Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2021; 27(35): 5932-5945
Published online Sep 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i35.5932
Published online Sep 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i35.5932
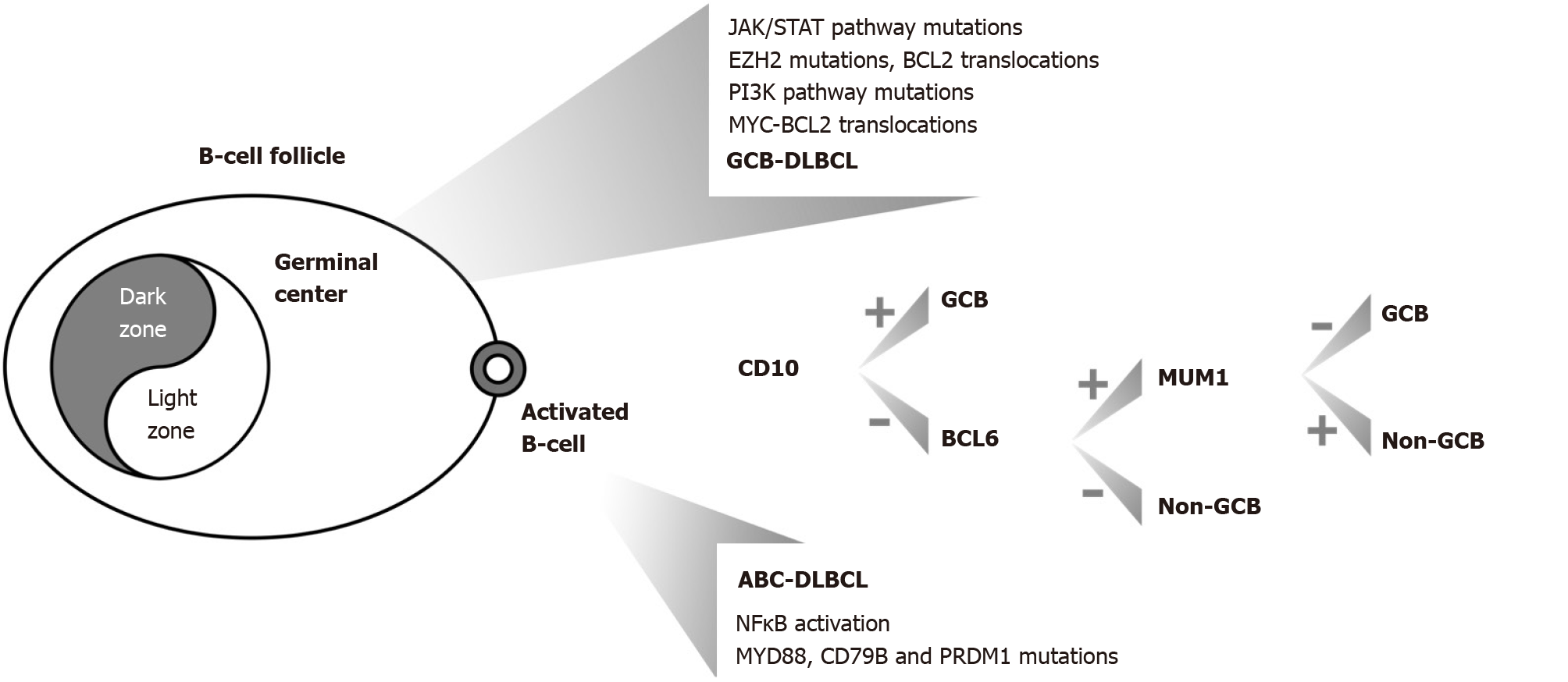
Figure 1 Primary gastric diffuse large B-cell lymphoma lymphomas and related molecular lesions.
GCB: Germinal center B-cell lymphoma; ABC: Activated B-cell-like lymphoma; the combination of MYC plus BCL2 translocations corresponds to ‘double hit lymphomas’; DLBCL: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; NF-κβ: Nuclear factor κappa beta.
