Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2022; 28(11): 1123-1138
Published online Mar 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i11.1123
Published online Mar 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i11.1123
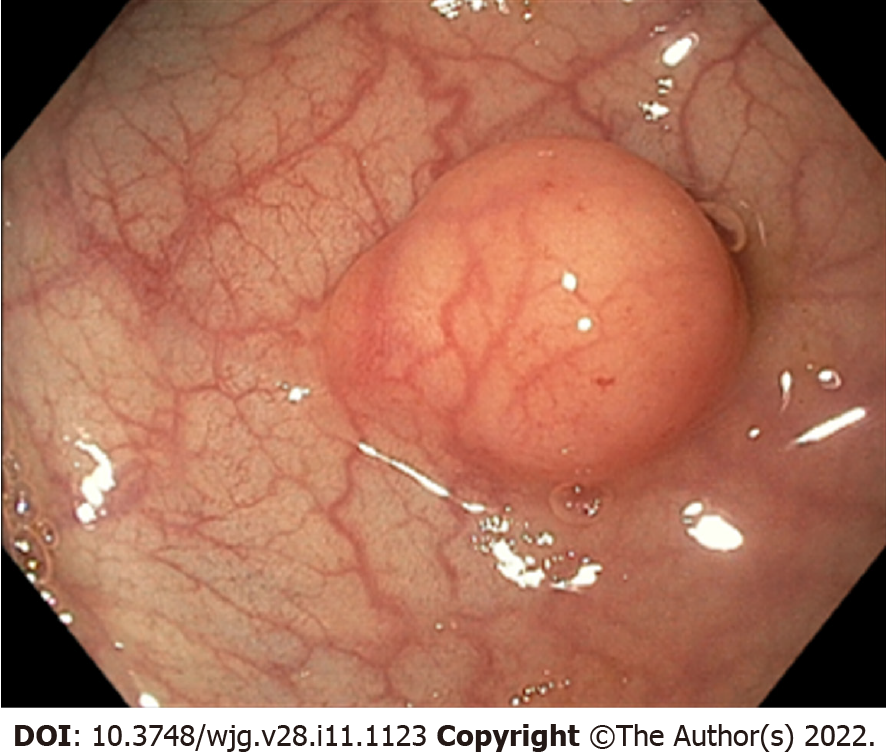
Figure 1 Endoscopic aspect of a rectal neuroendocrine neoplasm.
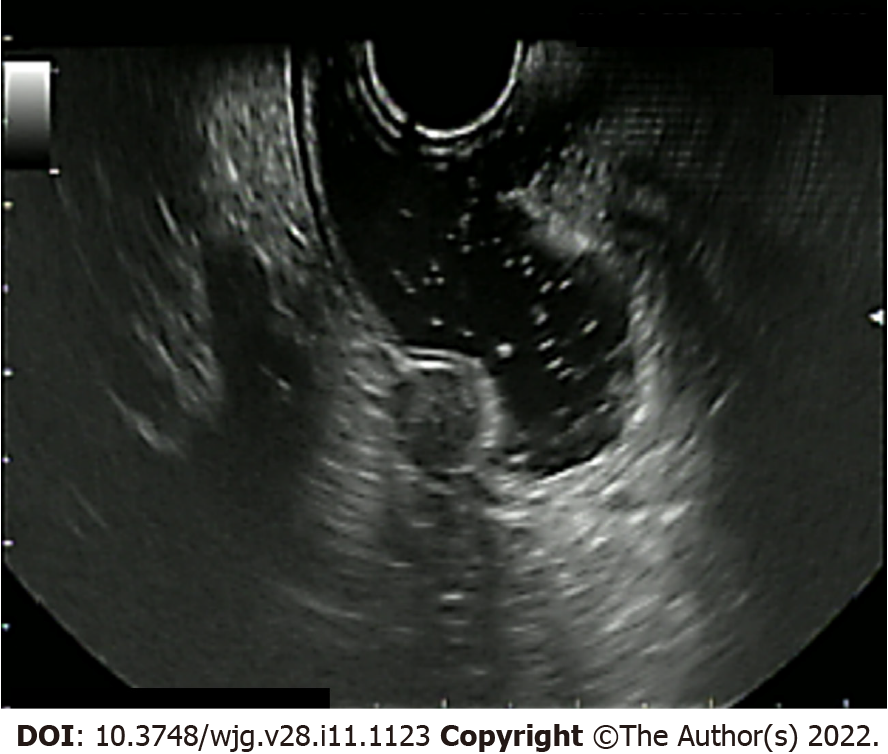
Figure 2 Endoscopic ultrasound aspect of a rectal neuroendocrine neoplasm.
