Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2022; 28(31): 4249-4262
Published online Aug 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4249
Published online Aug 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4249
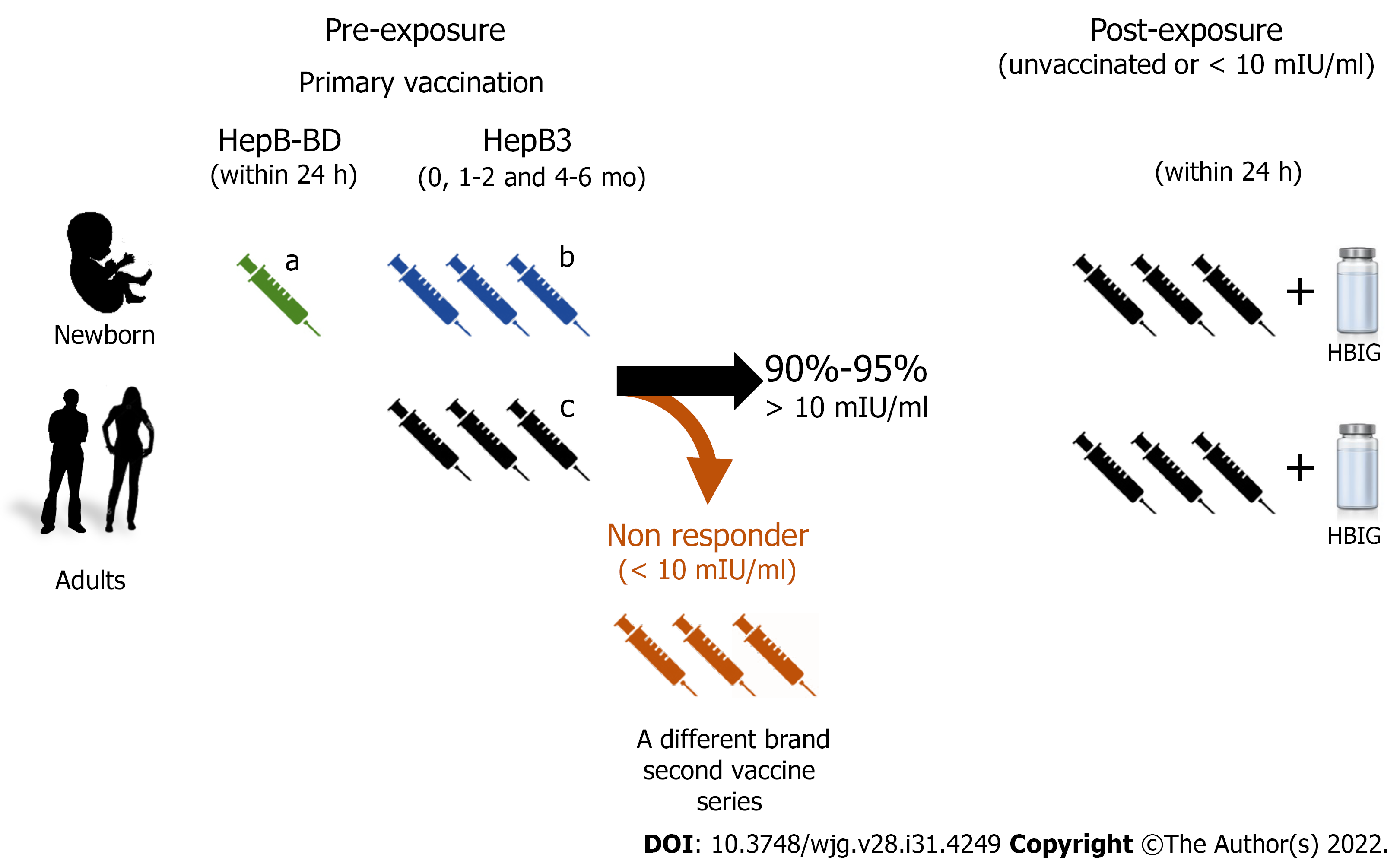
Figure 1 Recommended hepatitis B virus vaccination schemes.
The hepatitis B immunization schedule is flexible, but minimal intervals and ages need to be observed. The recommended dose varies (5-40 μg of hepatitis B surface antigen protein/mL) depending on the individuals’ age and the vaccine brand. aMonovalent hepatitis B vaccine 0.5 mL must be used for the at birth immunization (HepB-BD). Immunocompromised adults or patients under dialysis require larger or additional doses of the hepatitis B vaccine; bCombined hepatitis B, diphtheria, tetanus, adsorbed acellular pertussis, inactivated poliovirus vaccine. This vaccine cannot be administered at birth, before 6 postnatal weeks, or at age ≥ 7 years; cHeplisav-B is a vaccine recently approved for adults; it has a novel adjuvant and its recommended schedule is two doses 1 mo apart. HepB3: Three doses of hepatitis B vaccine; HepB-BD: Monovalent single dose of the hepatitis B virus vaccine; HBIG: Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin.
