Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2022; 28(26): 3164-3176
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3164
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3164
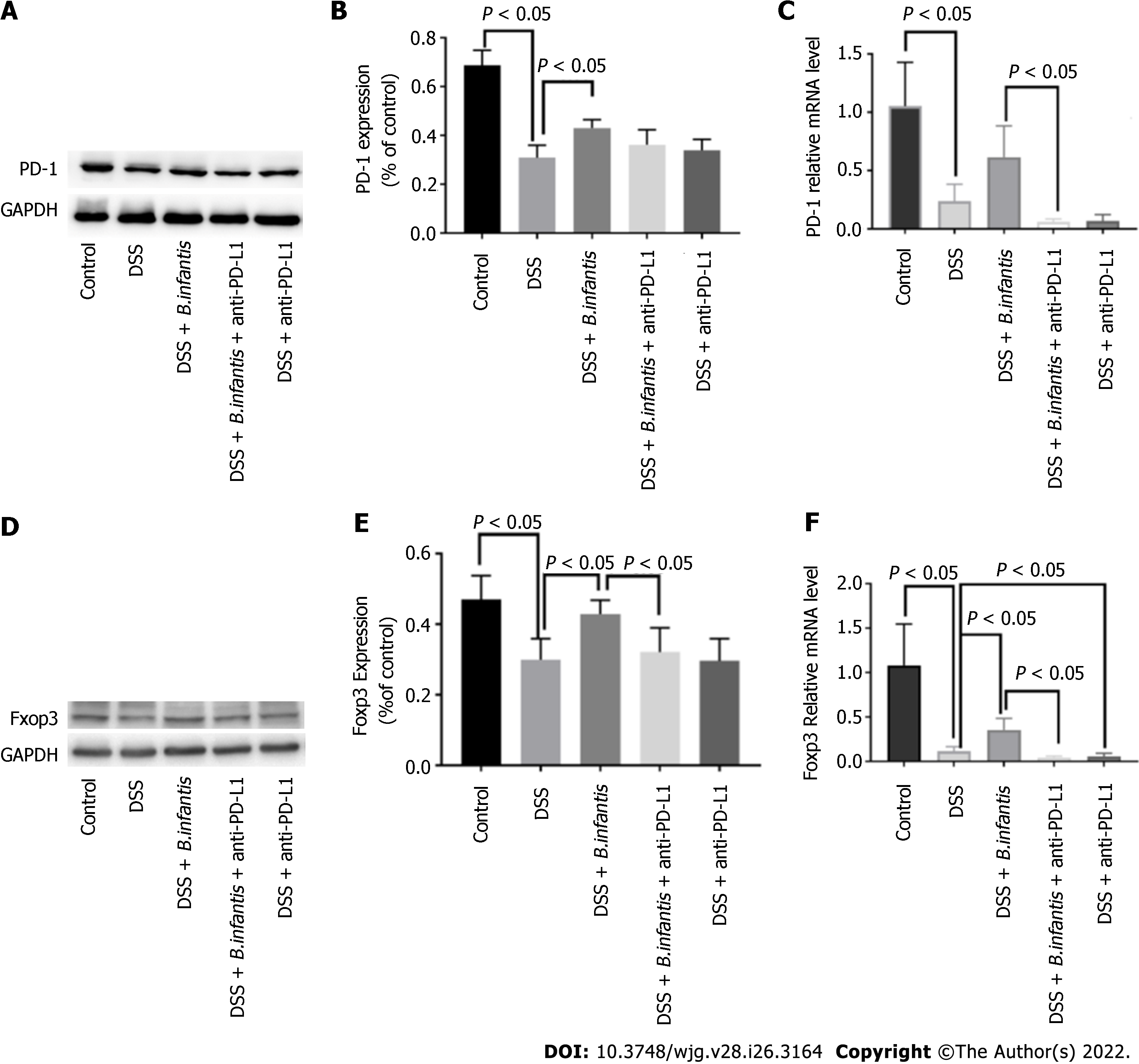
Figure 1 The effects of blocking programmed cell death ligand.
