Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2022; 28(21): 2291-2301
Published online Jun 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i21.2291
Published online Jun 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i21.2291
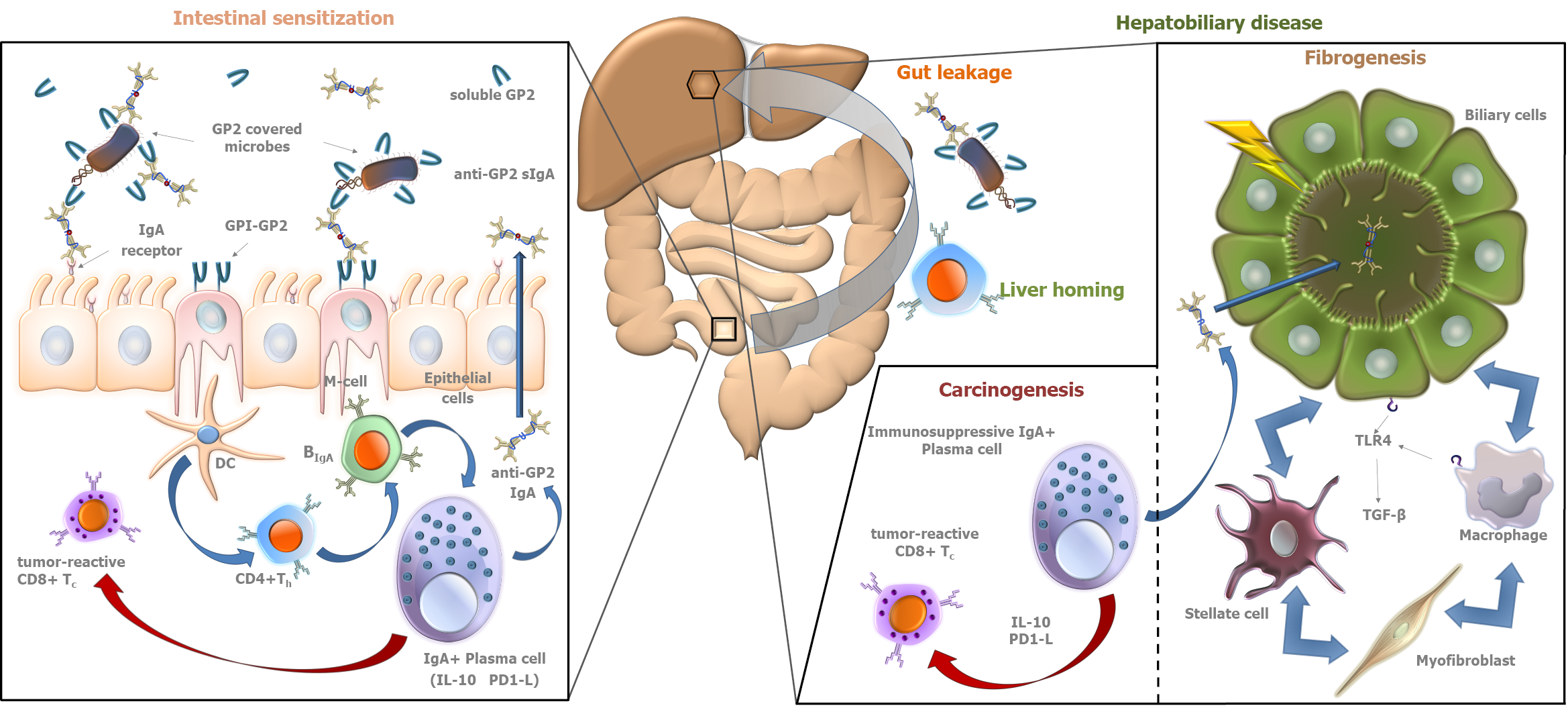
Figure 1 Autoimmunity-driven putative role of pancreatic glycoprotein 2 in fibro- and tumorigenesis in primary sclerosing cholangitis.
Along with digestive enzymes, glycoprotein 2 (GP2) is secreted from pancreatic acinar cells into the intestinal lumen. In addition, GP2 is also expressed on the luminal surface of microfold cells [M-cells in Peyer's patches anchored by glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)]. Both forms of the molecule interact with FimH+ bacteria and opsonize them. The anchored form may be involved in the transcytosis of bound ligands (FimH+ microbes) through M cells, which pass them to antigen-presenting cells like dendritic cells (DC) located in the mucosa-associated immune system. Microbe-bound GP2 epitopes are presented to CD4-positive T helper cells (CD4+ Th) along with bacterial antigens that lead to loss of tolerance to GP2. After clonal expansion, these sensitized cells can “home” to both the gut and the liver where they trigger (blue arrows) the differentiation of IgA+ B cells into IgA+ plasma cells. The produced anti-GP2 IgA is actively transported by epithelial cells to the intestinal and biliary lumens as secretory IgA (sIgA), where it binds to GP2. Epithelial cells express IgA receptors on their luminal surface that are involved in active retrograde transport of sIgA molecules (typically coupled by antigens). This process may contribute to bacterial overload of the gut mucosa, elevating the levels of bacterial components in the circulation. In the hepato-biliary tract, bacterial components trigger the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) pathway, facilitating fibrosis and cirrhosis. Meanwhile, as a response to the continuous inflammation, a line of IgA+ plasma cells develops an immunosuppressor phenotype expressing interleukin-10 (IL-10) and programmed cell-death 1 Ligand (PD1-L). These molecules inhibit (red arrow) tumor-suppressing cytotoxic CD8+ T cells (CD8+ Tc), contributing to tumor development in the hepatobiliary and intestinal tract. Citation: Tornai D, Papp M. Editorial: serologic antibodies in primary sclerosing cholangitis a tell-tale sign of compromised gut-liver immunity? Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2021; 53: 350-351[8]. Copyright ©The Authors 2021. Published by John Wiley and Sons. (Supplementary material).
