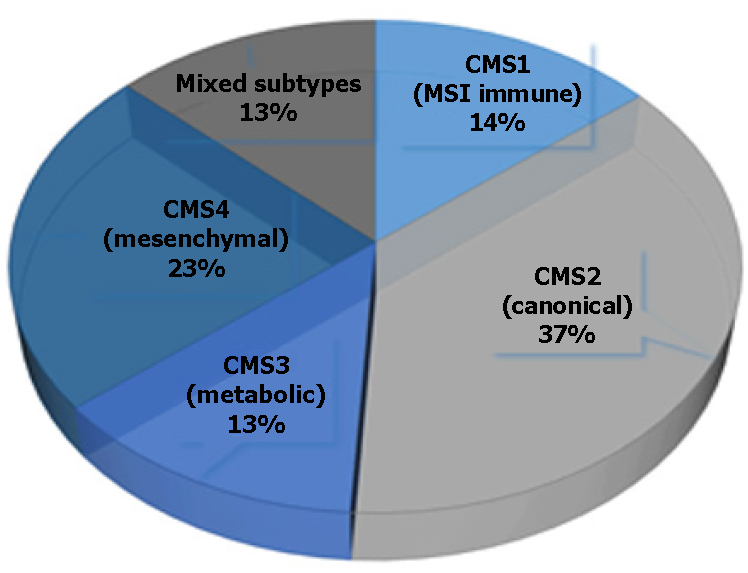
Figure 1 Representation of individual colorectal cancer subtypes.
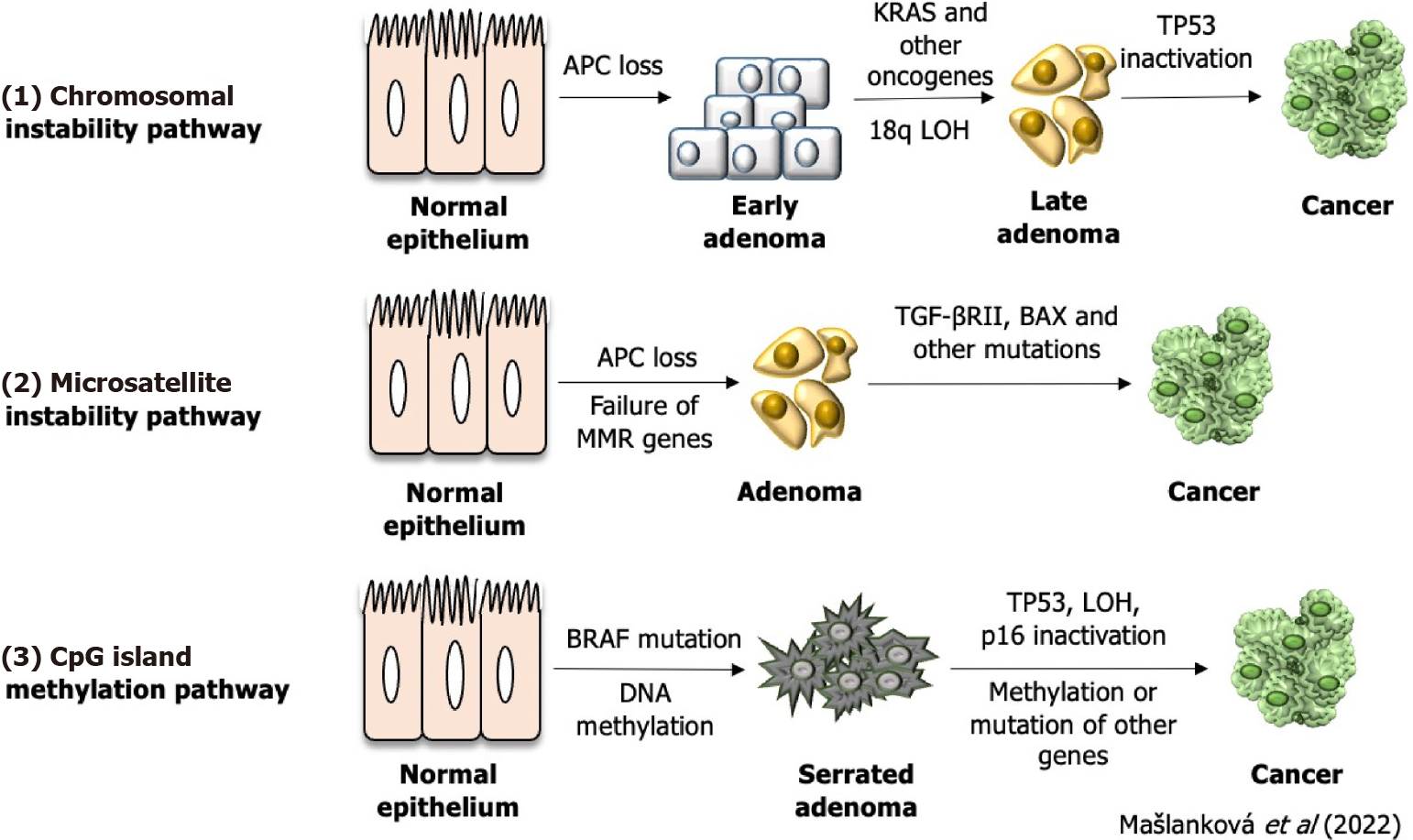
Figure 2 Three genetic and epigenetic aberrations of colorectal cancer formation.