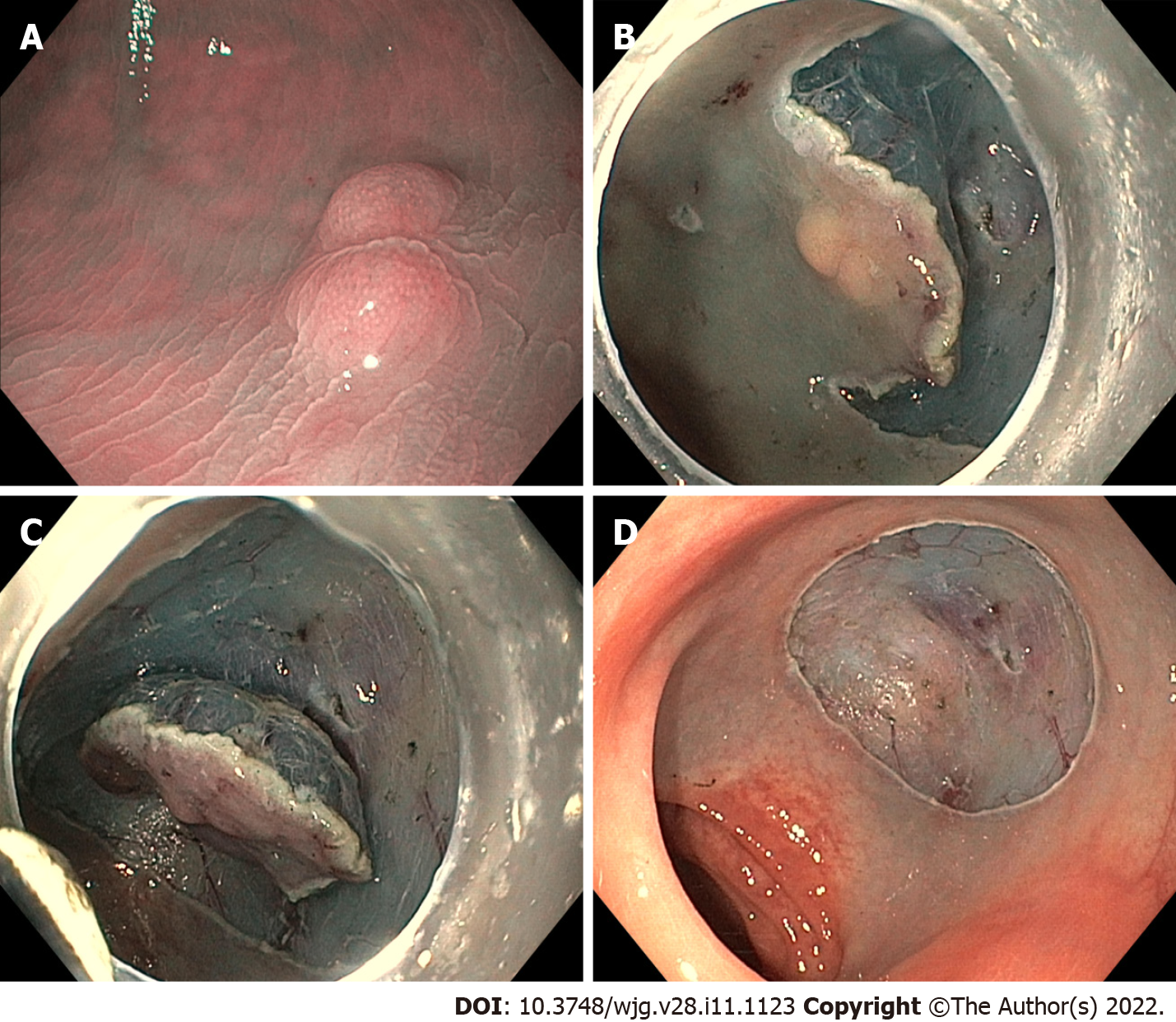
Figure 3 Endoscopic submucosal dissection of a rectal neuroendocrine neoplasm.