A: Expression of programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) protein; B: Statistical chart showing the differences in PD-1 protein expression; C: Statistical map showing the differences in PD-1 mRNA expression; D: Western blot showing forkhead box protein 3 protein (Foxp3) expression; E: Statistical chart showing the differences in Foxp3 expression; F: Statistical map showing the differences in Foxp3 mRNA levels. Data are presented as mean ± SD, and comparisons between groups were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance. Statistical significance was set as P < 0.05. PD-1: Programmed cell death 1; PD-L1: Programmed cell death ligand; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; B. infantis: Bifidobacterium infantis; Foxp3: Forkhead box protein 3.
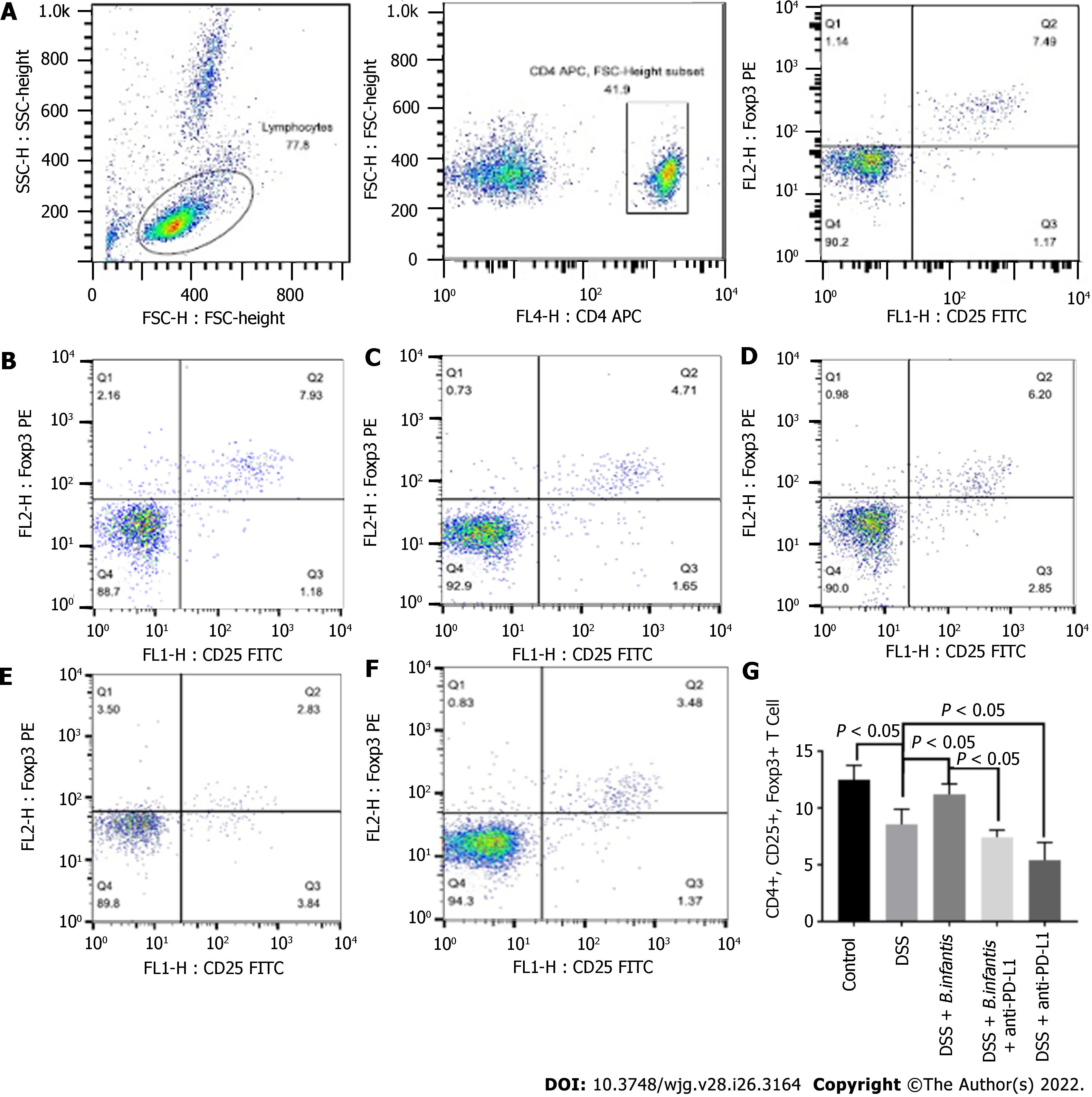
Figure 2 Effects of Bifidobacterium infantis and programmed cell death ligand inhibition on the proportion of CD4+, CD25+, and forkhead box protein 3+ cells in the blood.
