Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2021; 27(34): 5700-5714
Published online Sep 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i34.5700
Published online Sep 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i34.5700
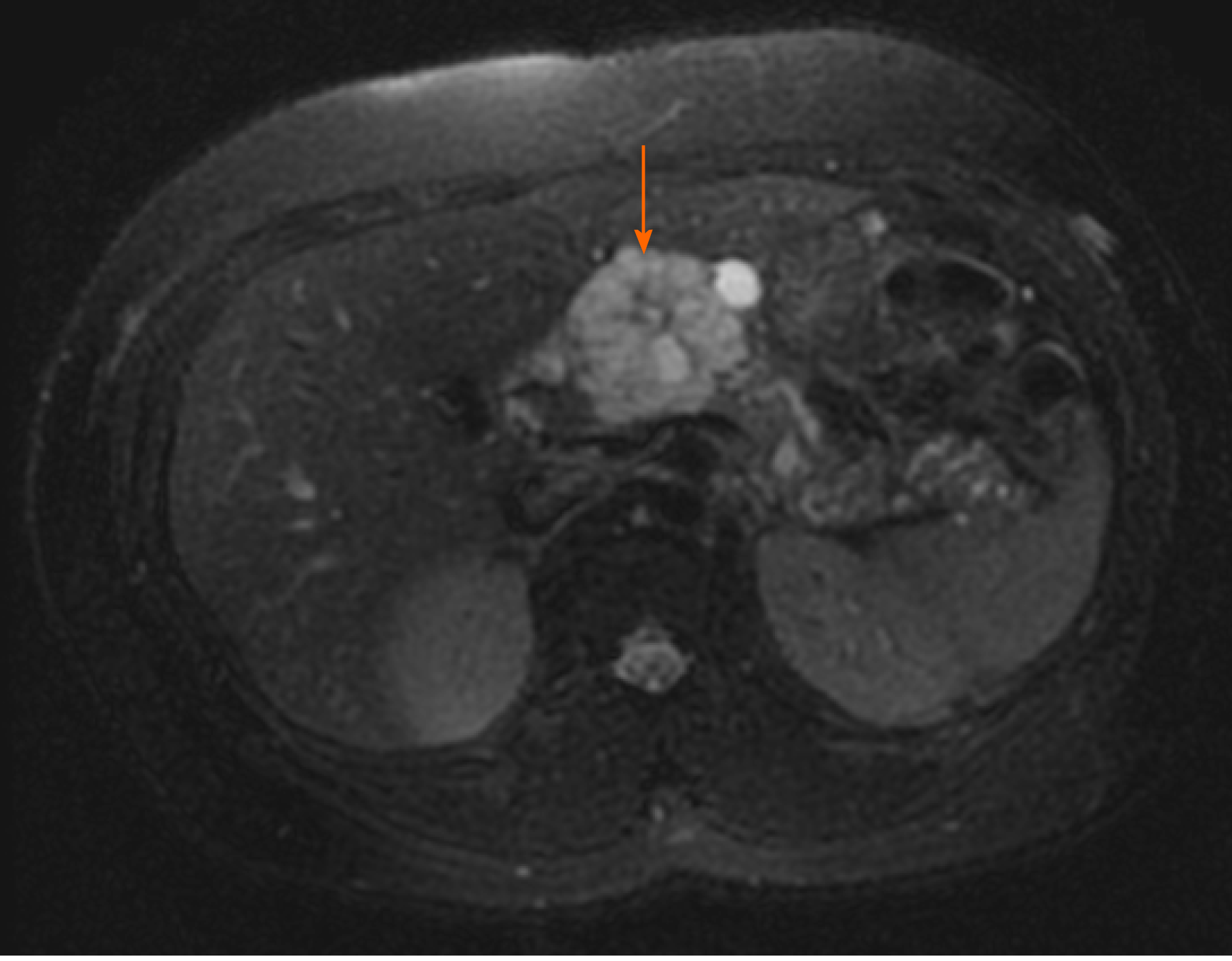
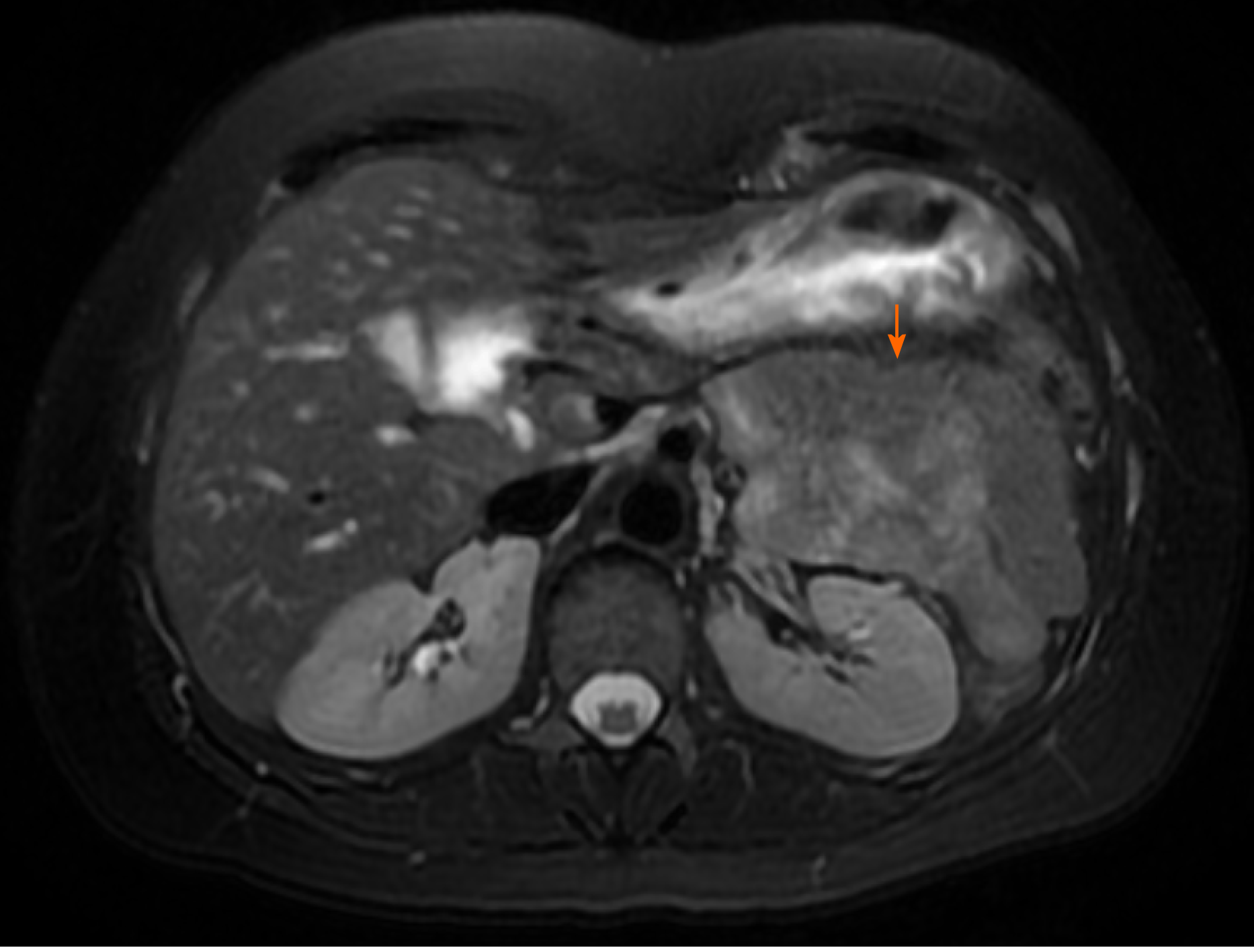
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance imaging of microcystic serous cystadenoma in body of pancreas (arrow)[23].
