Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2022; 28(21): 2302-2319
Published online Jun 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i21.2302
Published online Jun 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i21.2302
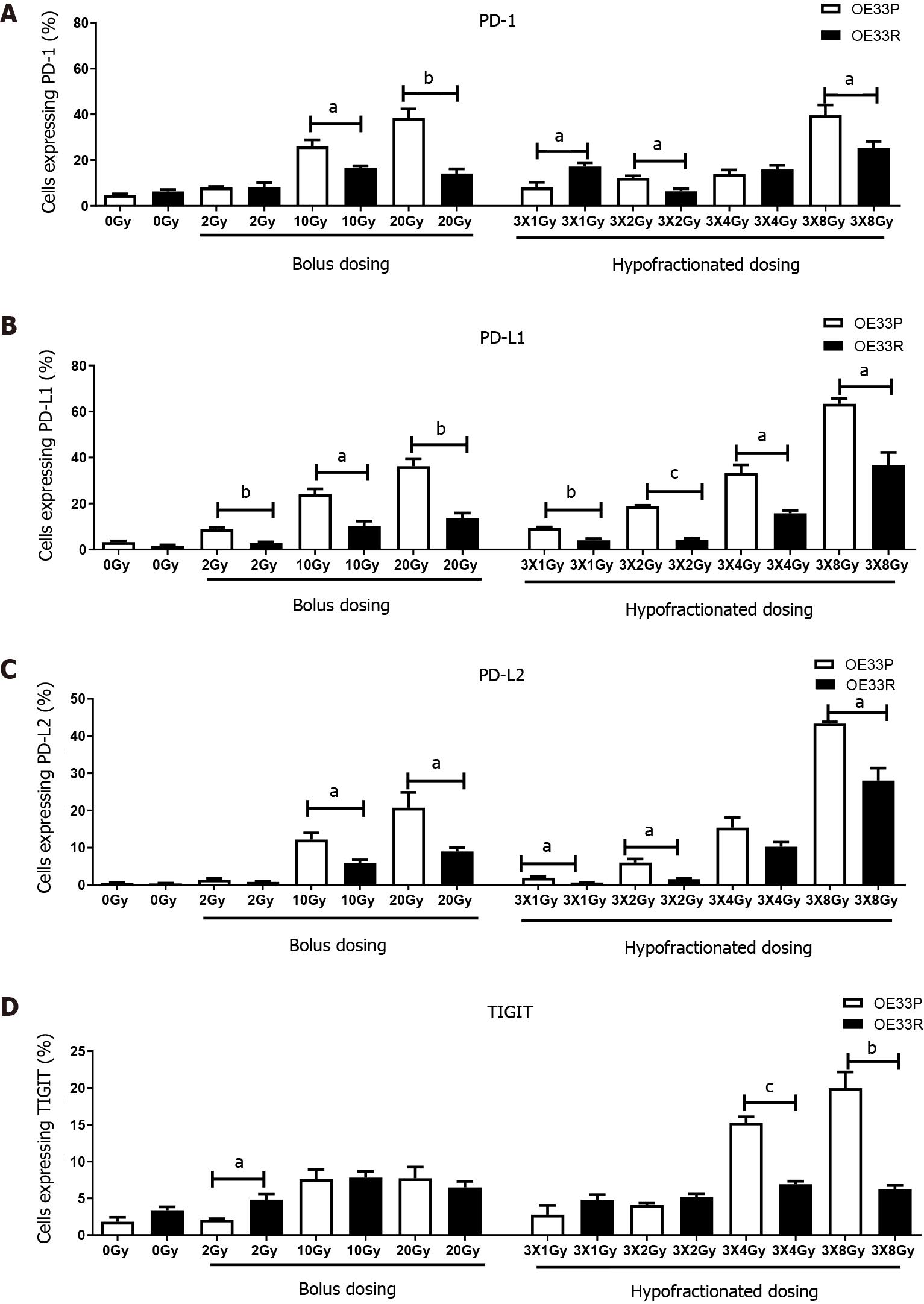
Figure 1 OE33P and R cell lines were screened for the surface expression of immune checkpoints by flow cytometry.