A: The strategy of CD4+, CD25+, and forkhead box protein (Foxp) 3+ cells; B-F: Flow cytometry results for the control group (B), the DSS model group (C), the DSS + B. infantis group (D), the DSS + B. infantis + anti-PD-L1 group (E), the DSS + anti-PD-L1 group (F); G: Statistical chart of the numbers of CD4+, CD25+, and Foxp3+ cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD, and the comparisons among each group were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance. Statistical significance was set as P < 0.05. PD-1: Programmed cell death 1; PD-L1: Programmed cell death ligand; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; B. infantis: Bifidobacterium infantis; Foxp3+: Forkhead box protein 3+; CD: Cluster of differentiation; SSC: Side scatter; FSC: Forward scatter; FL: Fluorescence; APC: Allophycocyanin; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; H: Height.
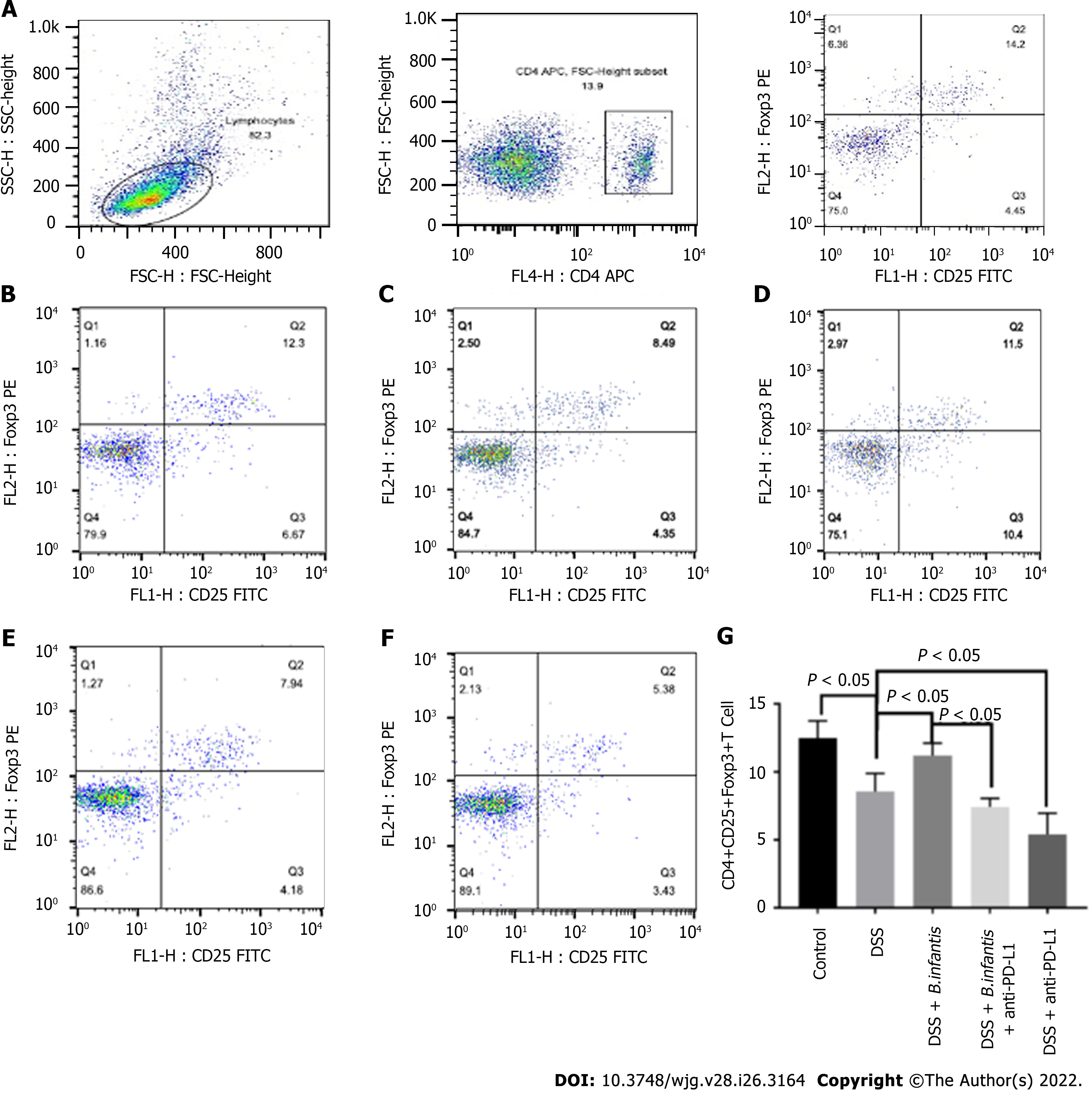
Figure 3 Effects of Bifidobacterium infantis and programmed cell death ligand inhibition on the proportion of splenic CD4+, CD25+, and forkhead box protein 3+ cells.
A: The strategy of CD4+, CD25+, and forkhead box protein (Foxp) 3+ cells; B-F: Flow cytometry results for the the control group (B), the DSS model group (C), the DSS + B. infantis group (D), the DSS + B. infantis + anti-PD-L1 group (E); and the DSS + anti-PD-L1 group (F); G: Statistical chart of the numbers of CD4+, CD25+, and Foxp3+ cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD, and the comparisons among each group were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance. Statistical significance was set as P < 0.05. PD-1: Programmed cell death 1; PD-L1: Programmed cell death ligand; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; B. infantis: Bifidobacterium infantis; Foxp3+: Forkhead box protein 3+; CD: Cluster of differentiation; SSC: Side scatter; FSC: Forward scatter; FL: Fluorescence; APC: Allophycocyanin; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; H: Height.
