Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2022; 28(16): 1692-1704
Published online Apr 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i16.1692
Published online Apr 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i16.1692
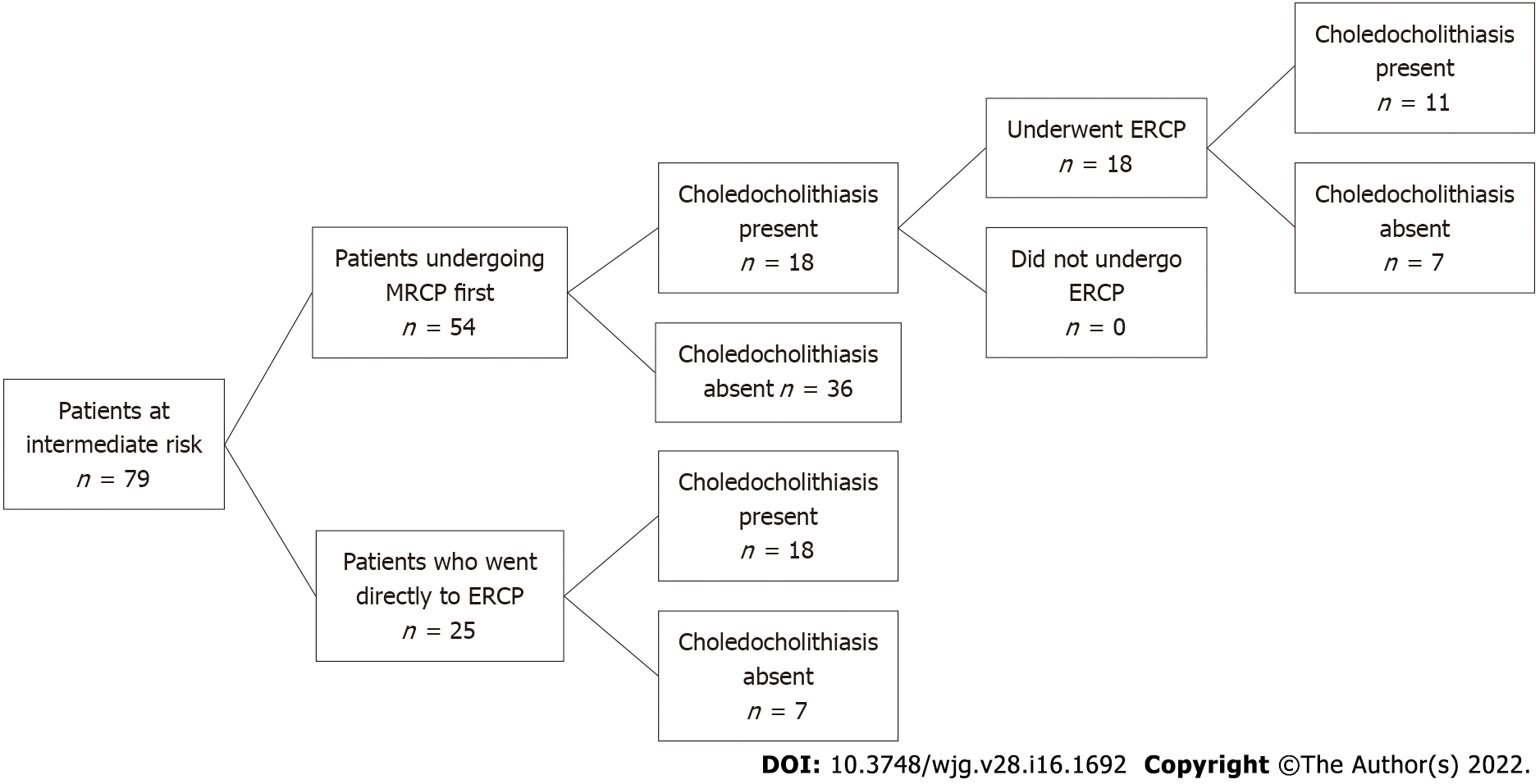
Figure 1 Patients at intermediate risk for choledocholithiasis.
