Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2022; 28(32): 4574-4599
Published online Aug 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4574
Published online Aug 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4574
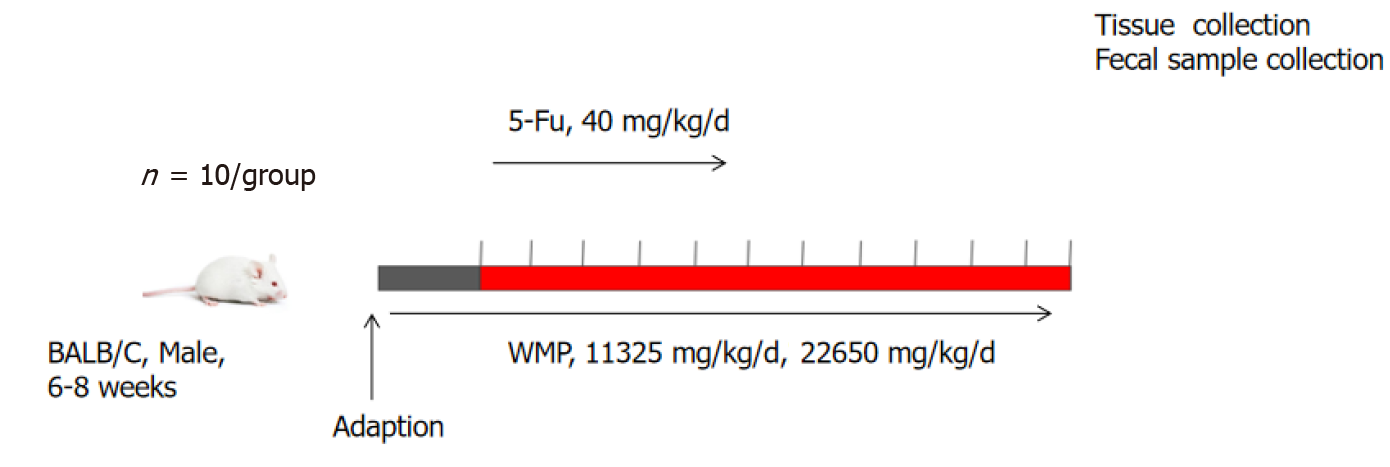
Figure 1 Flow chart of modeling and drug delivery.
WMP: Wumei pills; 5-Fu: 5-fluorouracil.
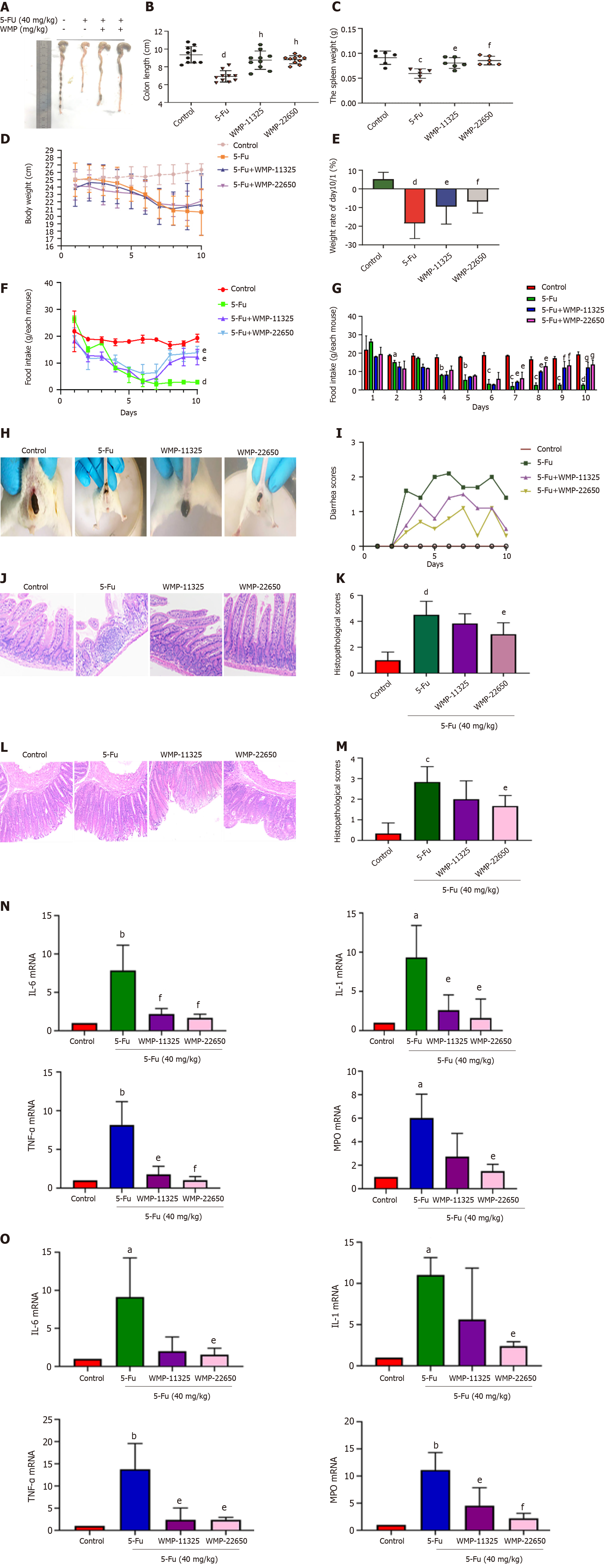
Figure 2 Effect of Wumei pills on routine observation, histopathological assessment (n = 10, 200 ×), and inflammatory cytokines on intestinal mucositis in mice.
A and B: Colon length; C: Spleen weight; D and E: Body weight; F and G: Food intake; H and I: Diarrhea scores; J and K: Histopathological assessment of the