Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2022; 28(31): 4351-4362
Published online Aug 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4351
Published online Aug 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4351
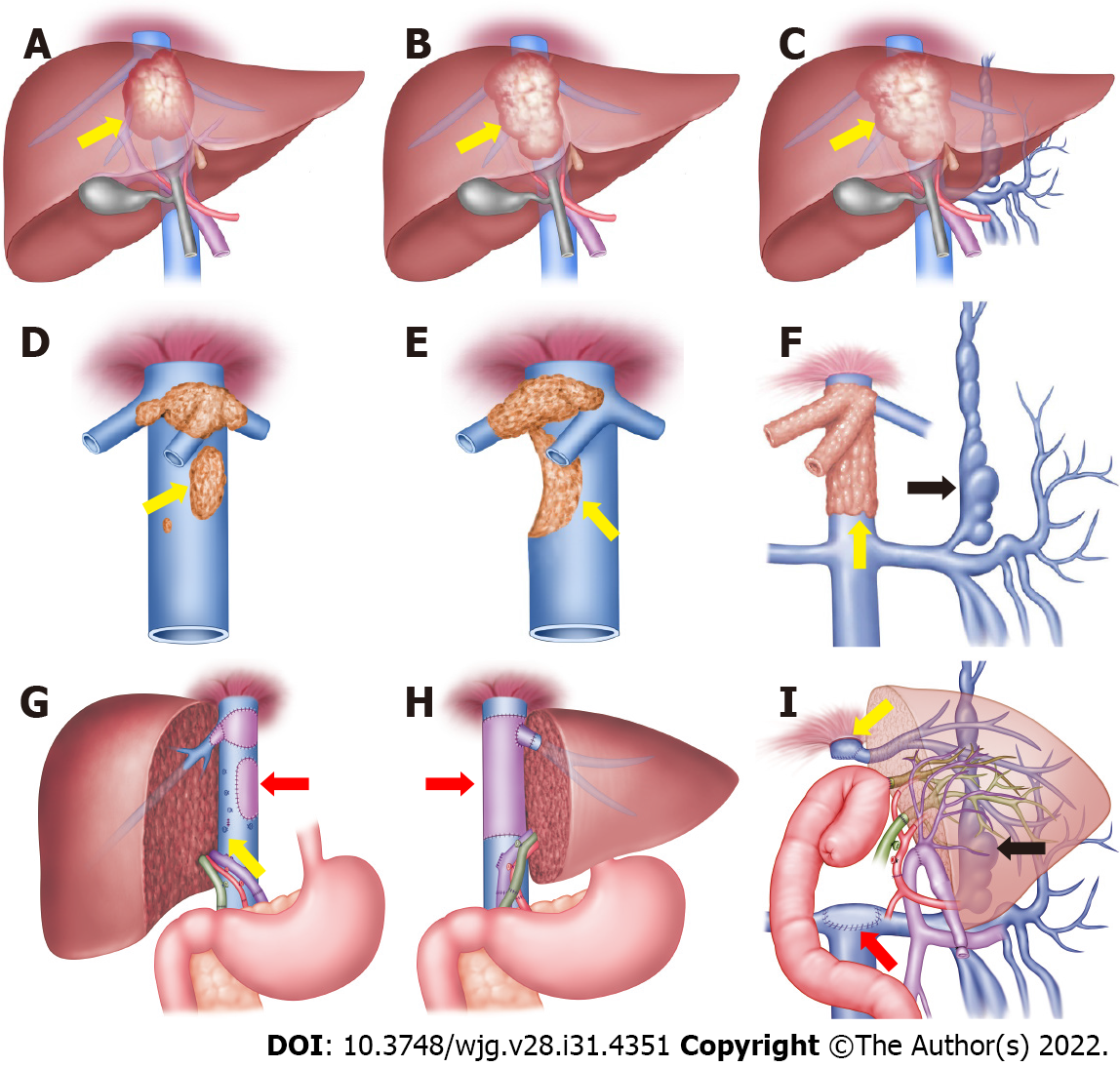
Figure 1 Schematic diagrams of retrohepatic inferior vena cava reconstruction methods.