MRCP: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
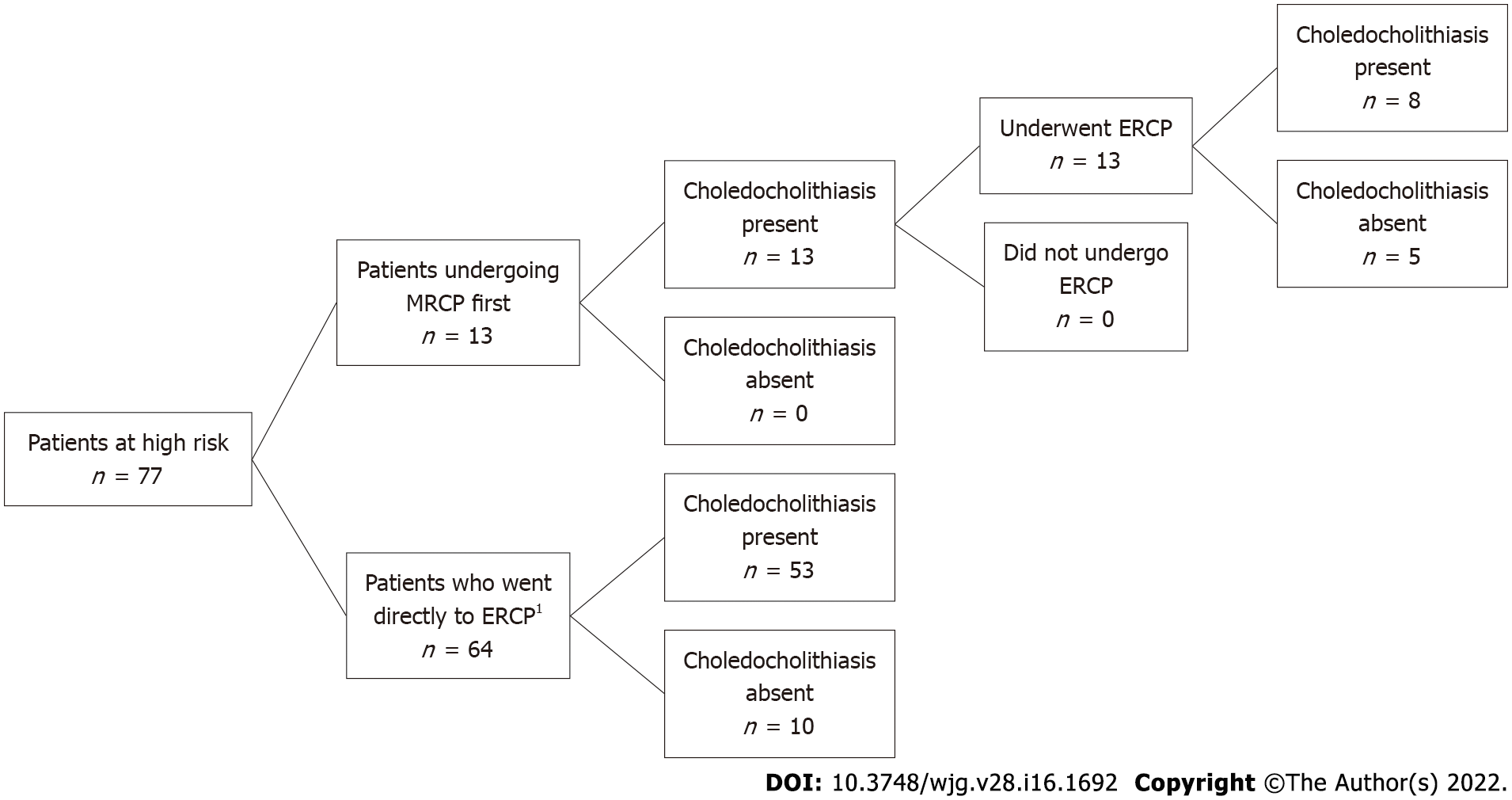
Figure 2 Patients categorized as high risk by American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guidelines.