jejunum; L and M: Histopathological assessment of the colon; N: Levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6, IL-10, and myeloperoxidase (MPO) in the jejunum; O: Levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, and MPO in the colon. Values represent the mean ± SEM. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control group and eP < 0.05, fP < 0.01 vs 5-fluorouracil group. WMP: Wumei pills; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; 5-Fu: 5-fluorouracil.
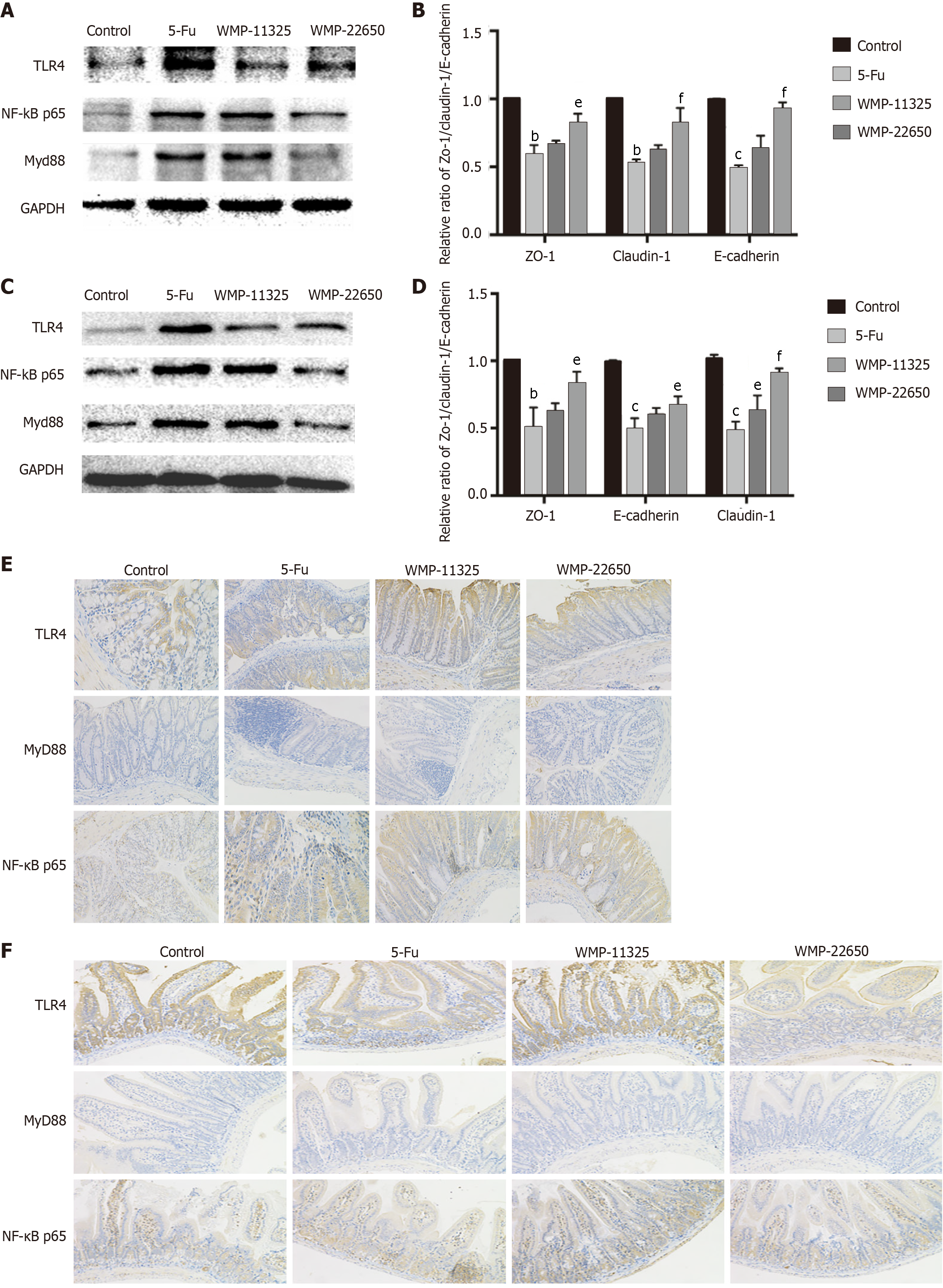
Figure 3 Effect of Wumei pills on expression of Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88/nuclear factor-κB pathway proteins as demonstrated by western blot and immunohistochemistry staining.