LOH: Loss of heterozygosity; TGF: Transforming growth factor.
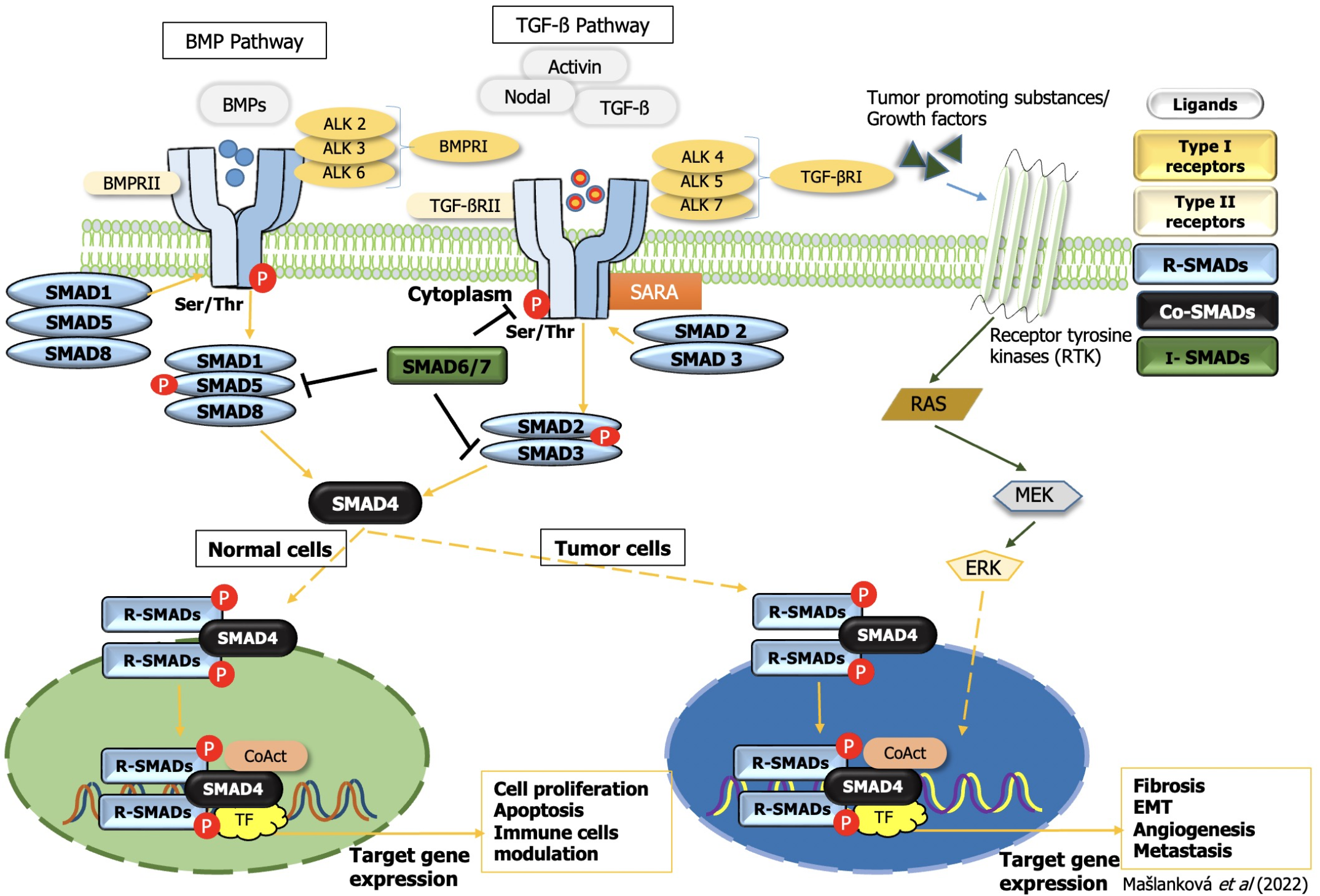
Figure 3 Transforming growth factor-beta superfamily signal transduction.
