Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2021; 27(46): 7982-7994
Published online Dec 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i46.7982
Published online Dec 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i46.7982
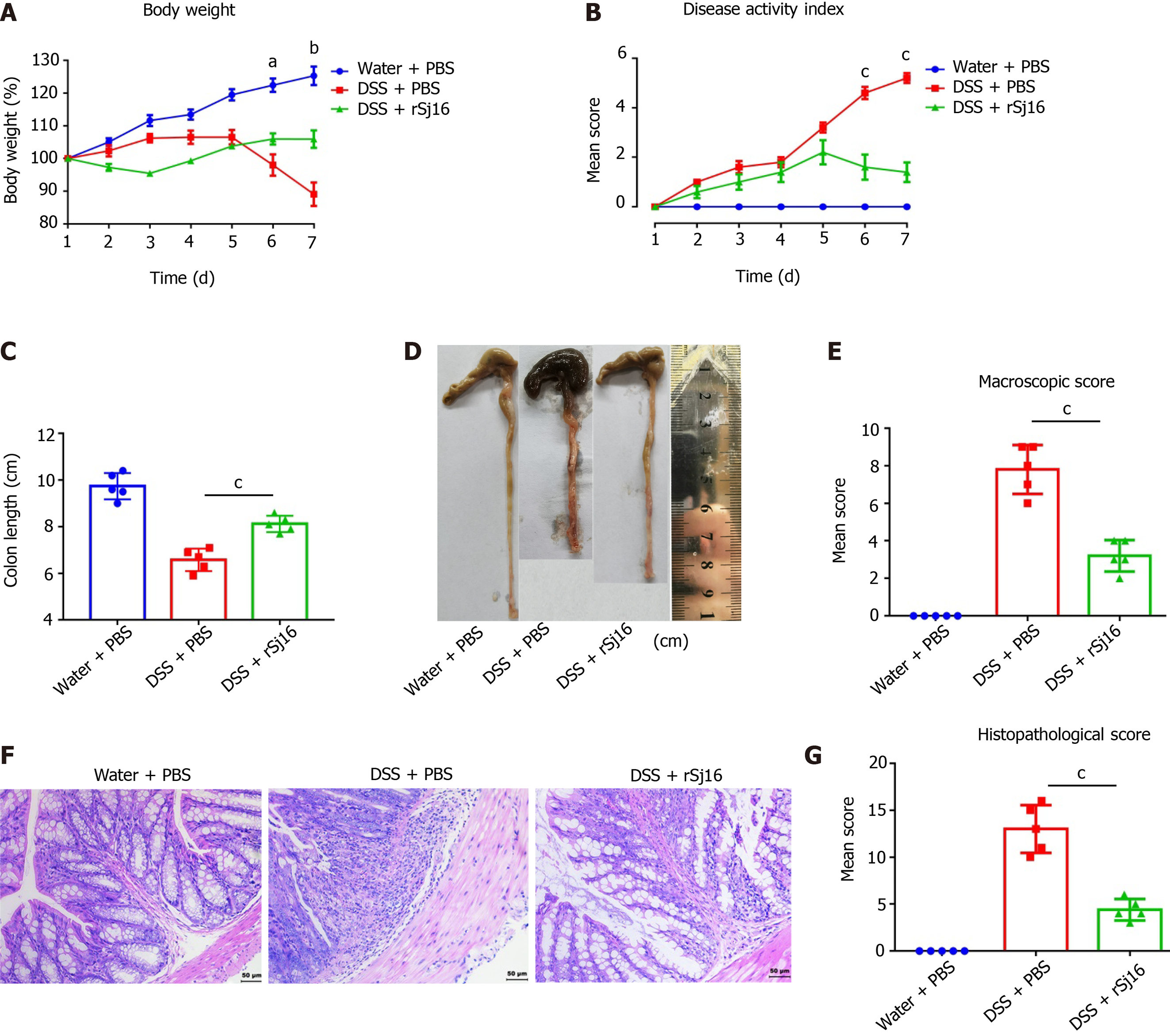
Figure 1 rSj16 protects against acute dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis.
