Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2022; 28(14): 1384-1393
Published online Apr 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i14.1384
Published online Apr 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i14.1384
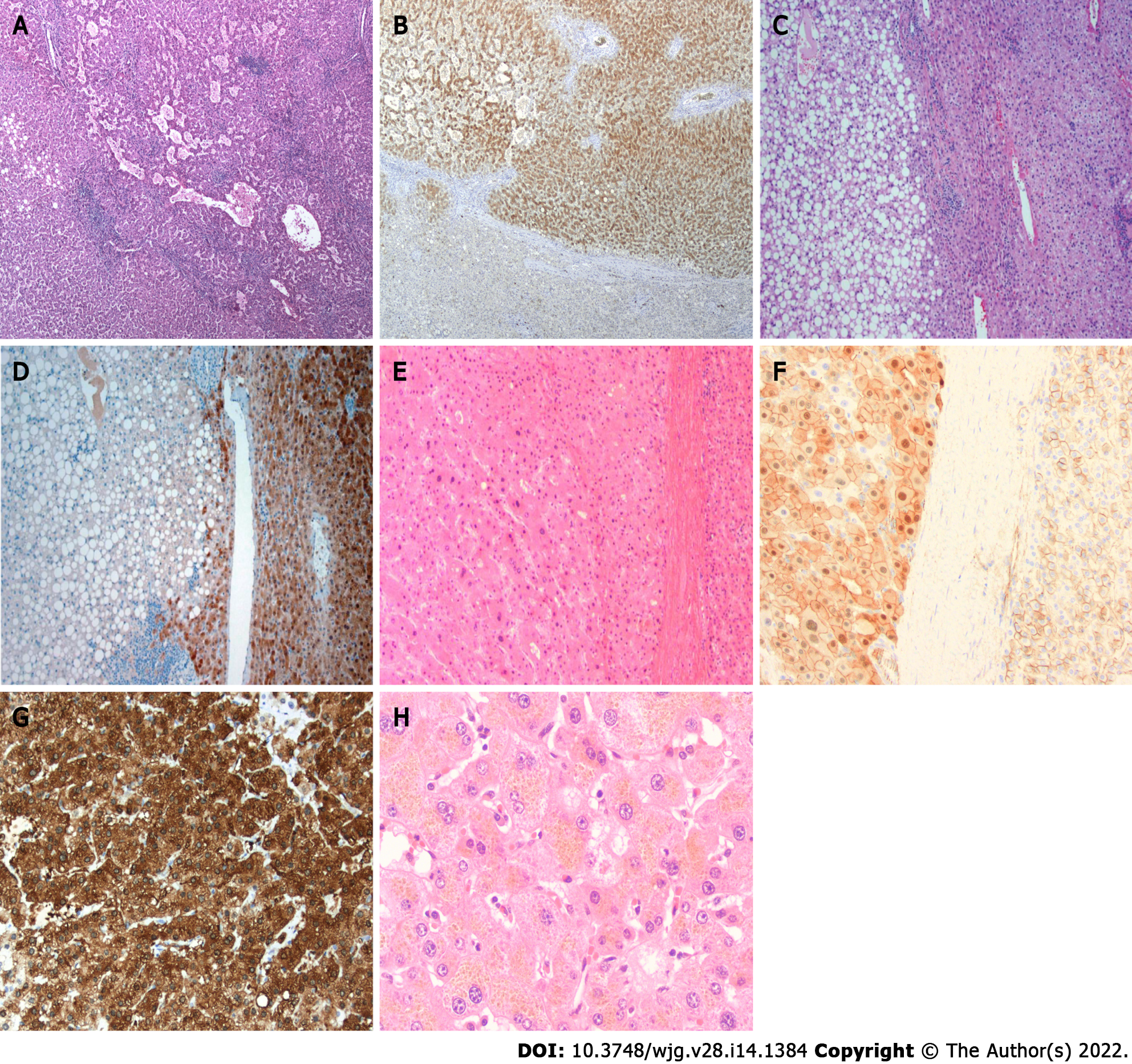
Figure 1 Histologic features of hepatocellular adenoma.
A: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1A (HNF-1A) inactivated hepatocellular adenoma showing marked steatosis (Hematoxylin-eosin stain, original magnification 200 ×); B: HNF-1A inactivated hepatocellular adenoma showing loss expression of liver fatty acid binding protein in tumor component (Immunohistochemical stain, original magnification 200 ×); C: Inflammatory hepatocellular adenoma showing marked sinusoidal dilatation and pseudoportal tract with inflammatory infiltrate and ductular reaction (Hematoxylin-eosin stain, original magnification 200 ×); D: Inflammatory hepatocellular adenoma showing strong and diffuse expression of C-reactive protein in tumor component (Immunohistochemical stain, original magnification 200 ×); E: β-catenin activated hepatocellular adenoma showing mild cytologic atypia and pseudoacini (Hematoxylin-eosin stain, original magnification 200 ×); F: β-catenin activated hepatocellular adenoma showing nuclear expression of β-catenin in tumor component (Immunohistochemical stain, original magnification 400 ×); G: β-catenin activated hepatocellular adenoma showing strong and diffuse expression of glutamine synthetase in tumor component (Immunohistochemical stain, original magnification 200 ×); H: Pigmented hepatocellular adenoma showing marked cytoplasmic lipofuscin (Hematoxylin-eosin stain, original magnification 400 ×).
- Citation: Wang X, Zhang X. Hepatocellular adenoma: Where are we now? World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(14): 1384-1393
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i14/1384.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i14.1384