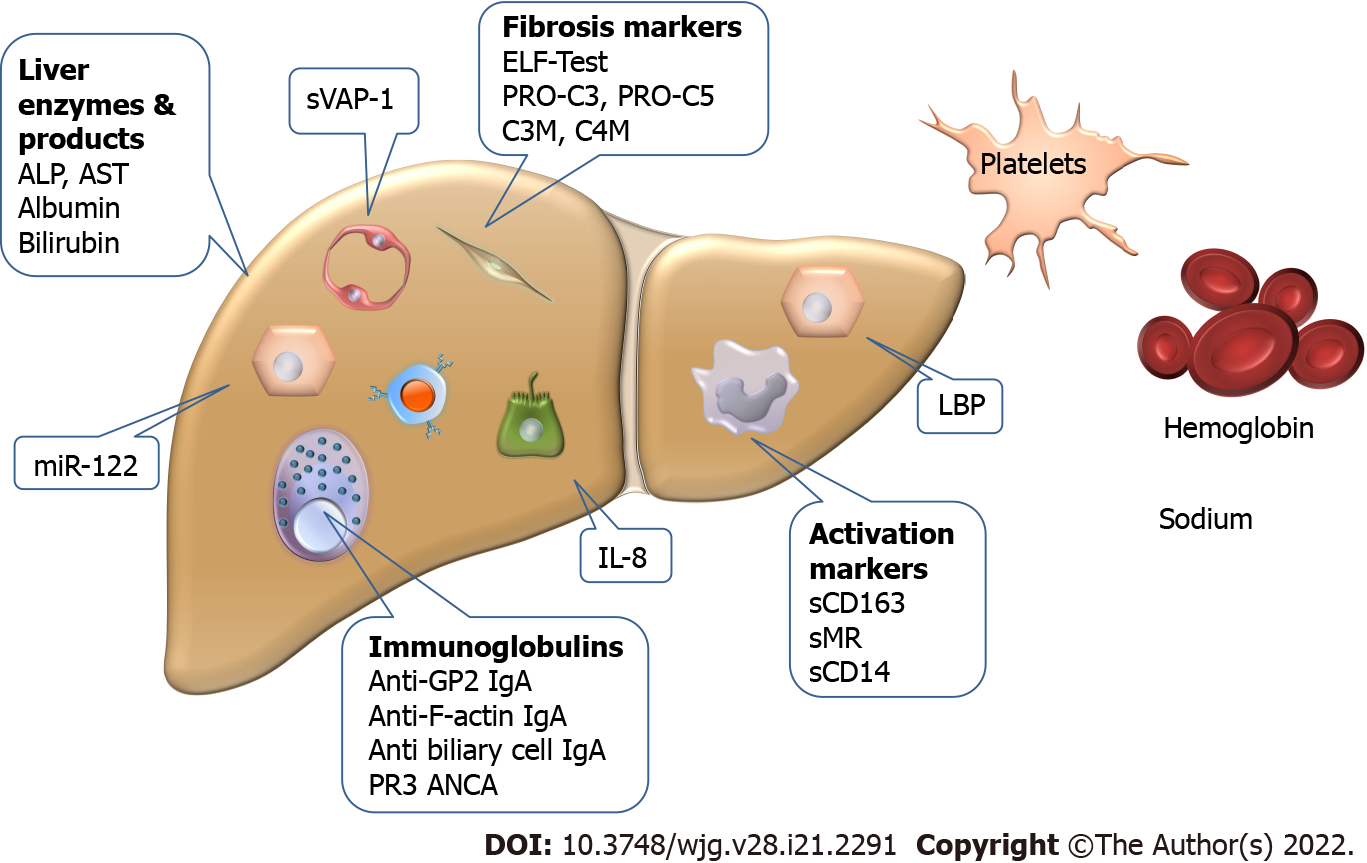
Figure 2 Biomarkers with potential to predict the clinical course of primary sclerosing cholangitis.
The markers have various cellular origins, and some (LPS-binding protein, interleukin-8, and enzymes) have multiple sources that limit their specificity. ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; GP2: Pancreatic glycoprotein 2; IL: Interleukin; LBP: Lipopolysaccharide binding protein; miR: Micro-ribonucleic acid; sMR: Soluble mannose receptor; sVAP: Soluble vascular adhesion protein.
- Citation: Tornai D, Ven PL, Lakatos PL, Papp M. Serological biomarkers for management of primary sclerosing cholangitis. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(21): 2291-2301
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i21/2291.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i21.2291