A: Daily changes in body weight [dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) + rSj16 vs DSS + PBS]; B: Changes in DAI (DSS + rSj16 vs DSS + PBS); C and D: Colon lengths were measured and recorded; E: Macroscopic appearance of the colons; F: The histopathological changes in the colons were examined by H&E staining (20×); G: Histopathological scores of the colons were determined. DSS: Dextran Sulfate Sodium Salt. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA. Data are presented as means ± SD; aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
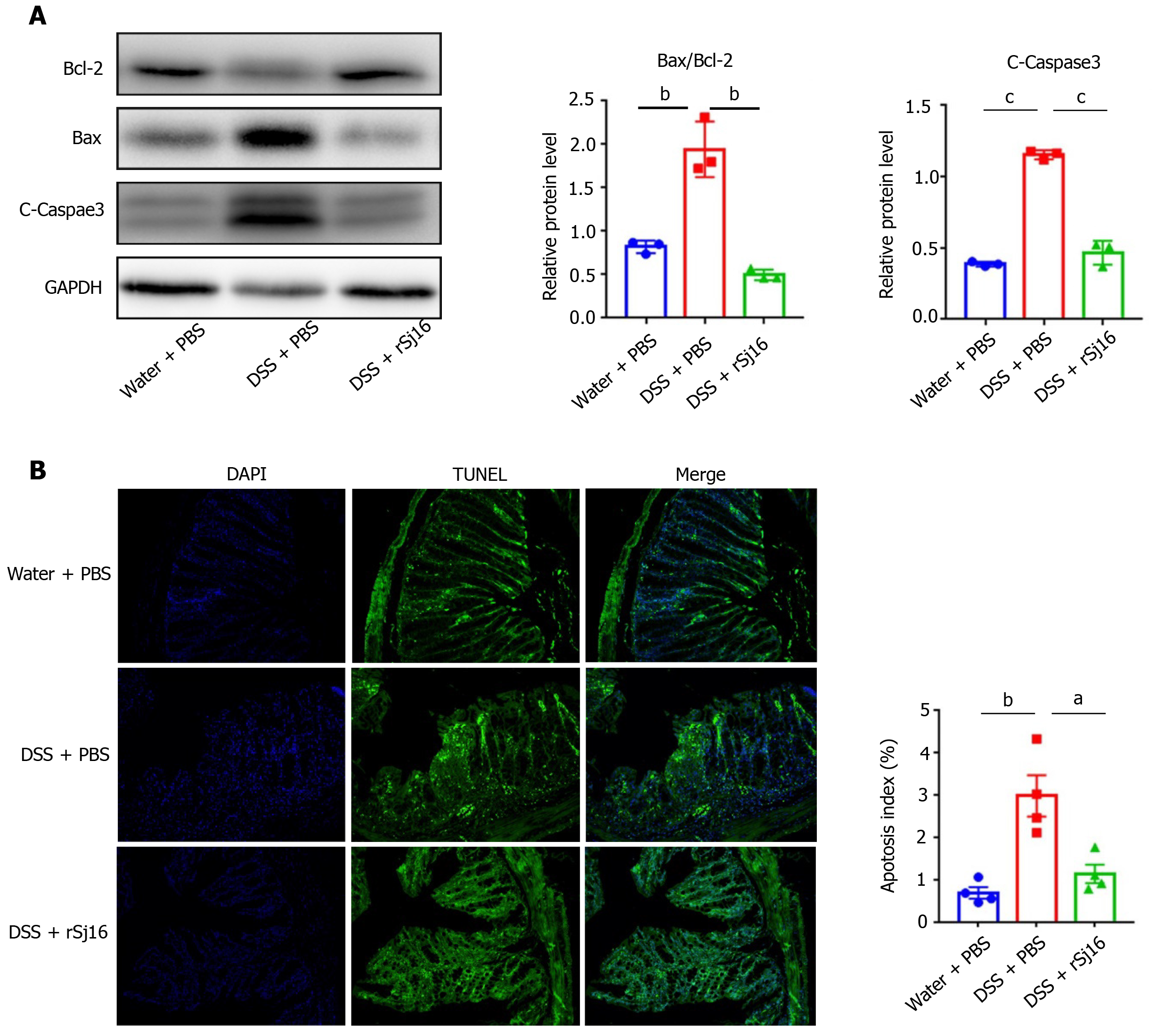
Figure 2 rSj16 inhibits dextran sulfate sodium induced apoptosis of colon epithelial cells.