TGF: Transforming growth factor; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; BMP: Bone morphogenetic protein; SMAD: Small mothers against decapentaplegic homolog.
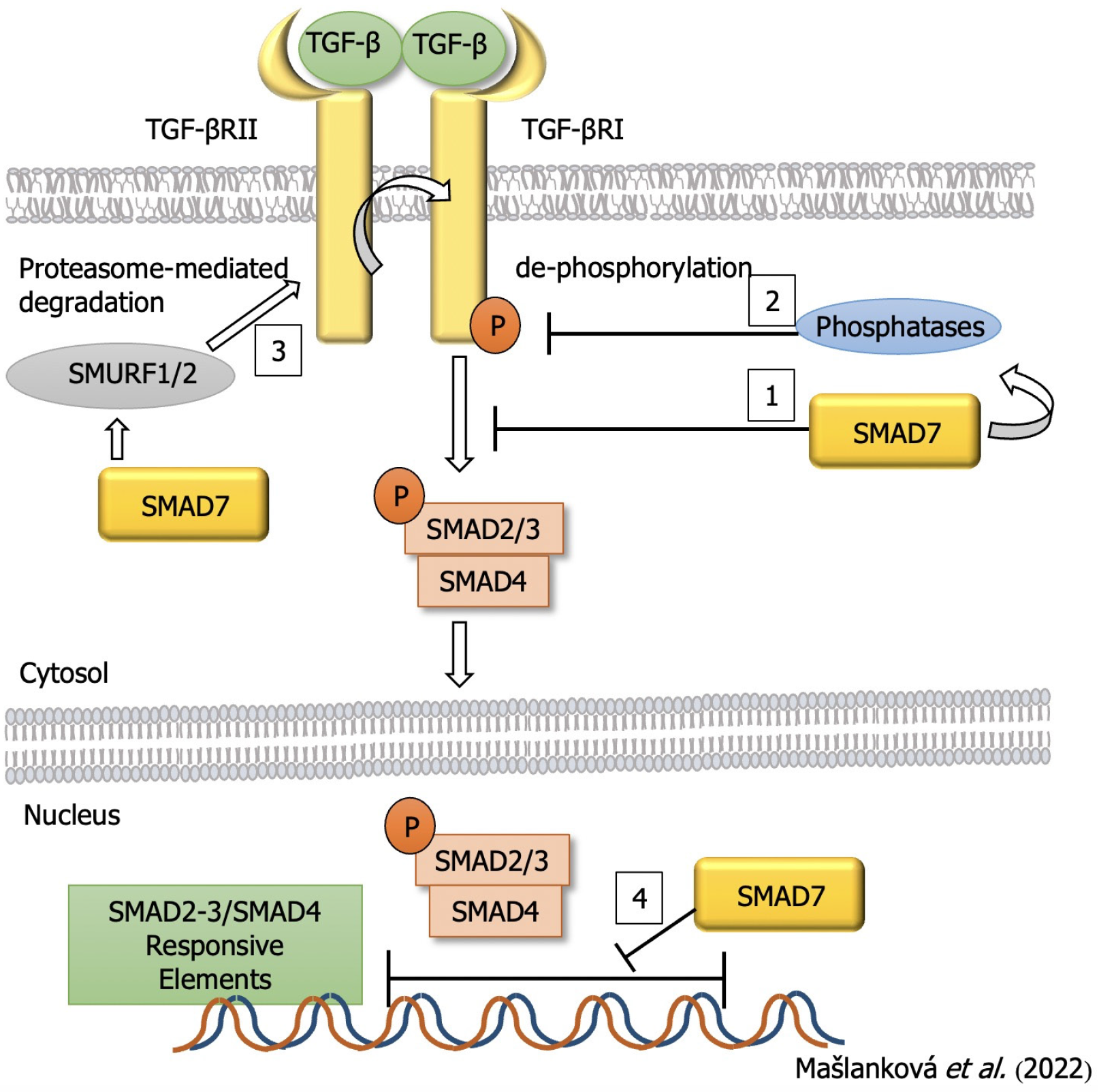
Figure 4 Inhibitory effect of small mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7 on the process of colorectal cancer development.
