Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2022; 28(26): 3063-3070
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3063
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3063
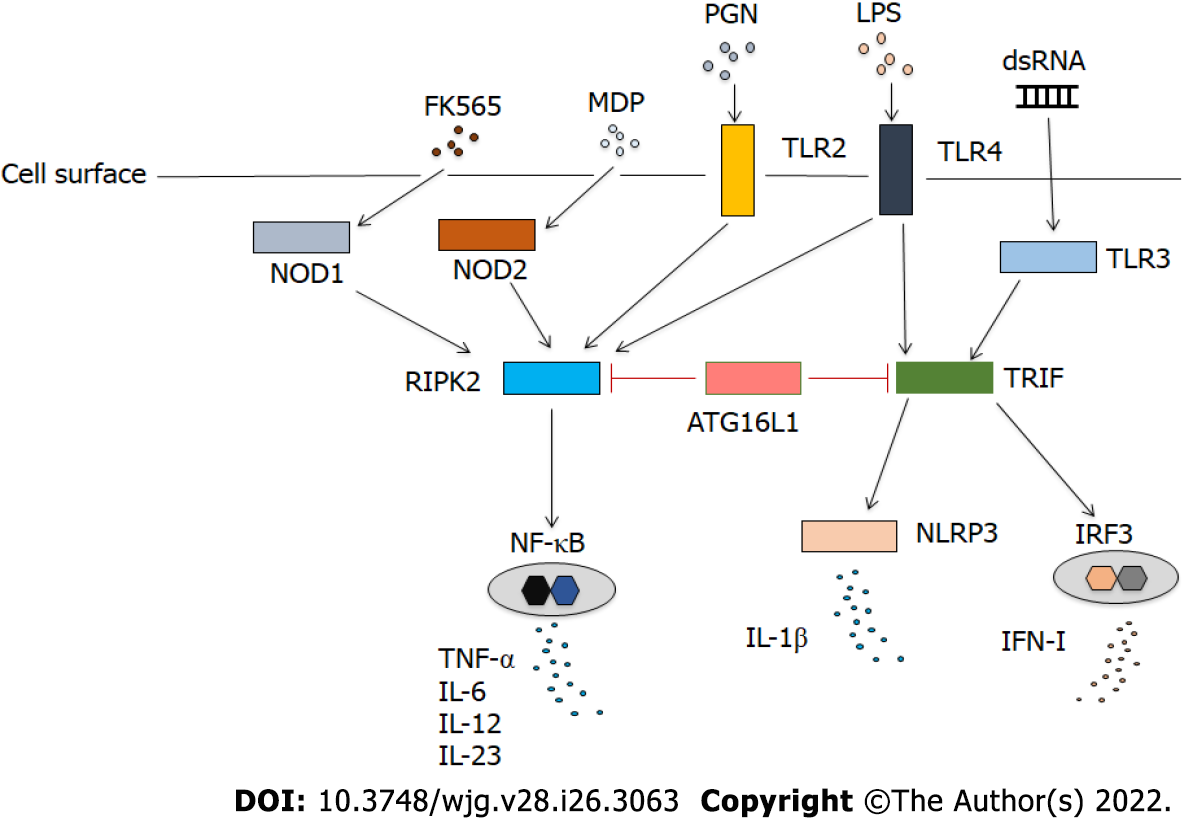
Figure 1 Negative effect of autophagy related 16 like 1 on pattern recognition receptor signaling pathways.
Autophagy related 16 like 1 (ATG16L1) negatively regulates pro-inflammatory and type I interferon (IFN-I) responses by toll-like receptors (TLRs) and nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptors (NLRs). Production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-12, and IL-23 mediated by TLRs is suppressed by ATG16L1 through the inhibition of activation of receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 and nuclear factor-kB. Production of IL-1β and IFN-I mediated by TLRs is suppressed by ATG16L1 through the inhibition of toll-IL-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-β, NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3, and interferon regulatory factor 3. MDP: Muramyl dipeptide; PGN: Peptidoglycan; TLR: Toll-like receptor; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; NOD: Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain; RIPK2: Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 2; ATG16L1: Autophagy related 16 like 1; IL: Interleukin; IFN: Interferon; TRIF: Toll-IL-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-β protein; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; NLRP3: NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3; IRF3: Interferon regulatory factor 3; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
- Citation: Okai N, Watanabe T, Minaga K, Kamata K, Honjo H, Kudo M. Alterations of autophagic and innate immune responses by the Crohn’s disease-associated ATG16L1 mutation. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(26): 3063-3070
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i26/3063.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3063