Inhibitory immune checkpoints are expressed at a higher level on parental cell lines than the passage matched radioresistant cell line (n = 3). A: PD-1; B: PD-L1; C: PD-L2; D: TIGIT. Graph shows % expression (± SE). aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001 by unpaired parametric t-test.
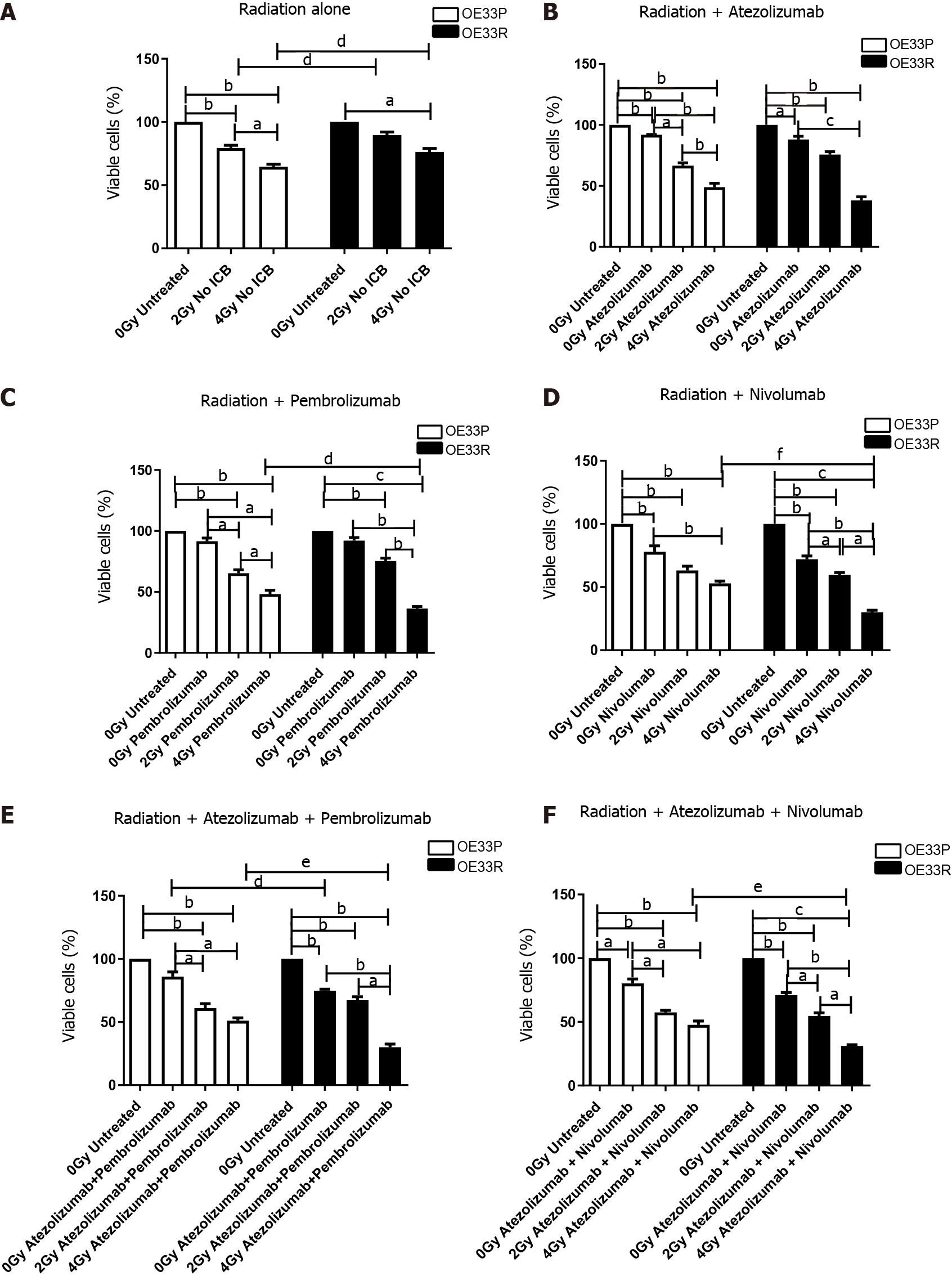
Figure 2 Viability (± SE) of OE33P and OE33R cells were assessed using a cell counting kit-8 assay with or without radiation (n = 3).