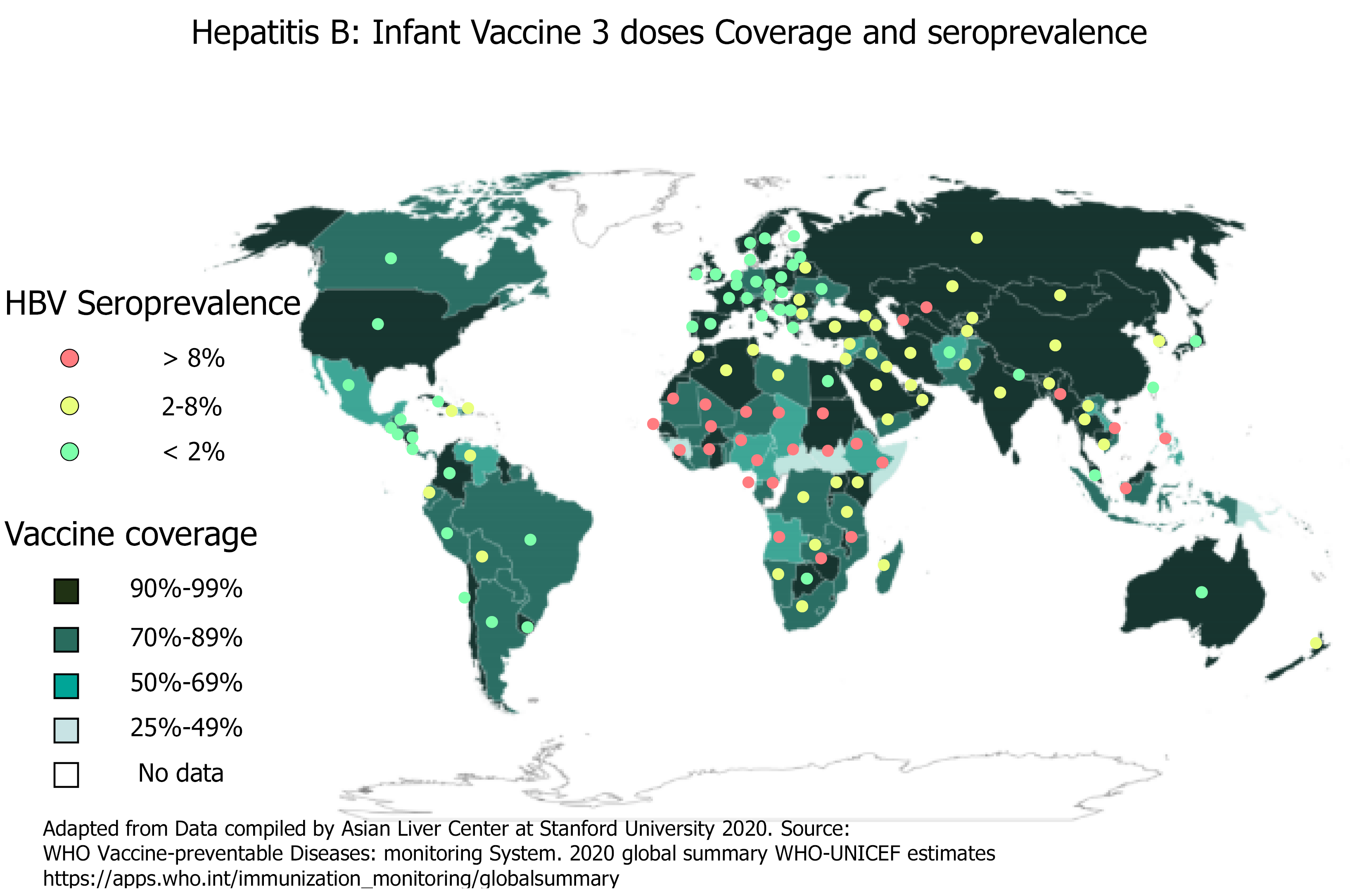
Figure 2 Hepatitis B three doses of infant vaccine coverage and seroprevalence.