A: Rectal neuroendocrine neoplasm aspect before the procedure; B: Initial submucosal dissection beneath the lesion; C: Almost completed submucosal dissection beneath the lesion; D: Final aspect of the endoscopic submucosal dissection eschar.
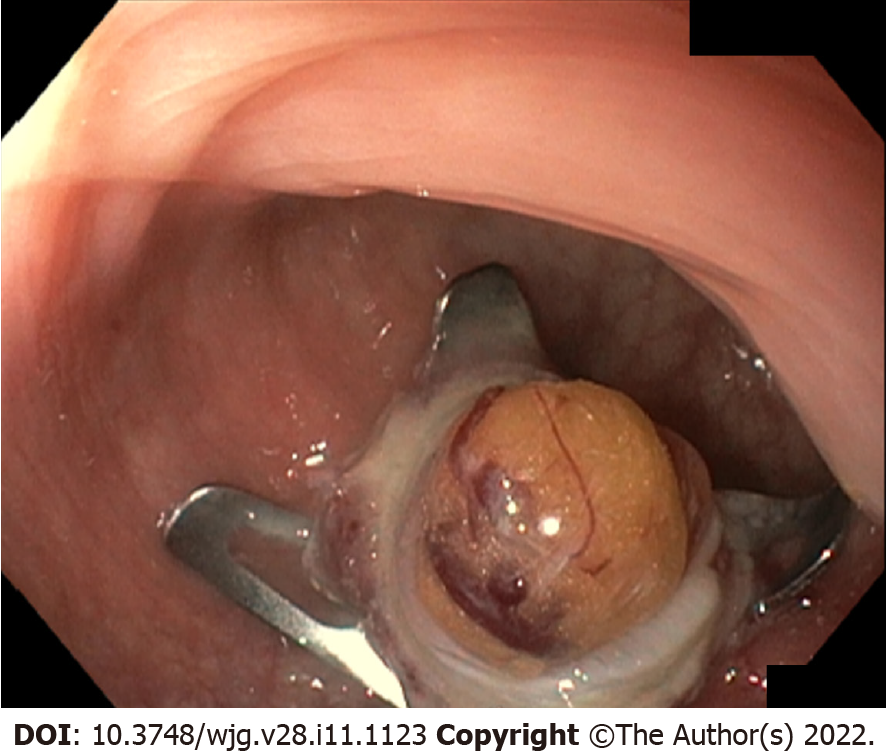
Figure 4 The full thickness resection device Ovesco over-the-scope OTSC system is a single-use metallic clip preloaded on an applicator cap that can be attached to any standard endoscope.
The endoscopic clip can be placed underneath an epithelial/subepithelial lesion and it guarantees at the same time its full-thickness removal and the wall defect closure. In this picture, the Ovesco clip is placed underneath a rectal neuroendocrine neoplasm and grabs its complete thickness.
