Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2021; 27(44): 7597-7611
Published online Nov 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i44.7597
Published online Nov 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i44.7597
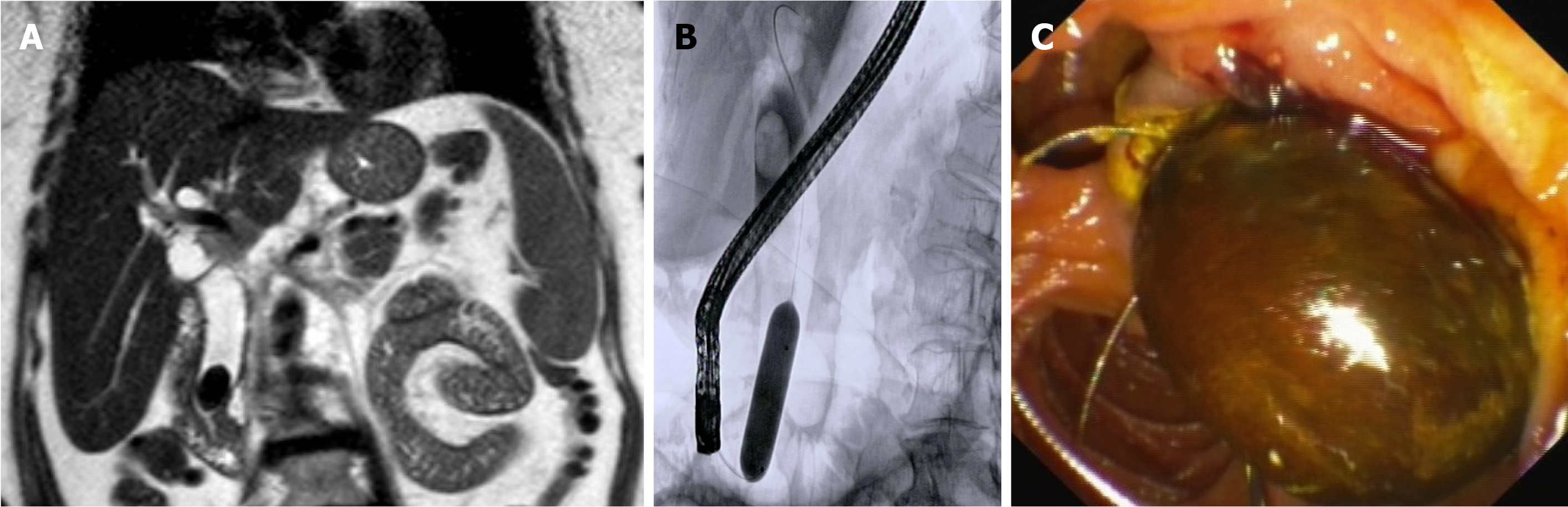
Figure 1 Management of difficult common bile duct stone by endoscopic sphincterotomy and large balloon dilation.
A: Magnetic resonance imaging showing a large stone in the distal common bile duct; B: Fluoroscopic appearance of endoscopic papillary large balloon dilation with a pneumatic balloon filled with contrast medium; C: Final endoscopic view of the stone extracted by a Dormia basket.
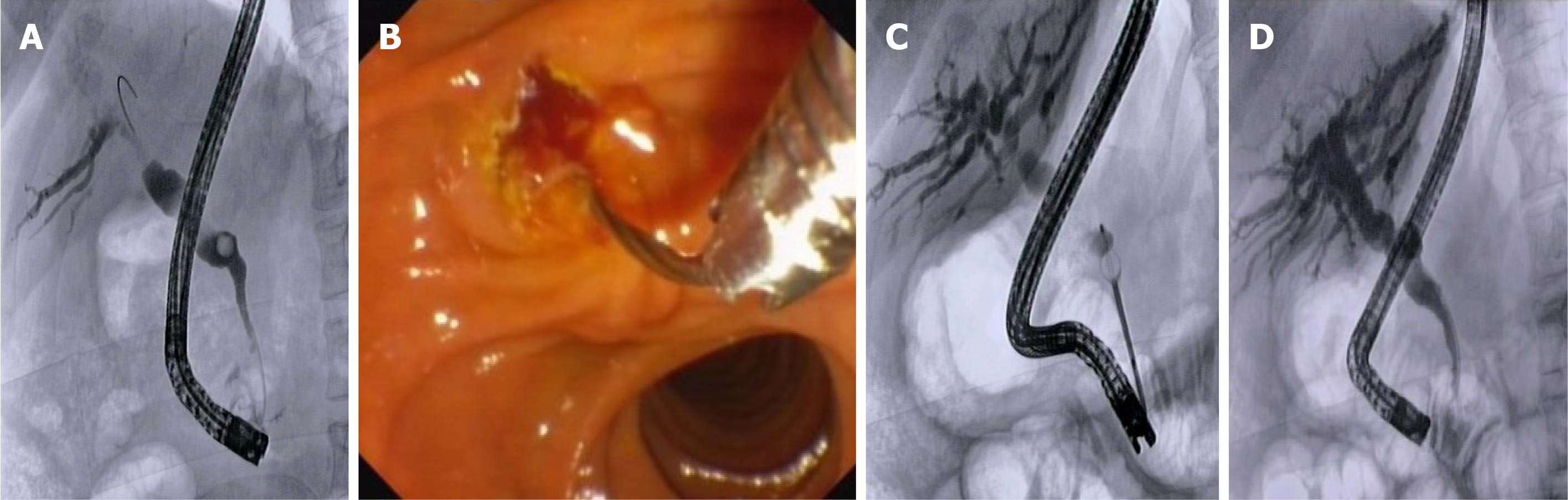
Figure 2 Management of common bile duct stones with distal biliary stricture by mechanical lithotripsy.