A: Western blot analysis for the expression of apoptosis relative proteins, including Bcl-2, Bax and cleaved-Caspase3; B: The apoptosis of colon tissue of mice treated with dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) + PBS and DSS + rSj16 was detected by TUNEL assay (20×), TUNEL positive cells were apoptotic cells, the number of TUNEL positive cells was quantified. TUNEL: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA (A) and Kruskal–Wallis test (non-parametric) (B). Data are presented as means ± SD; aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
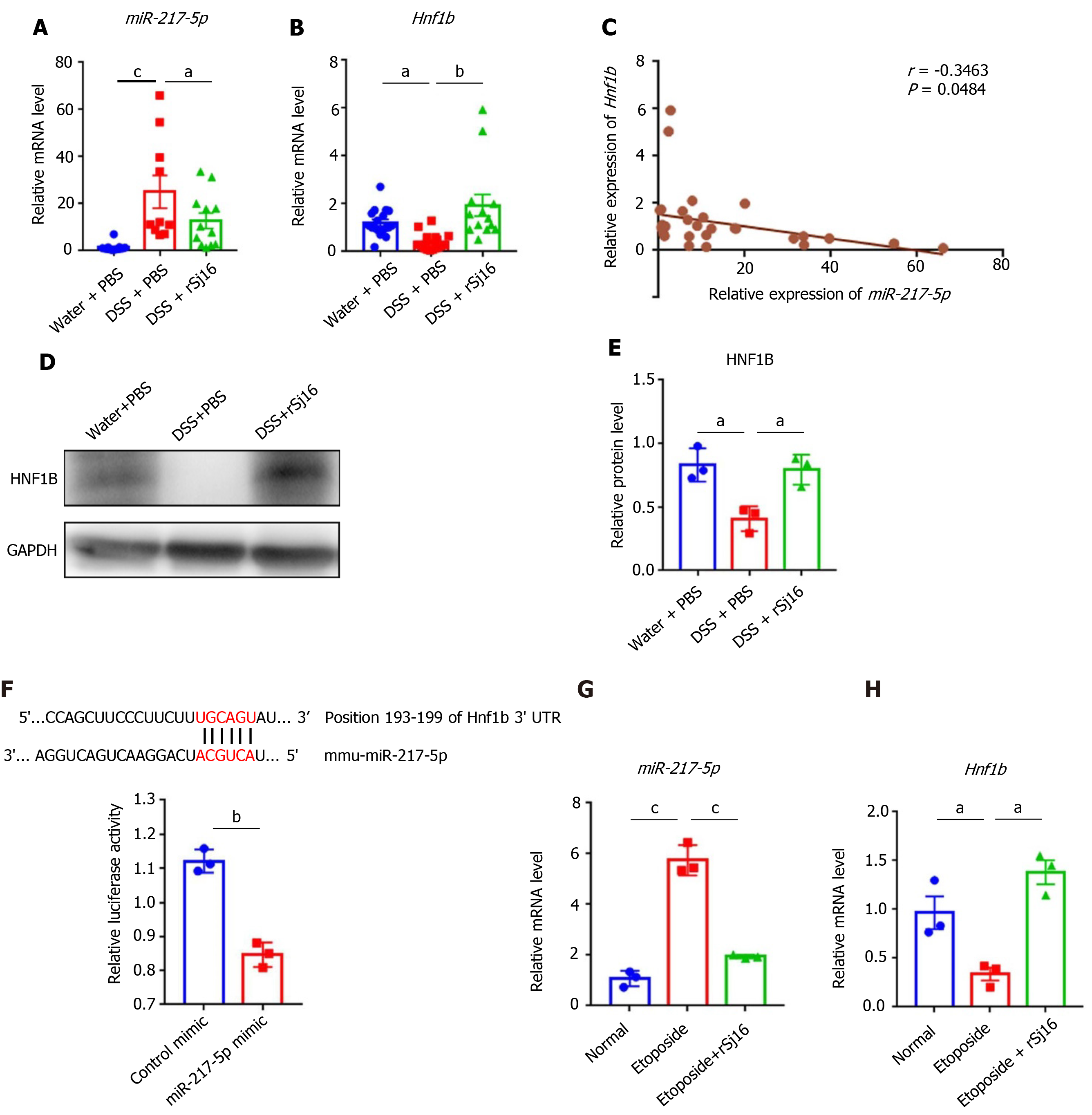
Figure 3 rSj16 can inhibit the expression of miR-217-5p in the colon of mice with dextran sulfate sodium-induced inflammatory bowel disease.