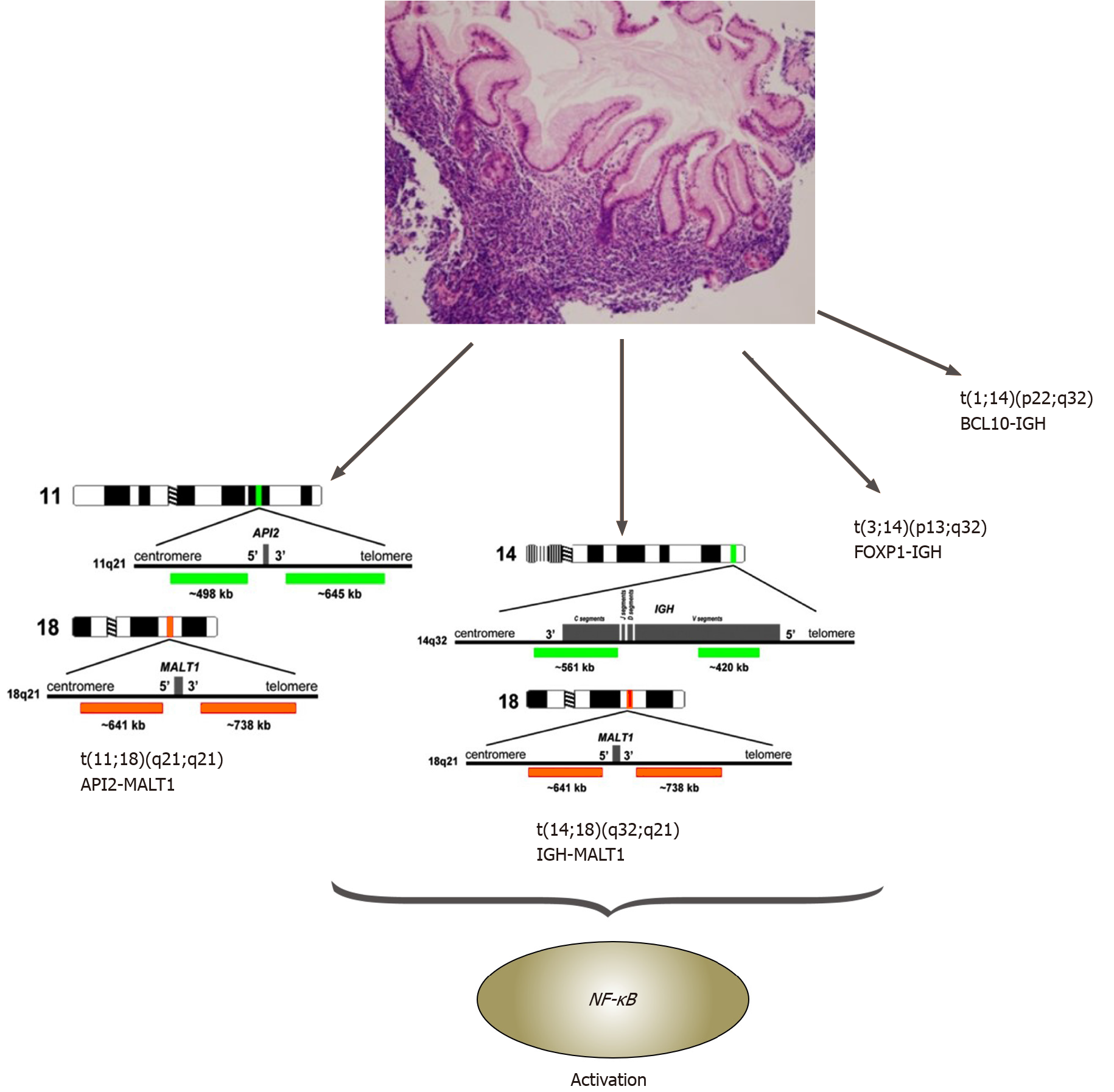
Figure 2 Gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas and related chromosomal translocations.
BCL: B-cell lymphoma; FOXP: Forkhead box protein; IGH: Immunoglobulin heavy (chain); MALT: Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue; NF-κB: Nuclear factor κappa beta.
