Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2022; 28(31): 4390-4398
Published online Aug 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4390
Published online Aug 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4390
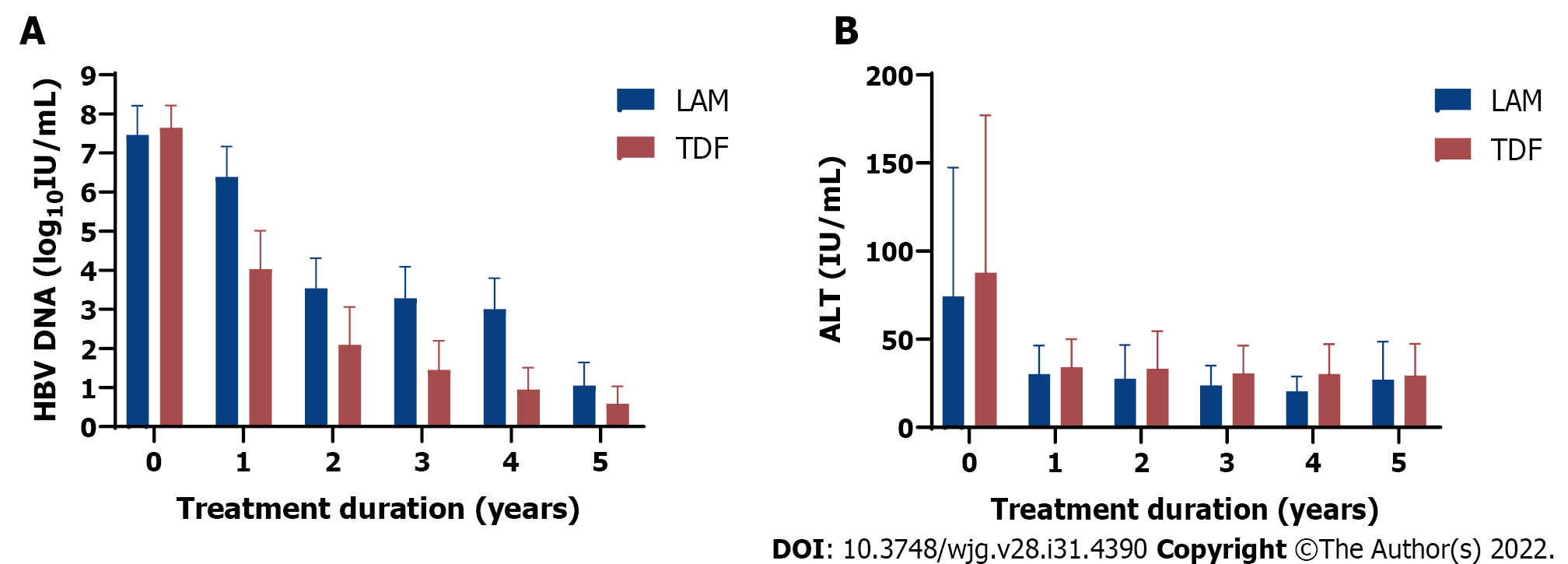
Figure 1 Comparison of clinical outcomes in 465 chronic hepatitis B patients receiving 1st generation (lamivudine or LAM, solid bar) vs 2nd generation (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate or TDF, dotted bar) hepatitis B virus nucleos(t)ide analog therapy from baseline (pre-treatment) followed for up to 5 years.
A: Hepatitis B virus DNA decline (log10 IU/mL); B: Mean alanine aminotransferase (IU/mL) decline from baseline after starting lamivudine or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. Mean with error bars representing standard deviation is plotted. LAM: Lamivudine; TDF: Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase.
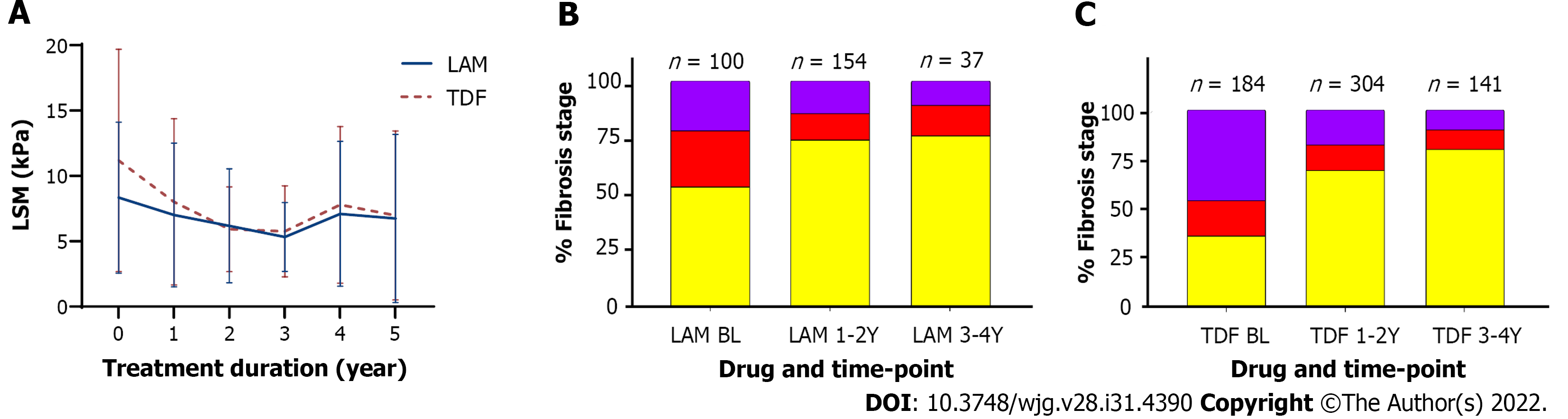
Figure 2 Comparison of lamivudine vs tenofovir disoproxil fumarate on liver stiffness measurement over time.
A: Liver stiffness measurement change from baseline (before treatment) and while on treatment; mean with error bars representing standard deviation is plotted; B and C: Comparison of fibrosis severity at baseline, 1-2 years, and 3-4 years post-treatment for lamivudine (B) and for tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (C). F0-F1 (yellow), F2-F3 (red), and F4 (purple). LSM: Liver stiffness measurement; LAM: Lamivudine; TDF: Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.
- Citation: Ramji A, Doucette K, Cooper C, Minuk GY, Ma M, Wong A, Wong D, Tam E, Conway B, Truong D, Wong P, Barrett L, Ko HH, Haylock-Jacobs S, Patel N, Kaplan GG, Fung S, Coffin CS. Nationwide retrospective study of hepatitis B virological response and liver stiffness improvement in 465 patients on nucleos(t)ide analogue. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(31): 4390-4398
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i31/4390.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4390