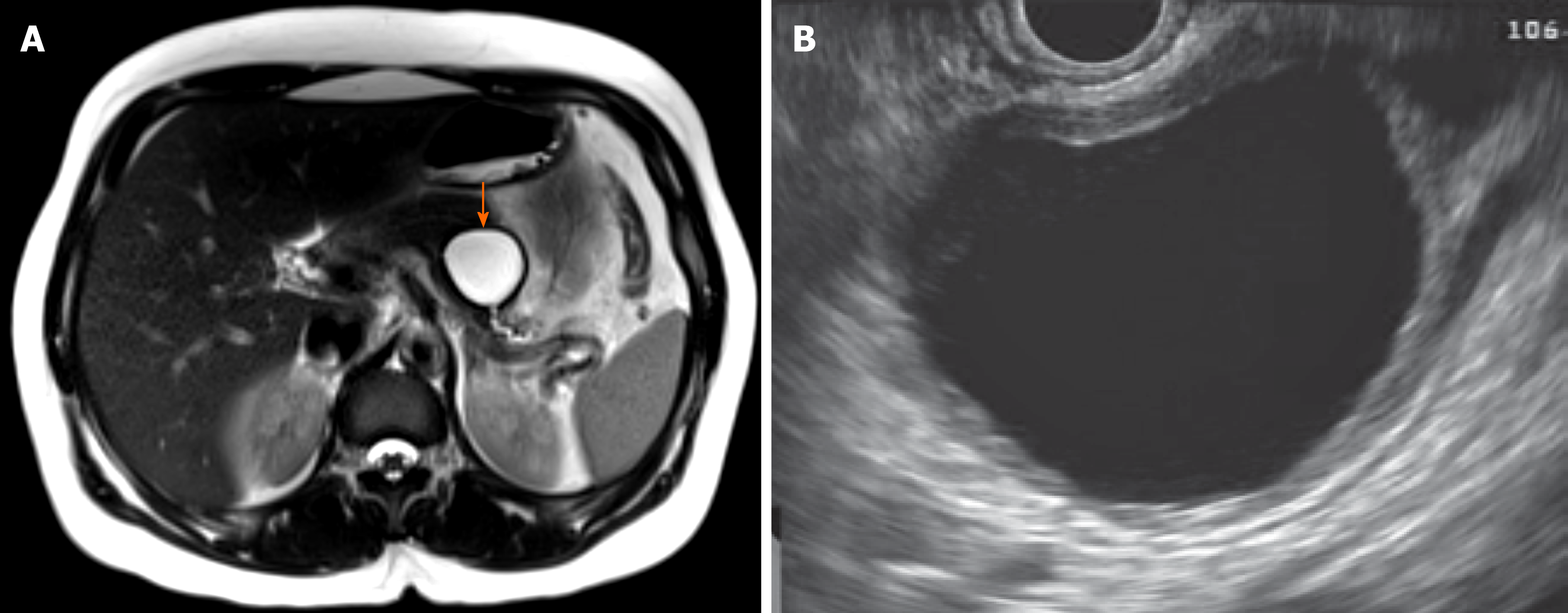
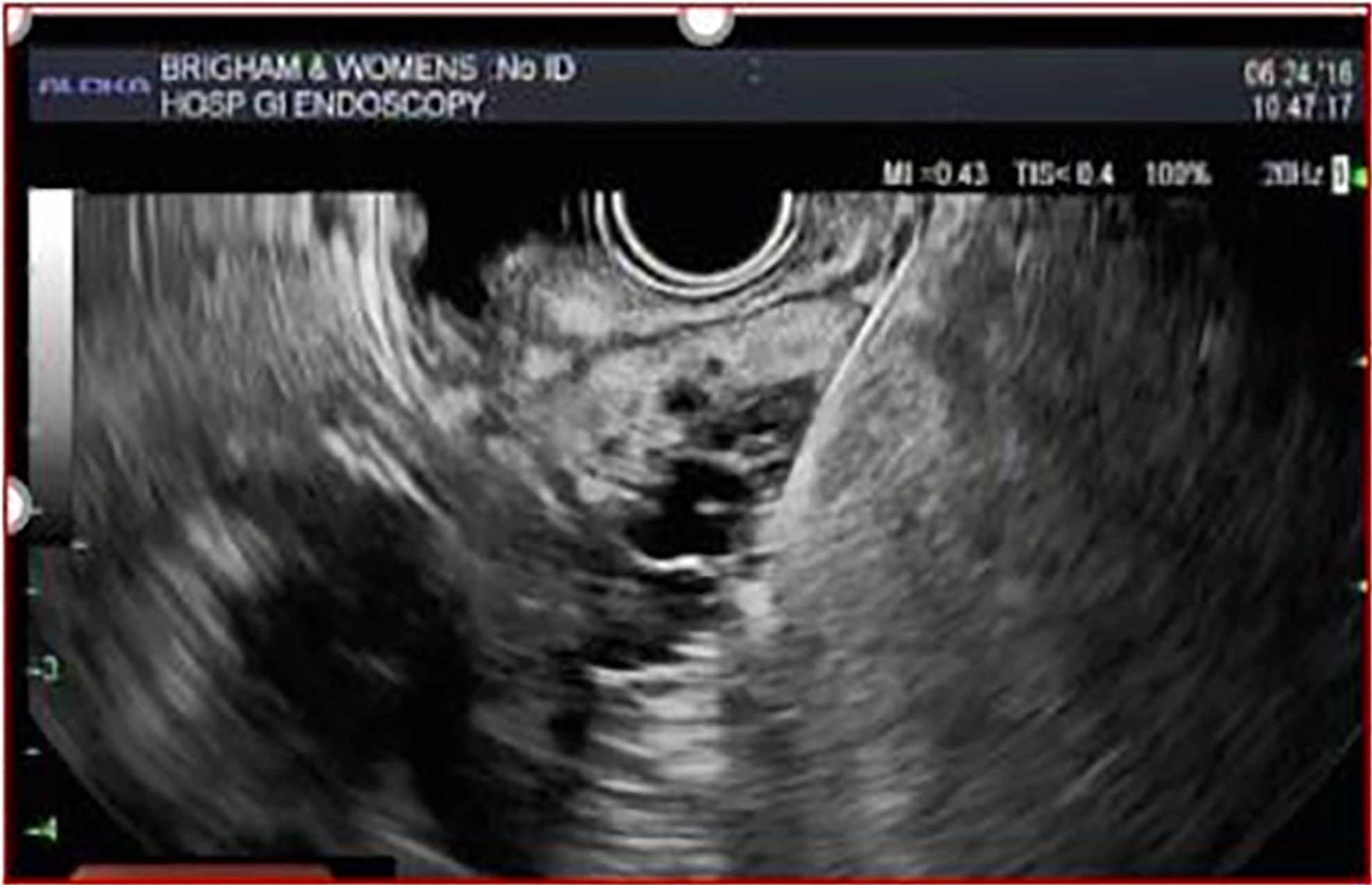
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging and endoscopic ultrasound of mucinous cystic neoplasm appearing unilocular with a thick wall (arrow)[23].
A: Magnetic resonance imaging; B: Endoscopic ultrasound.
Figure 3 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography of main duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm[23].