MRCP: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. 1One patient’s procedure could not be completed due to failure of bile duct cannulization.
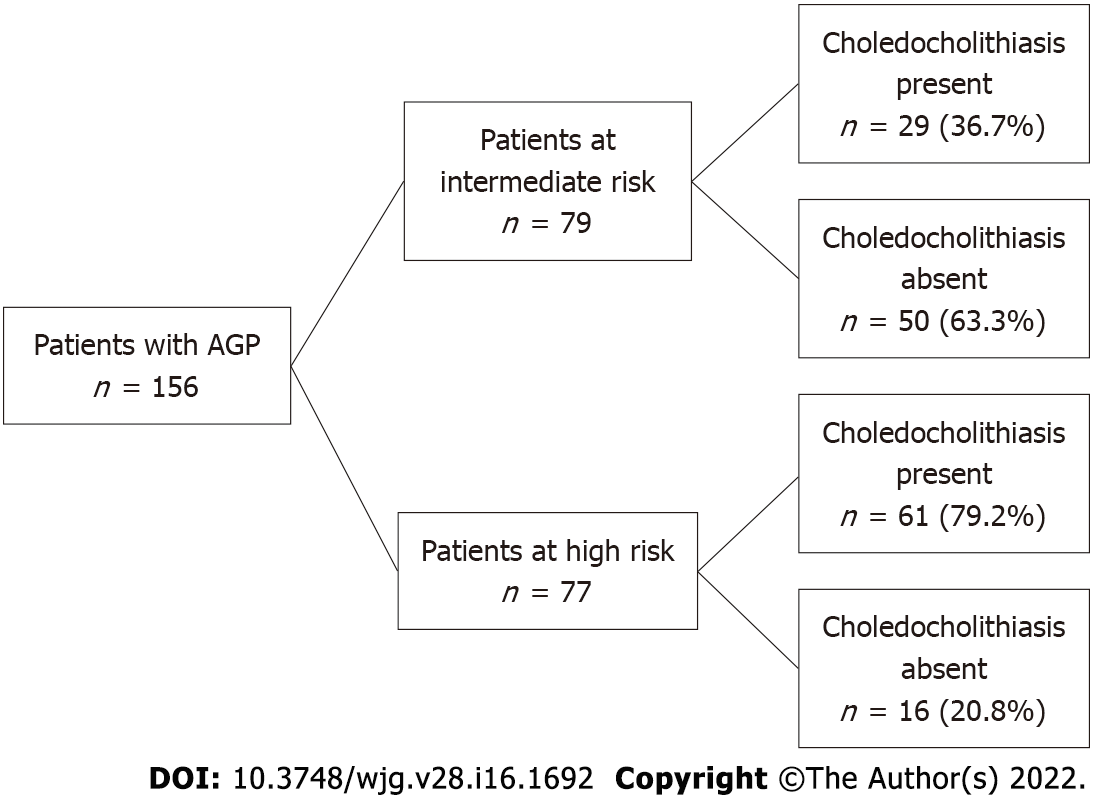
Figure 3 Patients with choledocholithiasis.
AGP: Acute gallstone pancreatitis.