A: Cholangiogram showing distal common bile duct (CBD) stricture with stone in the medium CBD; B: Introduction of a mechanical lithotripter over the Dormia basket; C: Mechanical lithotripsy under fluoroscopic control; D: Final cholangiogram showing complete CBD clearance.
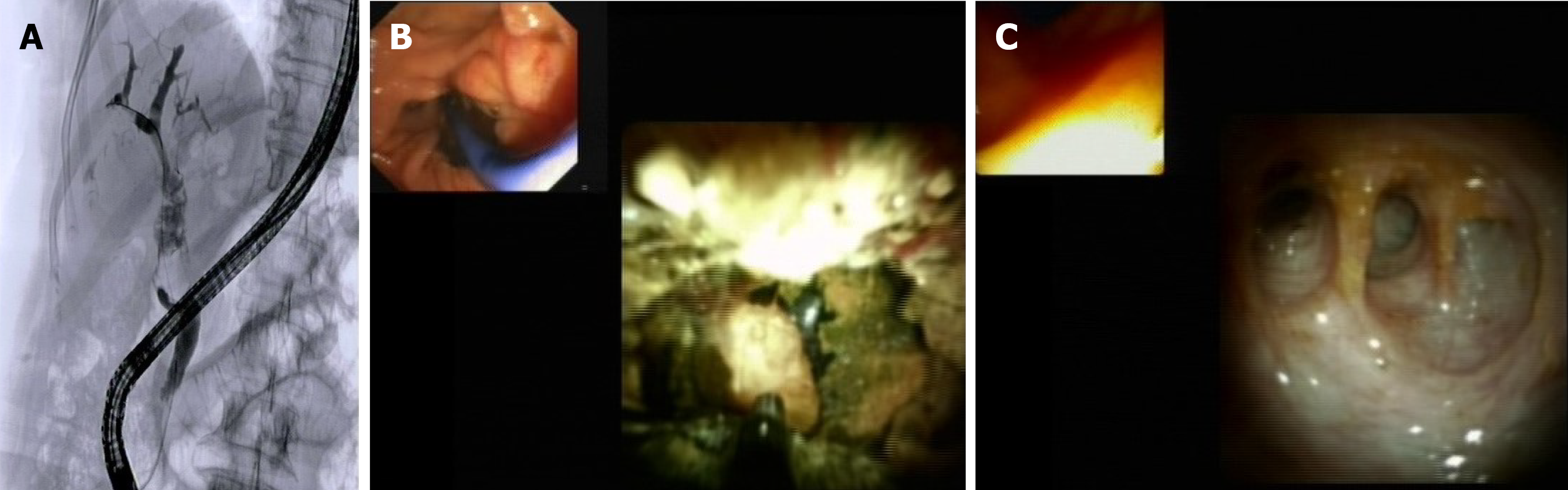
Figure 3 Management of impacted common bile duct stones with distal biliary stricture by cholangioscopy assisted lithotripsy.
A: Cholangiogram showing distal common bile duct (CBD) stricture with large impacted stone in the medium CBD and multiple stones above; B: Cholangioscopy assisted lithotripsy by electrohydraulic of the impacted stone; C: Final cholangioscopy showing complete CBD clearance with biliary confluence appearance.