A-C: Hepatic alveolar echinococcosis (AE) lesion invades the hepatocaval confluence; D: Retrohepatic inferior vena cava (RHIVC) is invaded by the AE lesion (yellow arrow); E: RHIVC is extensive invaded (yellow arrow); F: RHIVC completely occluded (yellow arrow), and compensation by the collateral branches (black arrow); G: Self-repairing reconstruction method, showed vascular patch repair (red arrow) and self-suture repair (yellow arrow); H: RHIVC replacement method, showed the RHIVC after replacement (red arrow); I: RHIVC resection without reconstruction method, showed IVC anastomoses with graft liver hepatic vein (yellow arrow) and adrenal vein (red arrow), the collateral circulation branches after operation (black arrow).
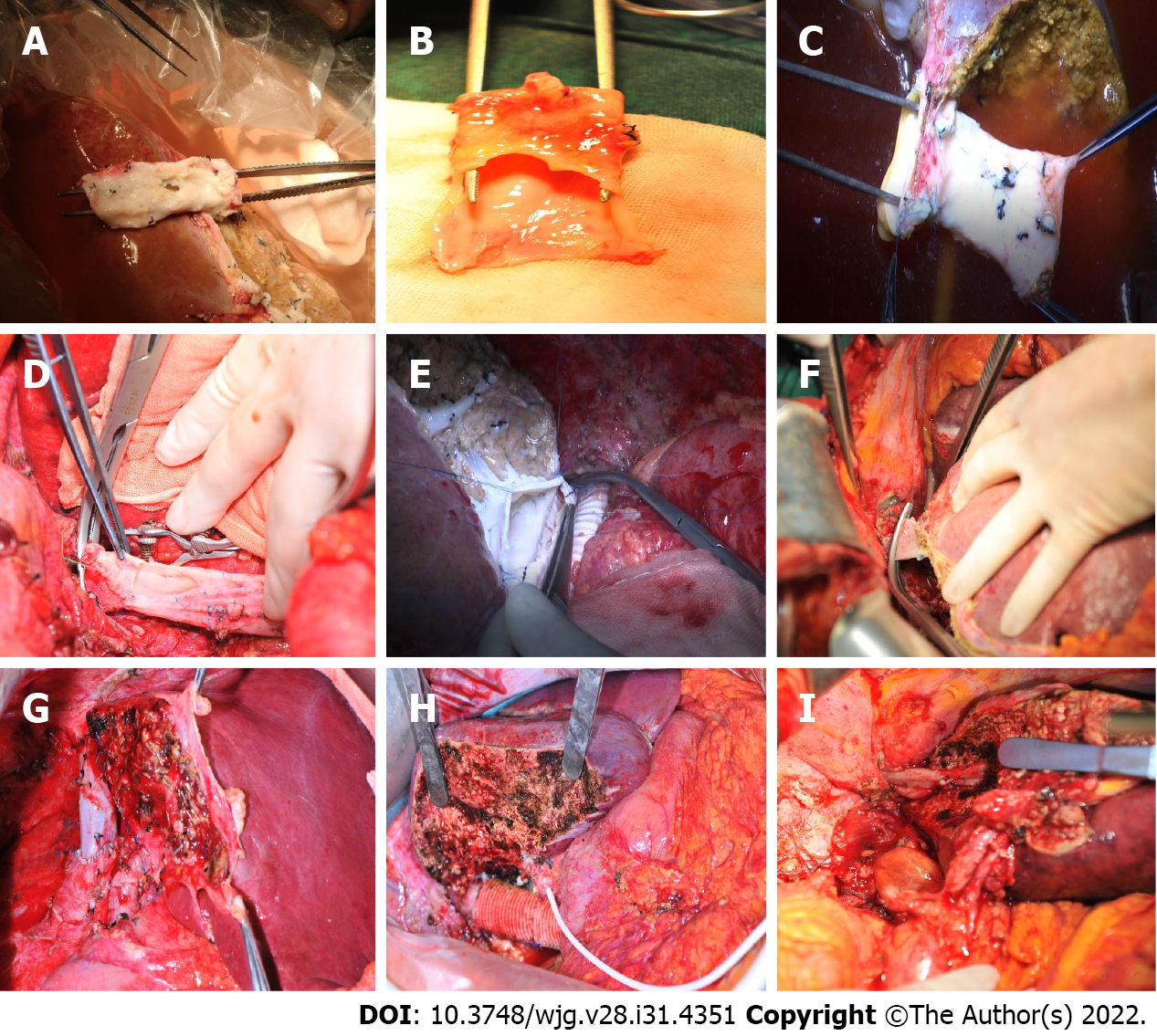
Figure 2 Intraoperative procedures.