Ionising radiation with immune checkpoint blockade results in a greater reduction in cell viability when compared to either modality alone. Graph shows % expression (± SE). A: Treatment with radiation dosing only; B: Treatment with radiation and single agent immunotherapy Atezolizumab; C: Treatment with radiation and single agent immunotherapy Pembrolizumab; D: Treatment with radiation and single agent immunotherapy Nivolumab; E: Treatment with radiation and dual immunotherapy agents Atezolizumab & Pembrolizumab; F: Treatment with radiation and dual immunotherapy agents Atezolizumab & Nivolumab. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 paired t-test; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 unpaired t-test.
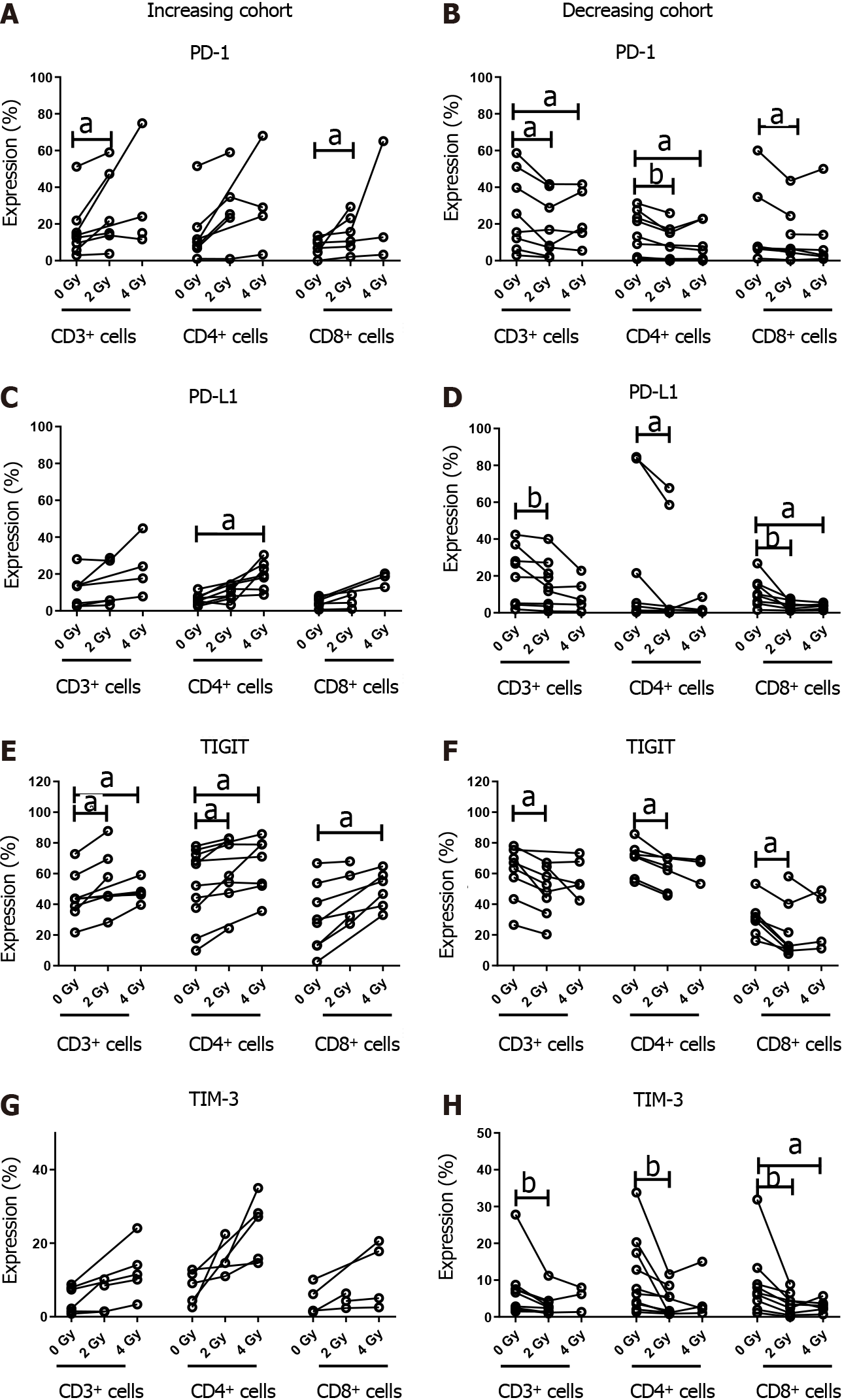
Figure 3 Oesophageal adenocarcinoma patients were screened for the surface expression of immune checkpoints ex vivo by flow cytometric analysis.
Subcohorts where ionising radiation induced upregulation and downregulation of immune checkpoints (ICs). Inhibitory ICs are expressed at a higher level with conventional and hypofractionated dosing regimens in one cohort (n = 8). Inhibitory ICs are expressed at a lower level with conventional and hypofractionated dosing regimens in a separate cohort (n = 9). A and B: Increasing and decreasing cohort of PD-1; C and D: Increasing and decreasing cohort of PD-L1; E and F: Increasing and decreasing cohort of TIGIT; G and H: Increasing and decreasing cohort of TIM-3. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01 by Wilcoxon signed rank test.
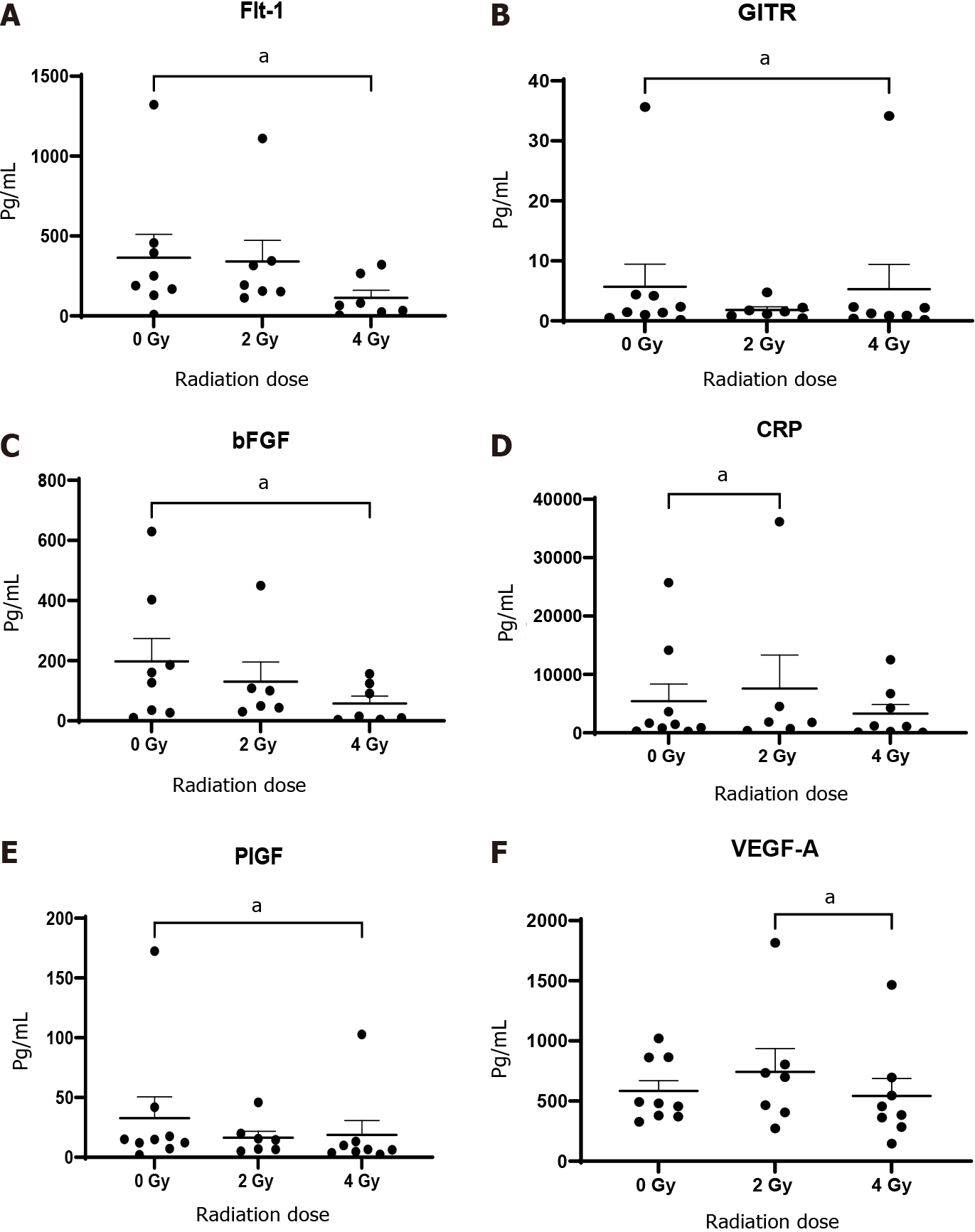
Figure 4 Conditioned media generated using oesophageal adenocarcinoma patient tumour was screened for markers by multiplex immunosorbent assay kit.
Angiogenic markers Flt-1, basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), placental growth factor (PIGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A and vascular