A and B: Expression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88), and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) proteins in the jejunum; C and D: Expression of TLR4, MyD88, and NF-κB proteins in the colon; E: Expression of TLR4, MyD88, and NF-κB proteins in the colon; F: Expression of TLR4, MyD88, and NF-κB proteins in the jejunum. WMP: Wumei pills; TLR4: Toll-like receptor4; MyD88: Myeloid differentiation factor 88; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; 5-Fu: 5-fluorouracil.
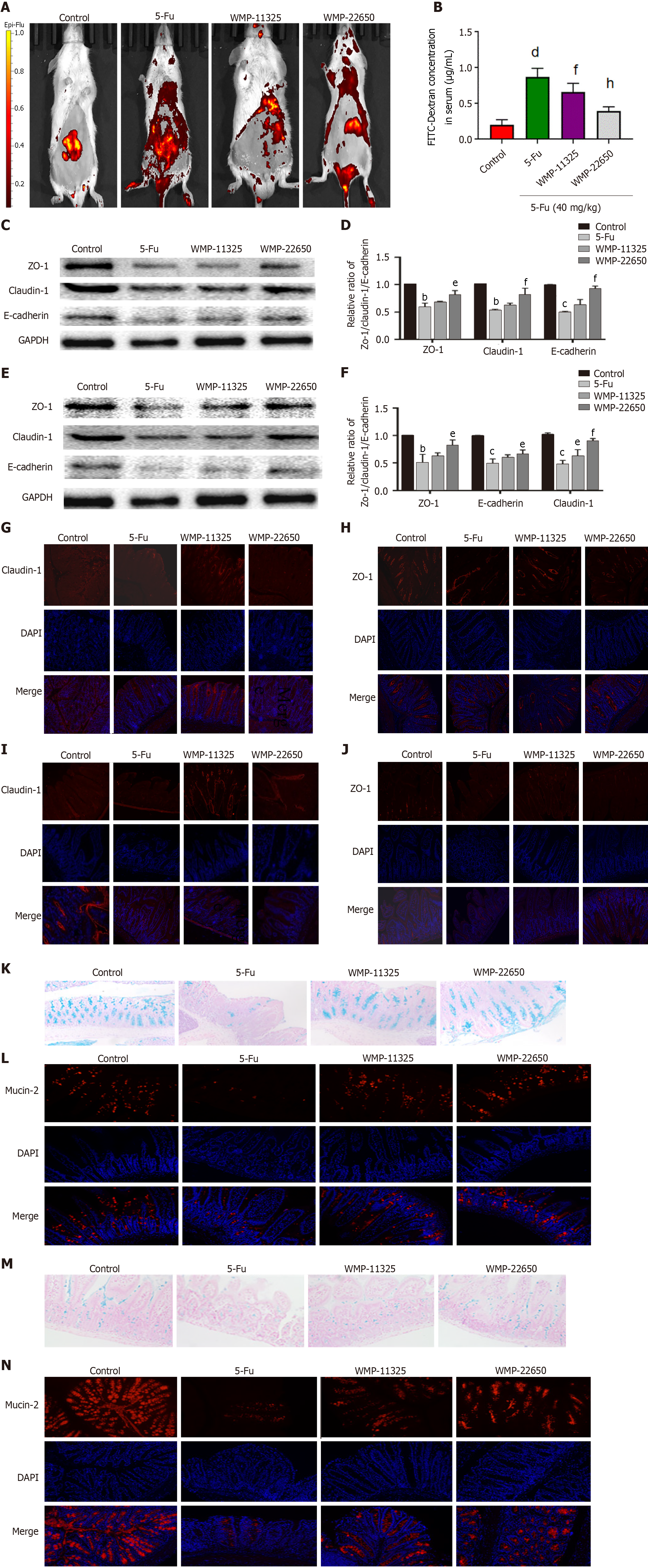
Figure 4 Effect of Wumei pills on intestinal leakage and expression of mucosal barrier proteins.