A and B: Relative RNA expression of miR-217-5p and hnf1b in colon tissue of mice; data were normalized to levels detected in colon tissue of mice after treatment with Water and PBS (control) group; C: Pearson’s correlation coefficient analysis showed a negative correlation between miR-217-5p and HNF1B in colon tissue of mice (r = -0.3463, P < 0.05); D and E: Western blot was used to detect the expression of HNF1B in protein levels; F: The wild-type HNF1B -3′- untranslated region (UTR) was cloned into psi-CHECK-2 to predict the binding site of miR-217-5p in the 3′-UTR of hnf1b gene. Dual-luciferase reporter assay was performed on HEK 293Tcells transfected with HNF1B UTR reporter plasmid together with miR-217-5p mimic or control mimic; G and H:MODE-K cells were treated with Etoposide or Etoposide + rSj16. The expression of miR-217-5p and hnf1b were determined using quantitative PCR. HNF1B: Hepatic nuclear factor-1beta. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA (B and E) and Kruskal–Wallis test (non-parametric) (A), and unpaired two-sample t-test (F, G and H). Data are presented as means ± SD; aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
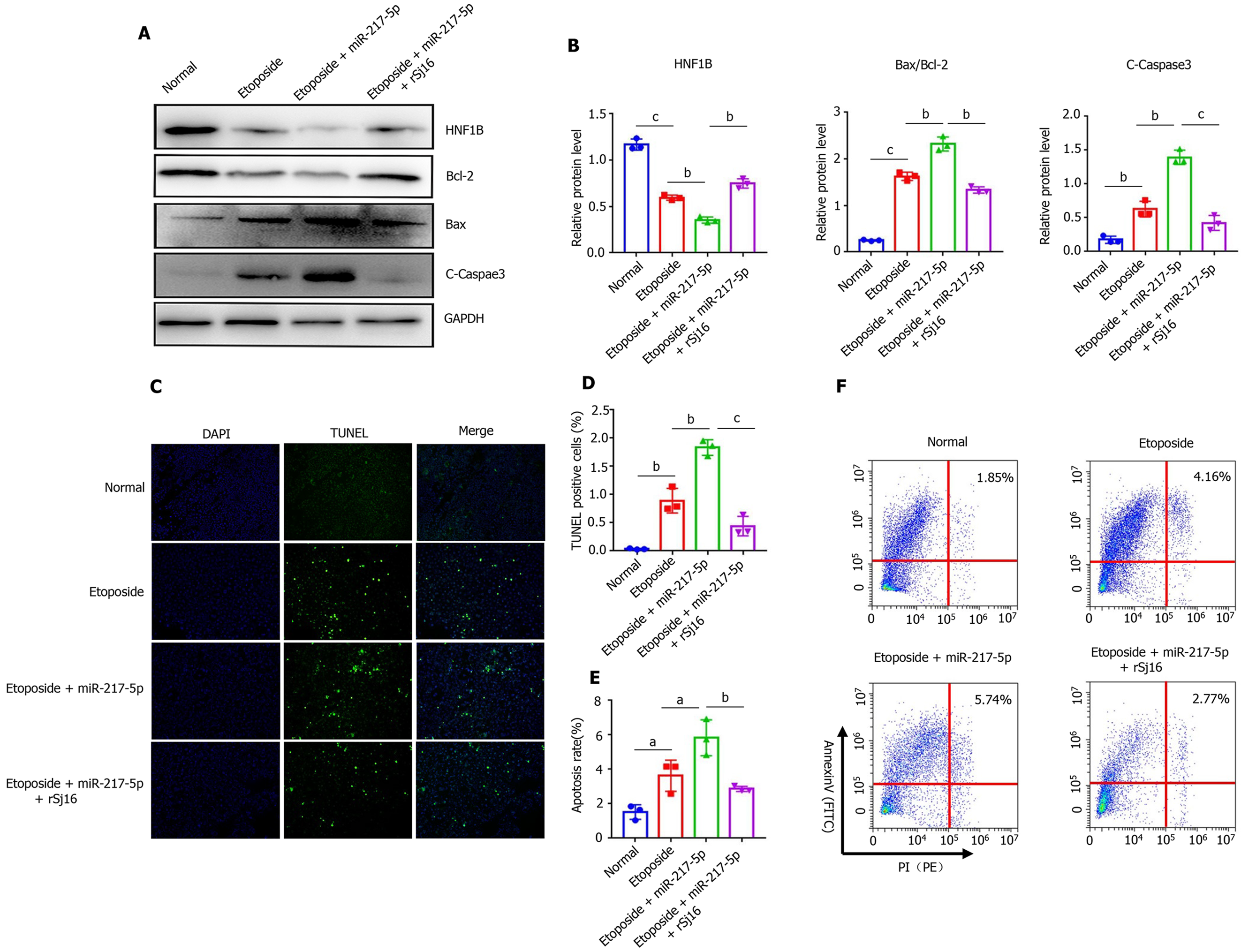
Figure 4 rSj16 have anti-apoptotic action by regulating the miR-217-5p/HNF1B axis.
A and B: MODE-K cells were treated with Etoposide, Etoposide + miR-217-5p, and Etoposide + miR-217-5p + rSj16. The expression of apoptosis relative proteins, including Bcl-2, Bax and cleaved-Caspase3 was analyzed by Western blotting; C and D: The apoptosis of MODE-K cells was detected by TUNEL assay after treatment with Etoposide + miR-217-5p, and Etoposide + miR-217-5p + rSj16 (10×), TUNEL positive cells were apoptotic cells, the number of TUNEL positive cells was quantified; E and F: Flow cytometry analysis of MODE-K cells treated with Etoposide + miR-217-5p, and Etoposide + miR-217-5p + rSj16. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA. PI: propidium iodide. Data are presented as means ± SD; aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
- Citation: Zhang LC, Wu XY, Yang RB, Chen F, Liu JH, Hu YY, Wu ZD, Wang LF, Sun X. Recombinant protein Schistosoma japonicum-derived molecule attenuates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by inhibiting miRNA-217-5p to alleviate apoptosis. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(46): 7982-7994
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i46/7982.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i46.7982