injury marker C-reactive protein (CRP) decrease significantly with 4 Gy radiation (n = 9). A: Flt-1; B: GITH; C: bFGF; D: CRP; E: PIGF; F: VEGF-A. aP < 0.05 by Wilcoxon signed rank test.
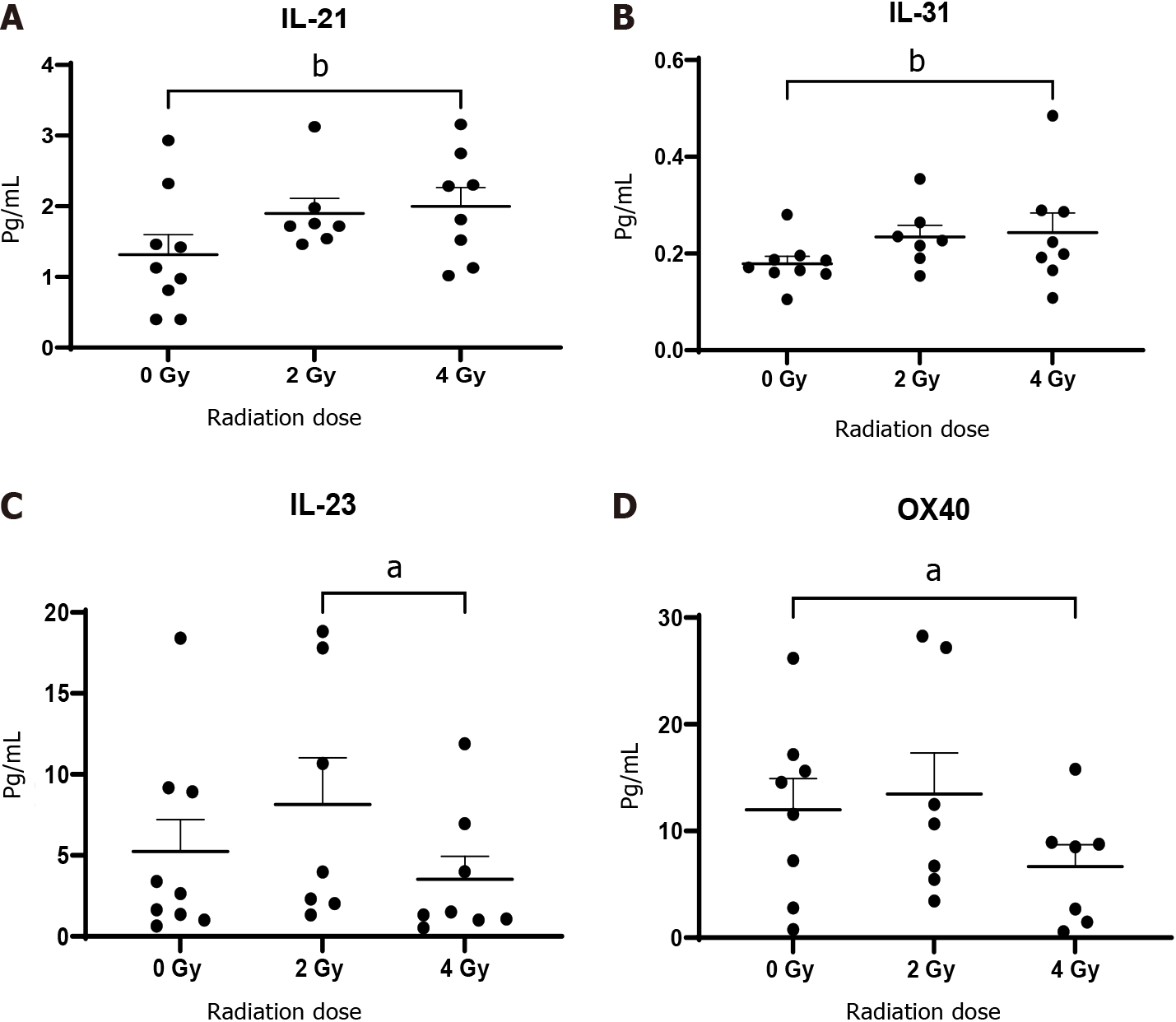
Figure 5 Oesophageal adenocarcinoma patients tumour conditioned media were screened by multiplex immunosorbent assay kit (n = 9).
The cytokines interleukin (IL)-21 and IL-31 increase with ionising radiation while IL-23 and OX-40 decrease. A: IL-21; B: IL-31; C: IL-23; D: OX-40. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. Wilcoxon signed rank test to compare expression between basal levels and dosing regimens.