A: Representative fluorescent images of mice assessed by IVIS. Excitation: 480 nm; emission: 520 nm; B: Concentration of dextran measured by mean fluorescence intensity of FITC in serum; C and D: Expression of zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), E-cadherin, and claudin-1 proteins in the jejunum; E and F: Expression of ZO-1, E-cadherin, and claudin-1 proteins in the colon; G and H: Expression of ZO-1 and claudin-1 proteins in the jejunum; I and J: Expression of ZO-1 and claudin-1 proteins in the colon; K and L: Alcian blue staining and immunofluorescence staining for mucin-2 in the jejunum; M and N: Alcian blue staining and immunofluorescence staining for mucin-2 in the jejunum. Values represent the mean ± SEM. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001 vs control group and eP < 0.05, fP < 0.01, hP < 0.0001 vs 5-fluorouracil group. WMP: Wumei pills; ZO-1: Zonula occludens-1; 5-Fu: 5-fluorouracil.
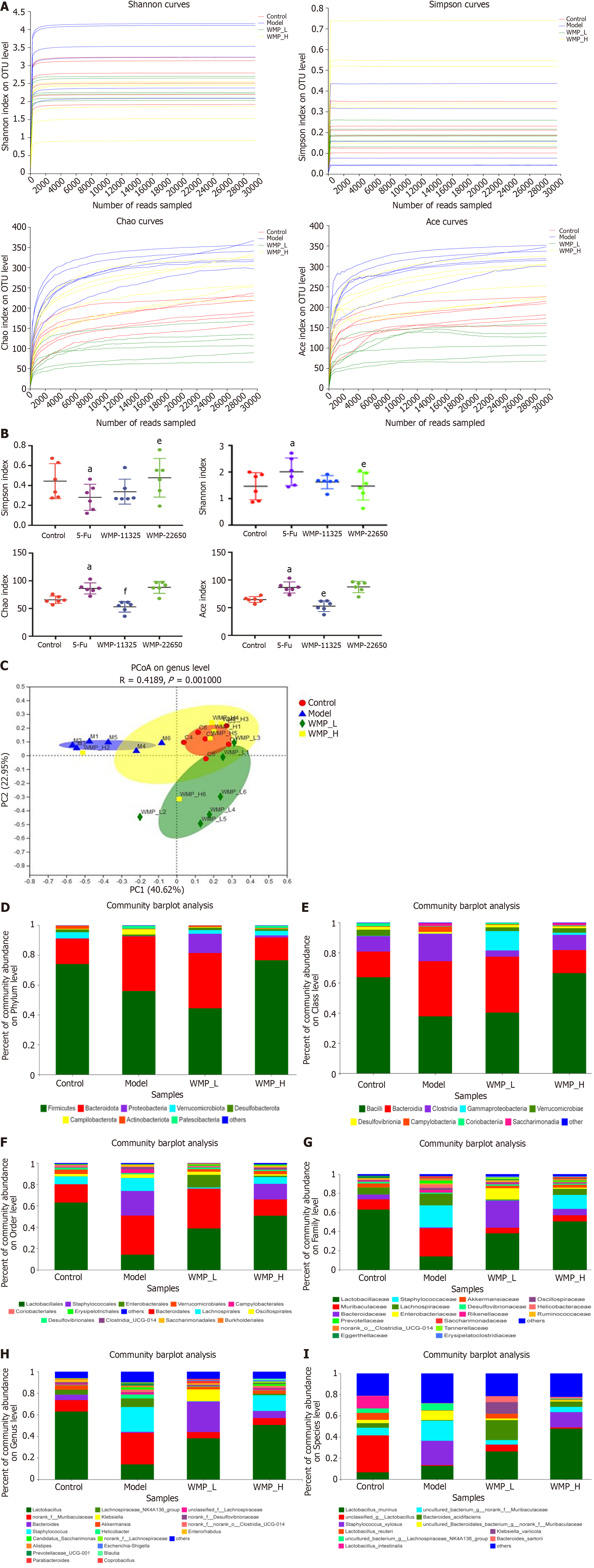
Figure 5 Microbial alpha, beta diversity, and taxonomy analysis.
A: Dilution curve analysis; B: Alpha diversity (Shannon index, Simpson index, Ace index, and Chao index); C: Beta diversity; D-I: Taxonomy analysis of microbiota community. Values represent the mean ± SEM. aP < 0.05 vs control group and eP < 0.05, fP < 0.01 vs 5-Fu group. WMP: Wumei pills; 5-Fu: 5-fluorouracil.
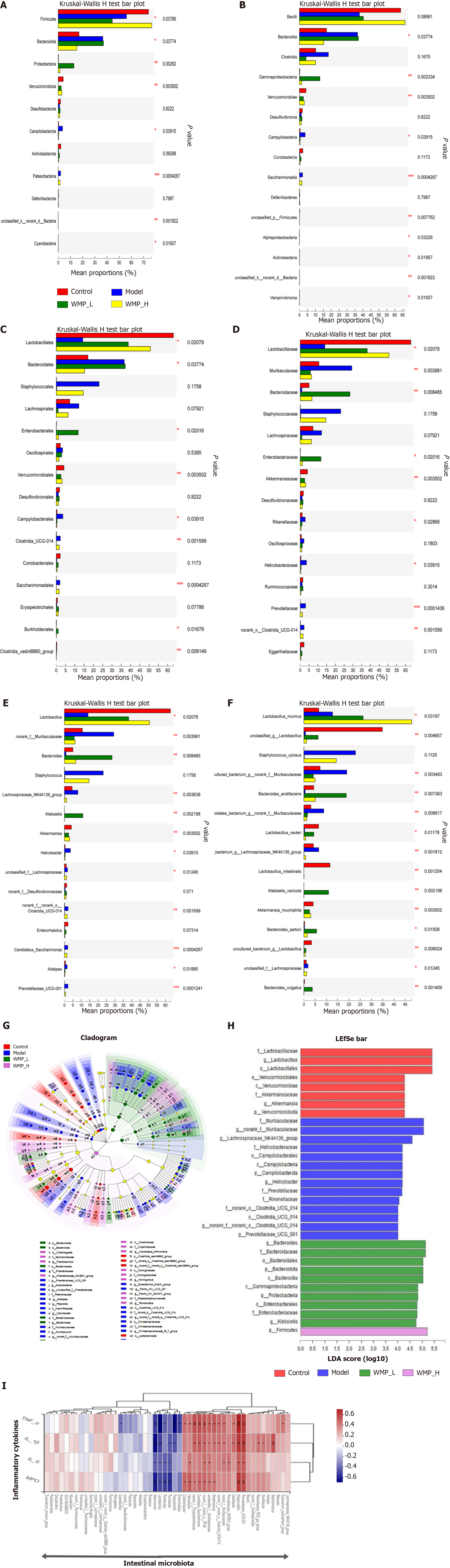
Figure 6 Kruskal-Wallis analysis of different bacterial groups, LEfse analysis, and microbiota-cytokine correlation.