Hepatitis B virus seroprevalence data is from Polaris Observatory Collaborators: Global Prevalence, Treatment, and Prevention of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in 2016: A Modelling Study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018; 3: 383–403. HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
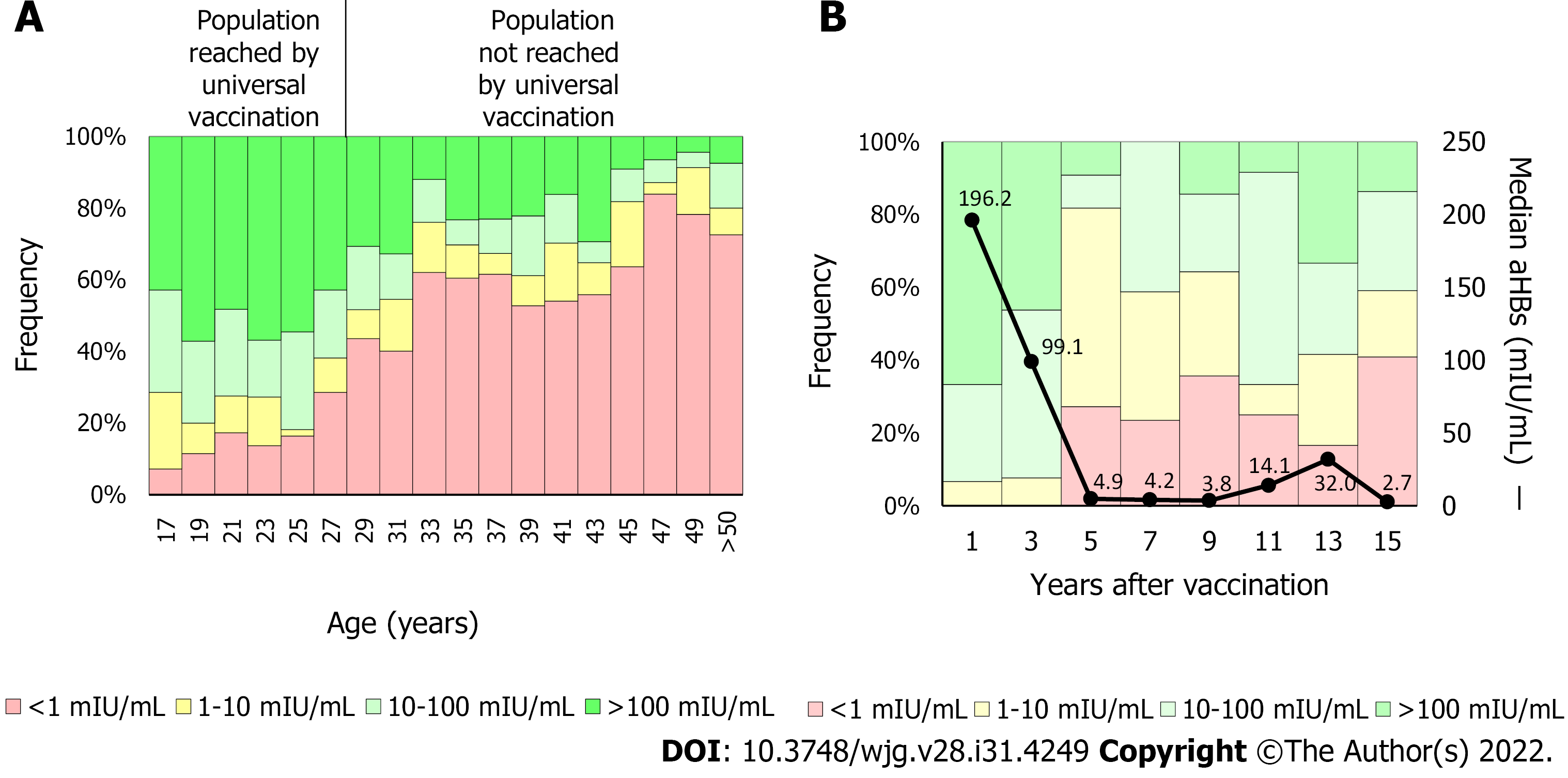
Figure 3 Anti-hepatitis B surface antibodies titers by age.
A: The anti-hepatitis B surface antibodies (anti-HBs) titer was determined in 765 blood donors. In 2000, vaccination against hepatitis B virus was included in the Argentine newborns’ National Vaccination Calendar. In 2003, the catch-up strategy for 11-year-old children was implemented. Therefore, individuals under 28-years-old are reached currently by the universal vaccine implementation. On average, protective levels of anti-HBs (> 10 mIU/mL) were detected in 75.2% of the population reached by universal vaccination (< 28-years-old) and in 32.2% of the not reached population (> 28-years-old); B: Anti-HBs kinetics. The anti-HBs titer was determined in 132 children born after 2000. In the first 2 years, the median anti-HBs titer fell from 196.2 mIU/mL to less than 10 mIU/mL (black line). Five years post-vaccination, about 20% of the population showed anti-HBs levels below 10 mIU/mL. aHBs: Anti-hepatitis B surface antibodies.
- Citation: Di Lello FA, Martínez AP, Flichman DM. Insights into induction of the immune response by the hepatitis B vaccine. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(31): 4249-4262
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i31/4249.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4249