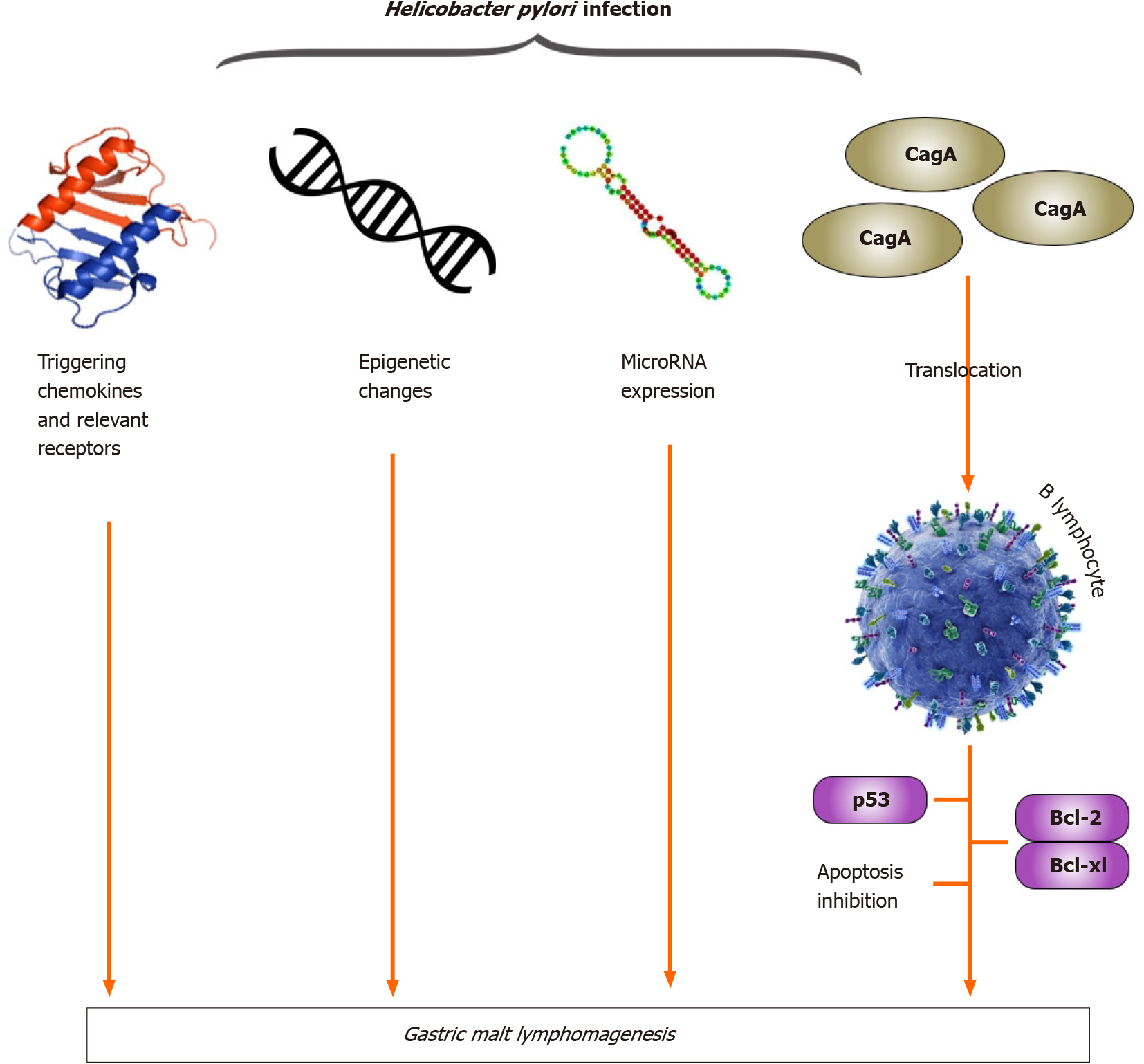
Figure 3 Helicobacter pylori infection, molecular mechanisms and gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomagenesis.
BCL: B-cell lymphoma; Bcl-XL: B-cell leukemia XL; CagA: Cytotoxin-associated gene A.
- Citation: Diamantidis MD, Papaioannou M, Hatjiharissi E. Primary gastric non-Hodgkin lymphomas: Recent advances regarding disease pathogenesis and treatment. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(35): 5932-5945
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i35/5932.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i35.5932