A: Phylum level; B: Class level; C: Order level; D: Family level; E: Genus level; F: Species level; G: Overall exhibition of LEfse analysis by cladogram; H: LDA scores of the specific enriched genera in each group; I: Spearman analysis of microbiota-cytokine correlation. WMP: Wumei pills; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; MPO: Myeloperoxidase.
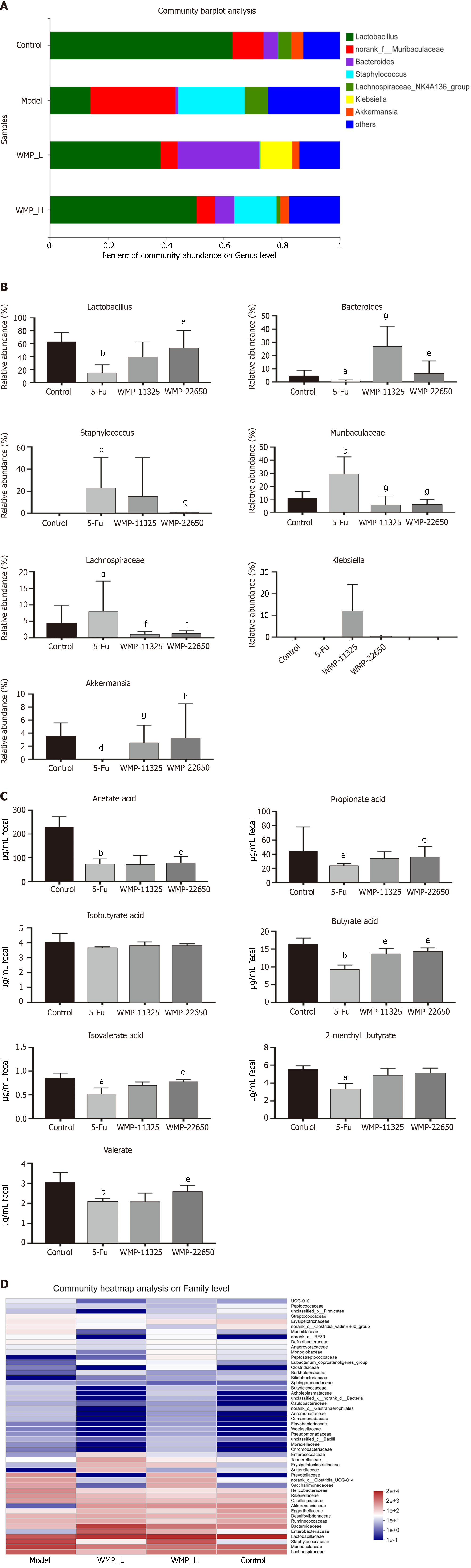
Figure 7 Effect of Wumei pills on taxonomy analysis of specific genera, the contents of short-chain fatty acids in feces, and heatmap of gut microbiota.
A: Relative abundance of specific genera at each sample; B: Relative abundance of Lactobacillus, Bacteroides, Staphylococcus, Muribaculaceae, Lachnospiraceae, Klebslella, and Akkermansla in each group; C: Effect of Wumei pills on the contents of short-chain fatty acids in feces; D: Heatmap of gut microbiota (family level). Values represent the mean ± SEM. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 and dP < 0.0001, compared with the normal group; eP < 0.05, fP < 0.01, gP < 0.001, and hP < 0.0001, compared with the 5-Fu group. WMP: Wumei pills; 5-Fu: 5-fluorouracil.