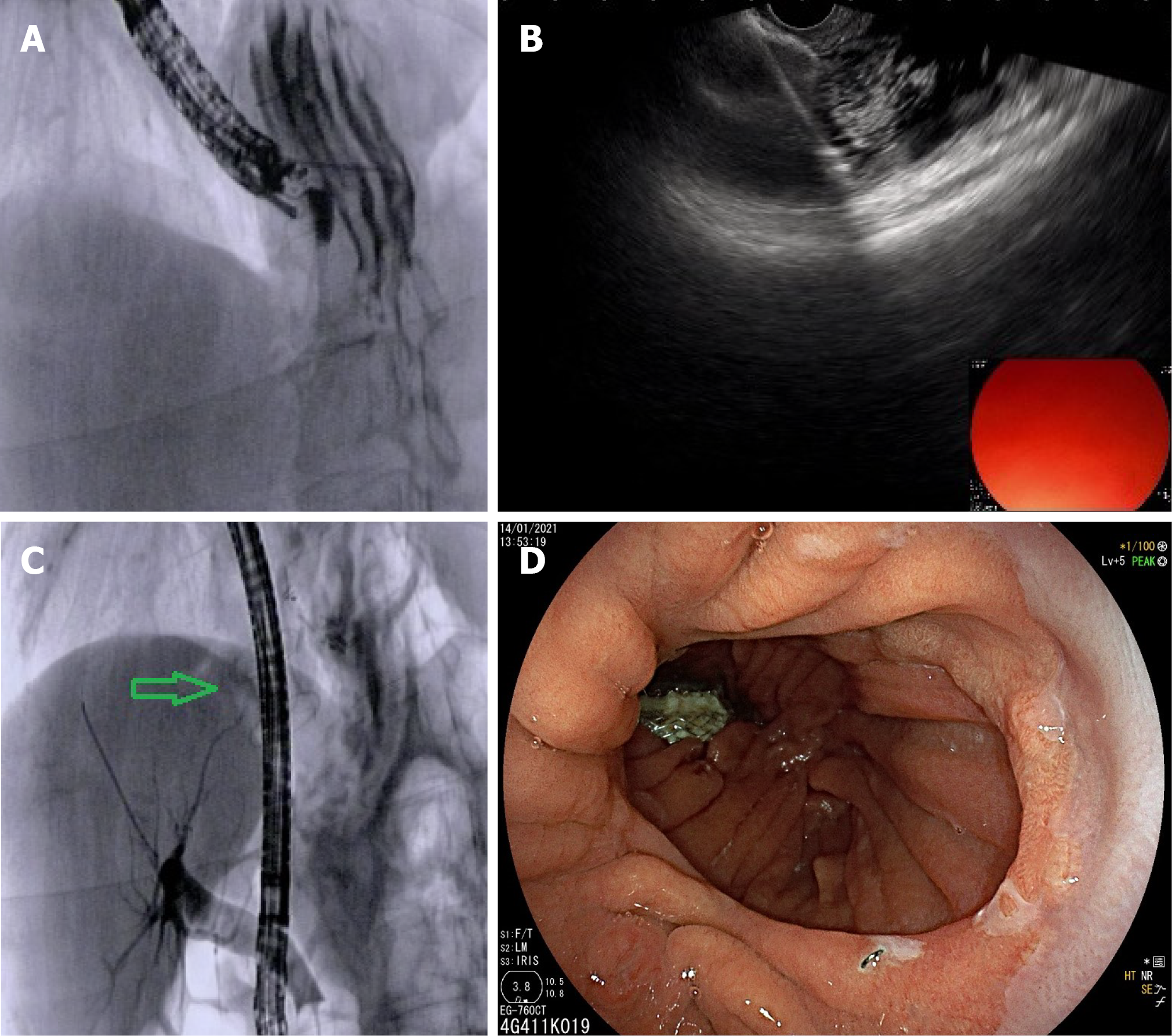
Figure 4 Endoscopic ultrasonography-directed transgastric endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography for management of common bile duct stone in patient with previous Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for bariatric surgery.
A: Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS)-guided puncture of the excluded stomach with a 19G EUS needle with injection of contrast medium and sterile saline for gastric distension under fluoroscopic control; B: EUS guided first flange deployment of 20 mm lumen apposing metal stent (LAMS) into the gastric remnant; C: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography for stone removal was performed after advancing the duodenoscope through the LAMS (green arrow); D: Endoscopic image confirming placement of the LAMS within the gastric pouch.
- Citation: Tringali A, Costa D, Fugazza A, Colombo M, Khalaf K, Repici A, Anderloni A. Endoscopic management of difficult common bile duct stones: Where are we now? A comprehensive review. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(44): 7597-7611
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i44/7597.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i44.7597