A: The infiltrated retrohepatic inferior vena cava (RHIVC); B: The large defect of RHIVC after radical resection; C: The RHIVC with self-suture repairing; D: The original RHIVC anastomoses with hepatic vein; E: The artificial blood vessel anastomoses with graft liver hepatic vein; F: The suprahepatic IVC anastomoses with left hepatic vein; G: The autologous RHIVC after reconstruction; H: Artificial RHIVC; I: Anastomotic stoma of suprahepatic IVC and hepatic vein.
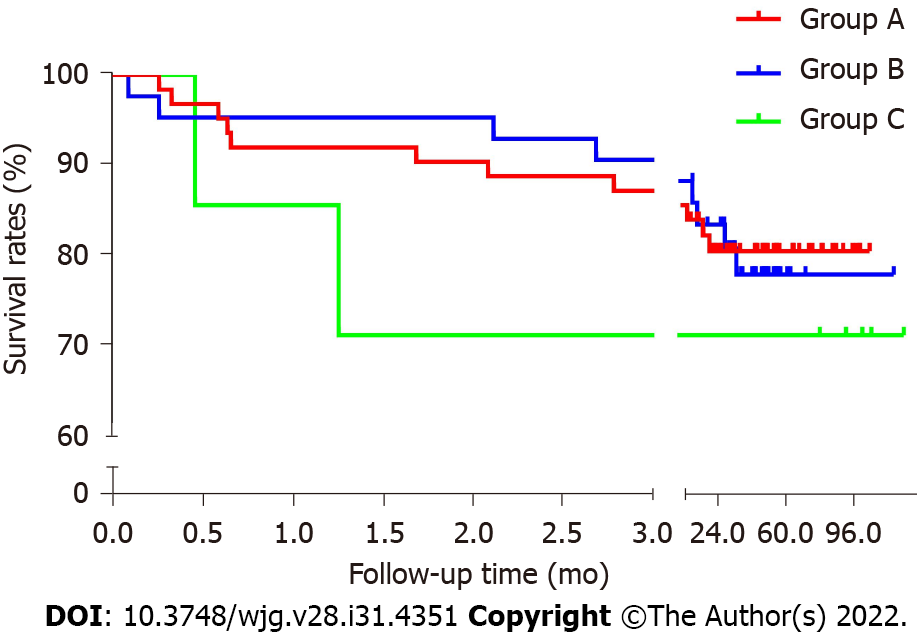
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier survival analysis curve.