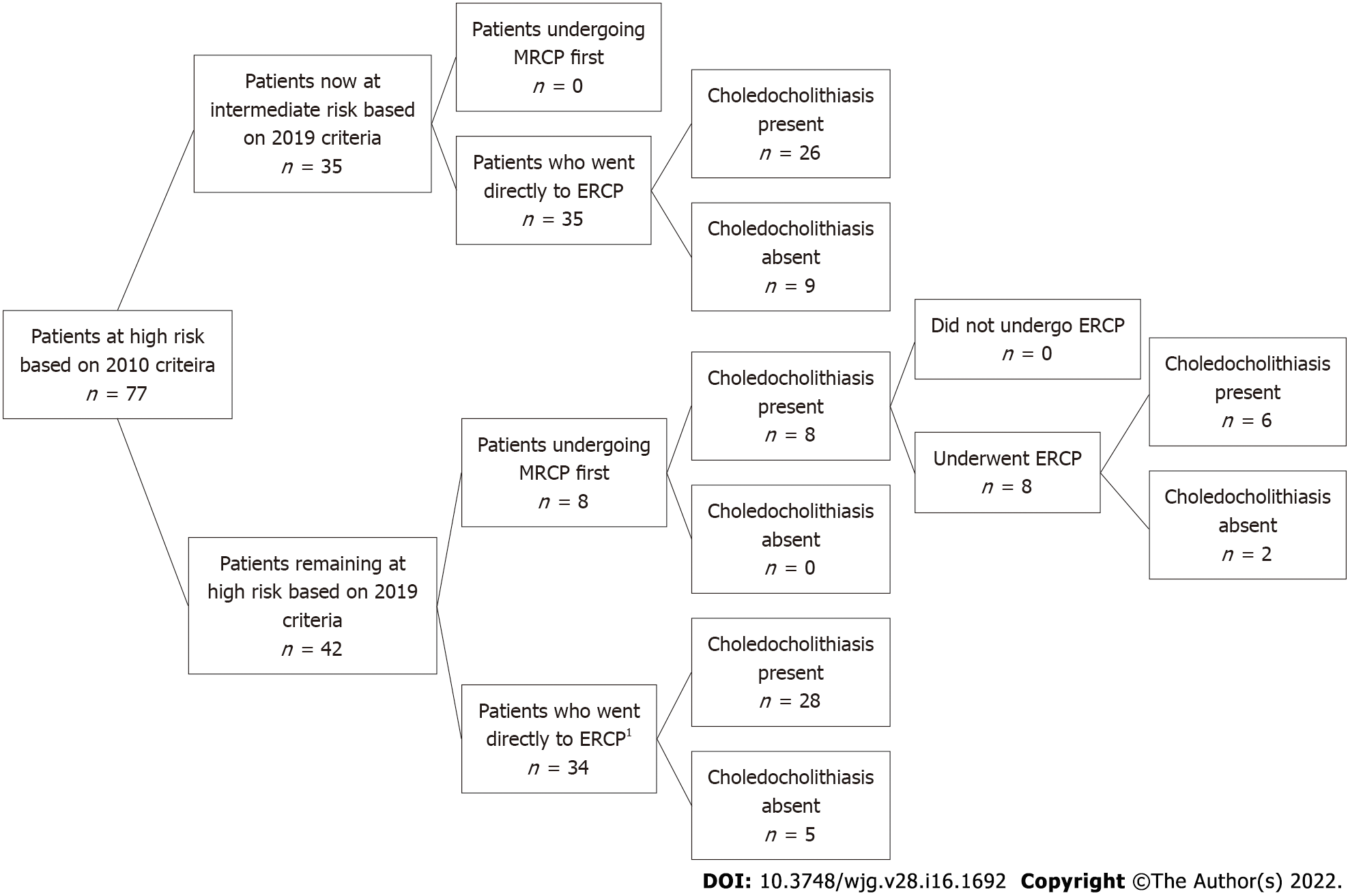
Figure 4 Patients at high risk based on 2010 American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guidelines now re-stratified based on 2019 guidelines.
MRCP: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. 1One patient’s procedure could not be completed due to failure of bile duct cannulization.
- Citation: Tintara S, Shah I, Yakah W, Ahmed A, Sorrento CS, Kandasamy C, Freedman SD, Kothari DJ, Sheth SG. Evaluating the accuracy of American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guidelines in patients with acute gallstone pancreatitis with choledocholithiasis. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(16): 1692-1704
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i16/1692.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i16.1692