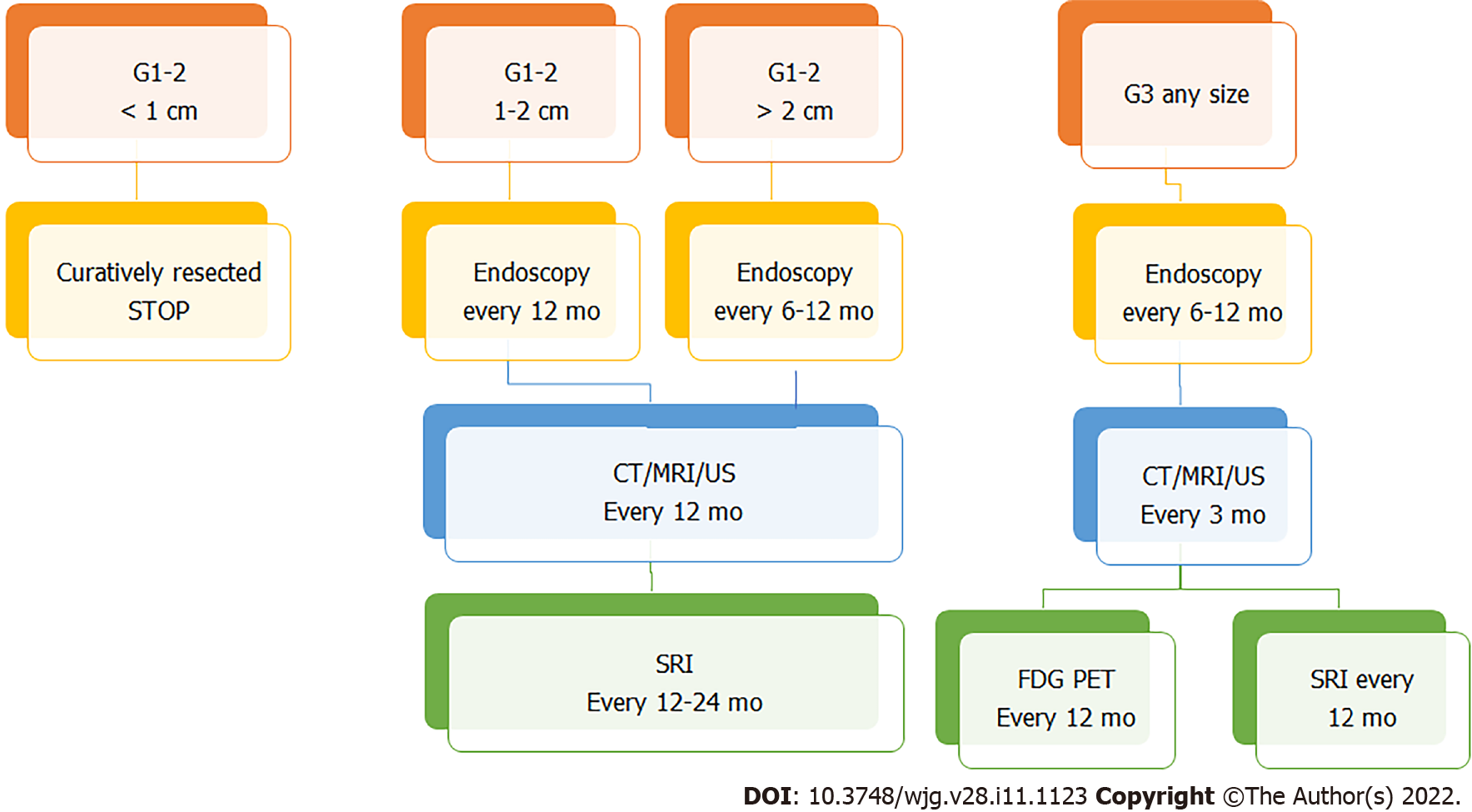
Figure 5 Surveillance flow-chart.
CT: Computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; US: Ultrasound; SRI: Somatostatin receptor imaging; FDG-PET: Positron emission tomography with 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose.
- Citation: Gallo C, Rossi RE, Cavalcoli F, Barbaro F, Boškoski I, Invernizzi P, Massironi S. Rectal neuroendocrine tumors: Current advances in management, treatment, and surveillance. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(11): 1123-1138
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i11/1123.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i11.1123