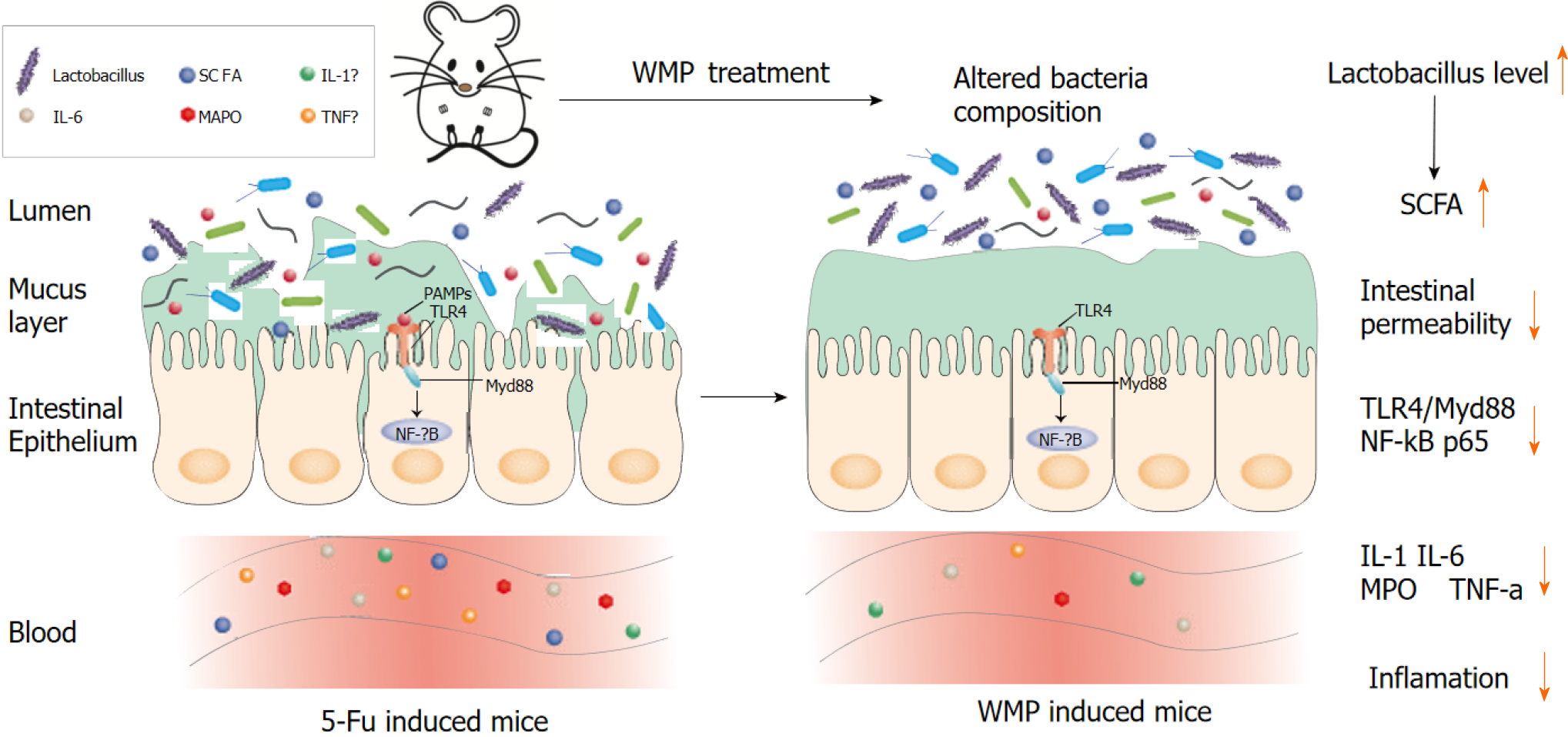
Figure 8 Schematic illustration of mechanisms for Wumei pills treatment in 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis.
WMP: Wumei pills; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; SCFAs: Short-chain fatty acids; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; MyD88: Myeloid differentiation factor 88; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; 5-Fu: 5-fluorouracil.
- Citation: Lu DX, Liu F, Wu H, Liu HX, Chen BY, Yan J, Lu Y, Sun ZG. Wumei pills attenuates 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis through Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88/nuclear factor-κB pathway and microbiota regulation. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(32): 4574-4599
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i32/4574.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4574