TGF: Transforming growth factor; SMAD: Small mothers against decapentaplegic homolog.
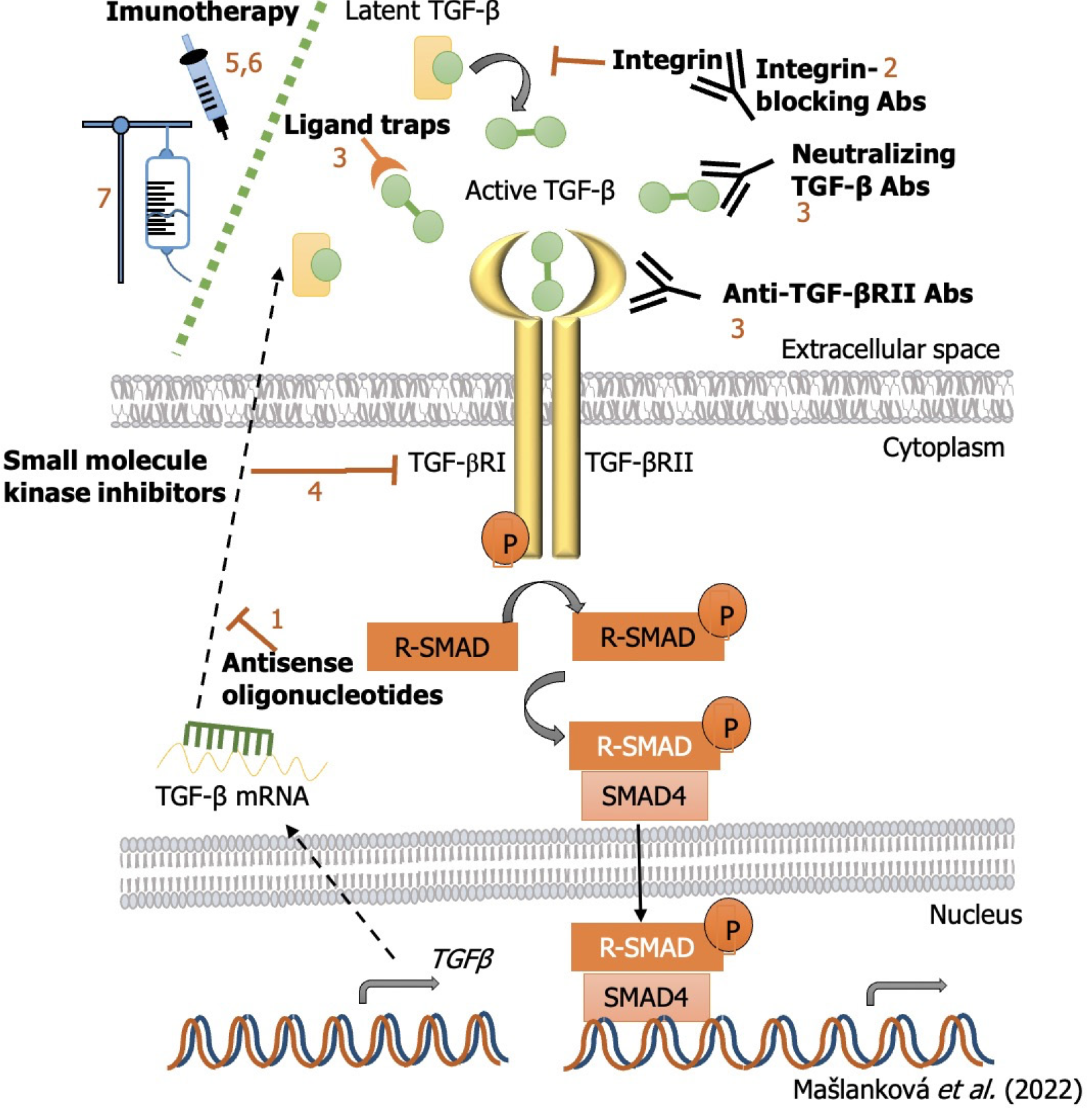
Figure 5 Inhibition strategies of transforming growth factor-β signaling pathway and miRNAs targets for colorectal cancer treatment.
TGF: Transforming growth factor; SMAD: Small mothers against decapentaplegic homolog.
- Citation: Maslankova J, Vecurkovska I, Rabajdova M, Katuchova J, Kicka M, Gayova M, Katuch V. Regulation of transforming growth factor-β signaling as a therapeutic approach to treating colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(33): 4744-4761
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i33/4744.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i33.4744