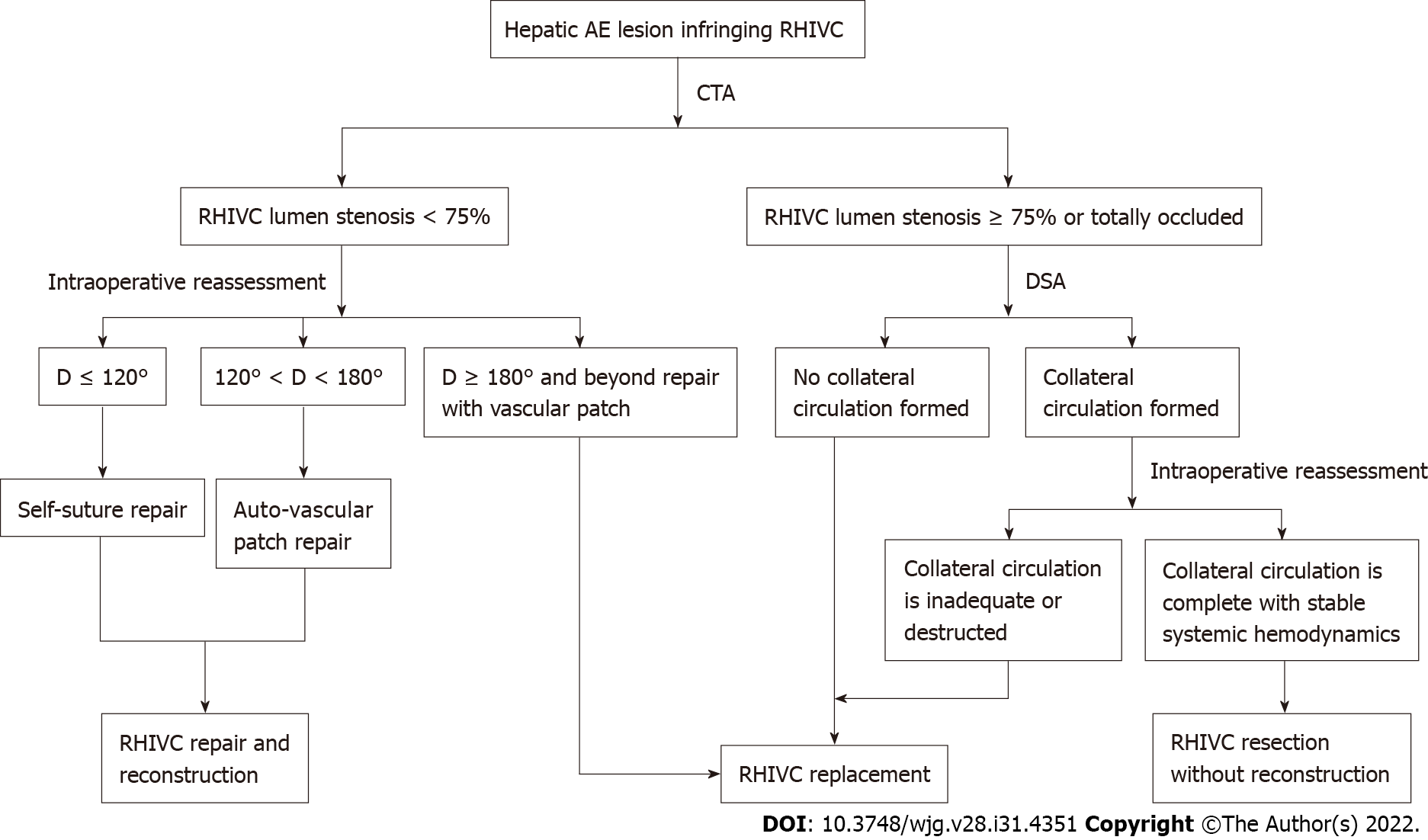
Figure 4 Strategy for retrohepatic inferior vena cava reconstruction in exvivo liver resection and autotransplantation.
CTA: Computed tomography angiography; D represents the defect of retrohepatic inferior vena cava lumen after resection; DSA: Digital subtraction angiography; RHIVC: Retrohepatic inferior vena cava.
- Citation: Maimaitinijiati Y, AJi T, Jiang TM, Ran B, Shao YM, Zhang RQ, Guo Q, Wang ML, Wen H. Approaches to reconstruction of inferior vena cava by ex vivo liver resection and autotransplantation in 114 patients with hepatic alveolar echinococcosis. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(31): 4351-4362
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i31/4351.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4351