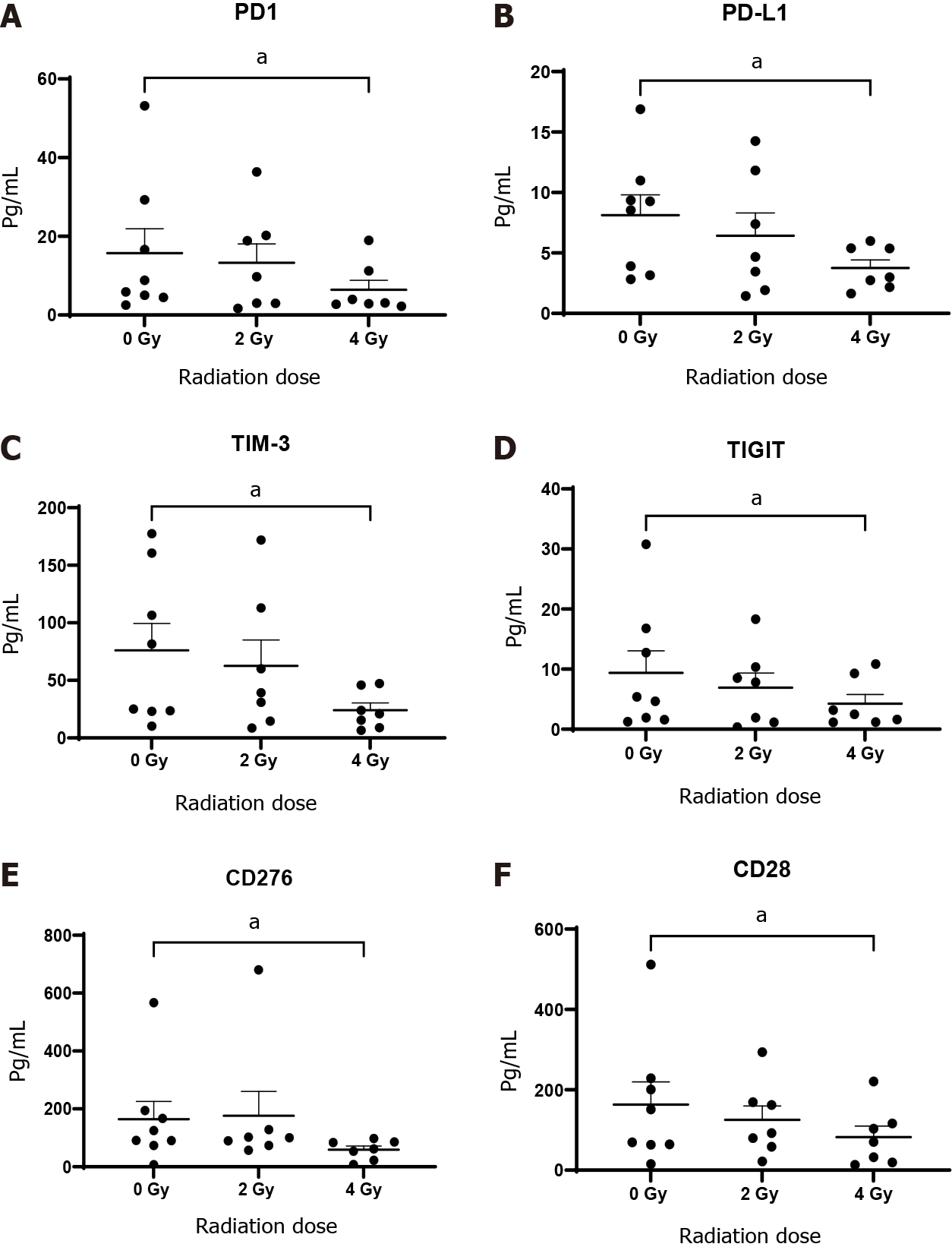
Figure 6 Oesophageal adenocarcinoma patient’s tumour conditioned media were screened by multiplex immunosorbent assay kit.
The inhibitory checkpoints PD-1 and its ligand PD-L1, TIGT, TIM3, immunosuppressive molecule and checkpoint CD276 (B7-H3) and costimulatory molecule CD28 significantly decrease with fractionated radiotherapy (n = 8). A: PD-1; B: PD-L1; C: TIM-3; D: TIGIT; E: CD276; F: CD28. aP < 0.05 by Wilcoxon signed rank test.
- Citation: Donlon NE, Davern M, O’Connell F, Sheppard A, Heeran A, Bhardwaj A, Butler C, Narayanasamy R, Donohoe C, Phelan JJ, Lynam-Lennon N, Dunne MR, Maher S, O’Sullivan J, Reynolds JV, Lysaght J. Impact of radiotherapy on the immune landscape in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(21): 2302-2319
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i21/2302.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i21.2302