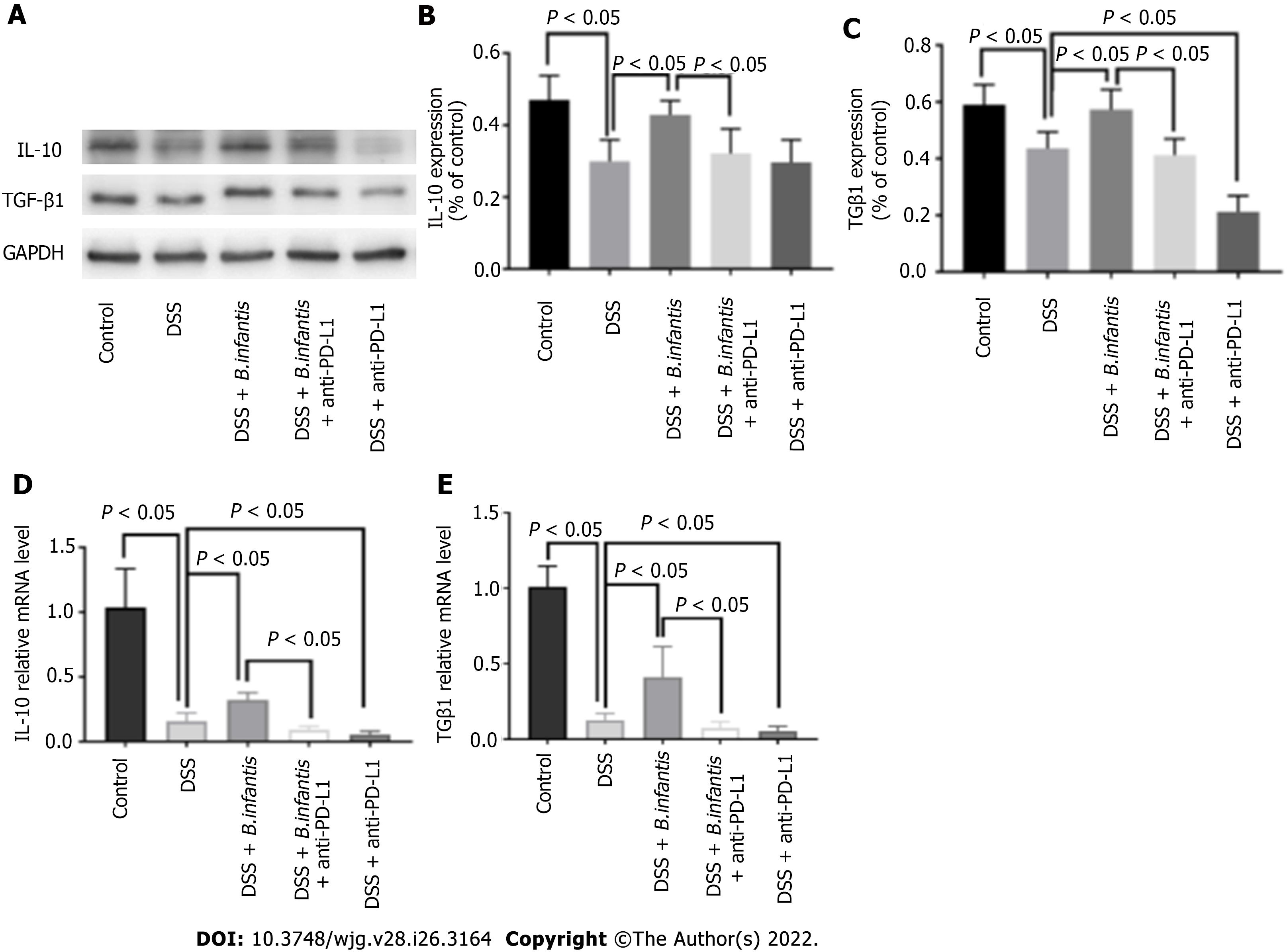
Figure 4 Effects of programmed cell death ligand inhibition on the expression of interleukin-10 and transforming growth factor β 1.
A: Western blot showing interleukin (IL)-10 and transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) 1 protein expression; B-E: Statistical maps of the differences in IL-10 protein expression (B), TGF-β1 protein expression (C), IL-10 mRNA expression (D), and TGF-β1 expression (E). Data are presented as mean ± SD, and the comparisons among each group were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance. Statistical significance was set as P < 0.05. PD-1: Programmed cell death 1; PD-L1: Programmed cell death ligand; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; B. infantis: Bifidobacterium infantis; IL: Interleukin; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor β; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; mRNA: Messenger ribonucleic acid.
- Citation: Zhou LY, Xie Y, Li Y. Bifidobacterium infantis regulates the programmed cell death 1 pathway and immune response in mice with inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(26): 3164-3176
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i26/3164.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3164