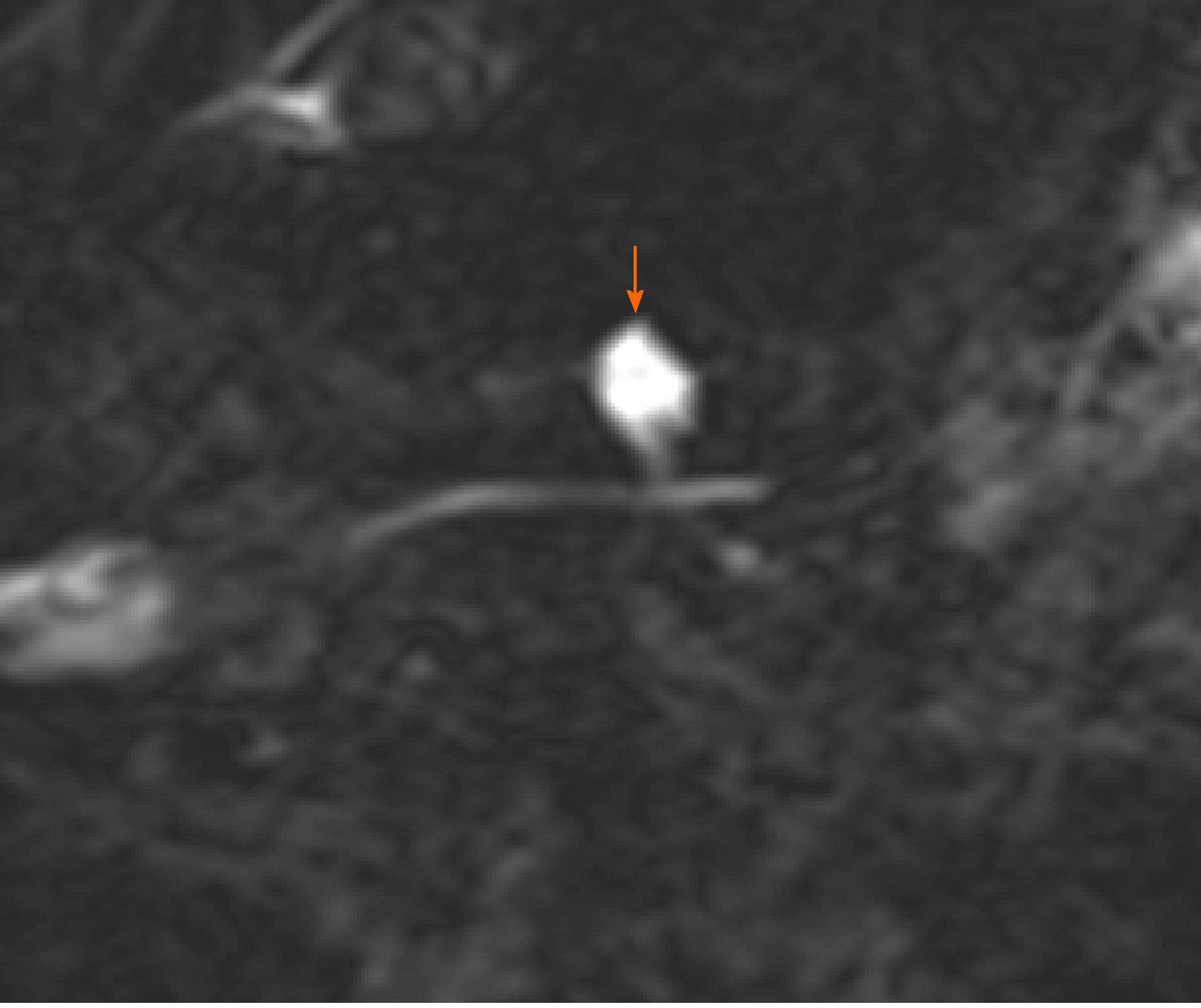
Figure 4 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography of branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm communicating with nondilated main pancreatic duct (arrow)[23].
Figure 5 Magnetic resonance imaging of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm (arrow)[23].
Figure 6 Microbiopsy forceps through endoscopic ultrasound needle.
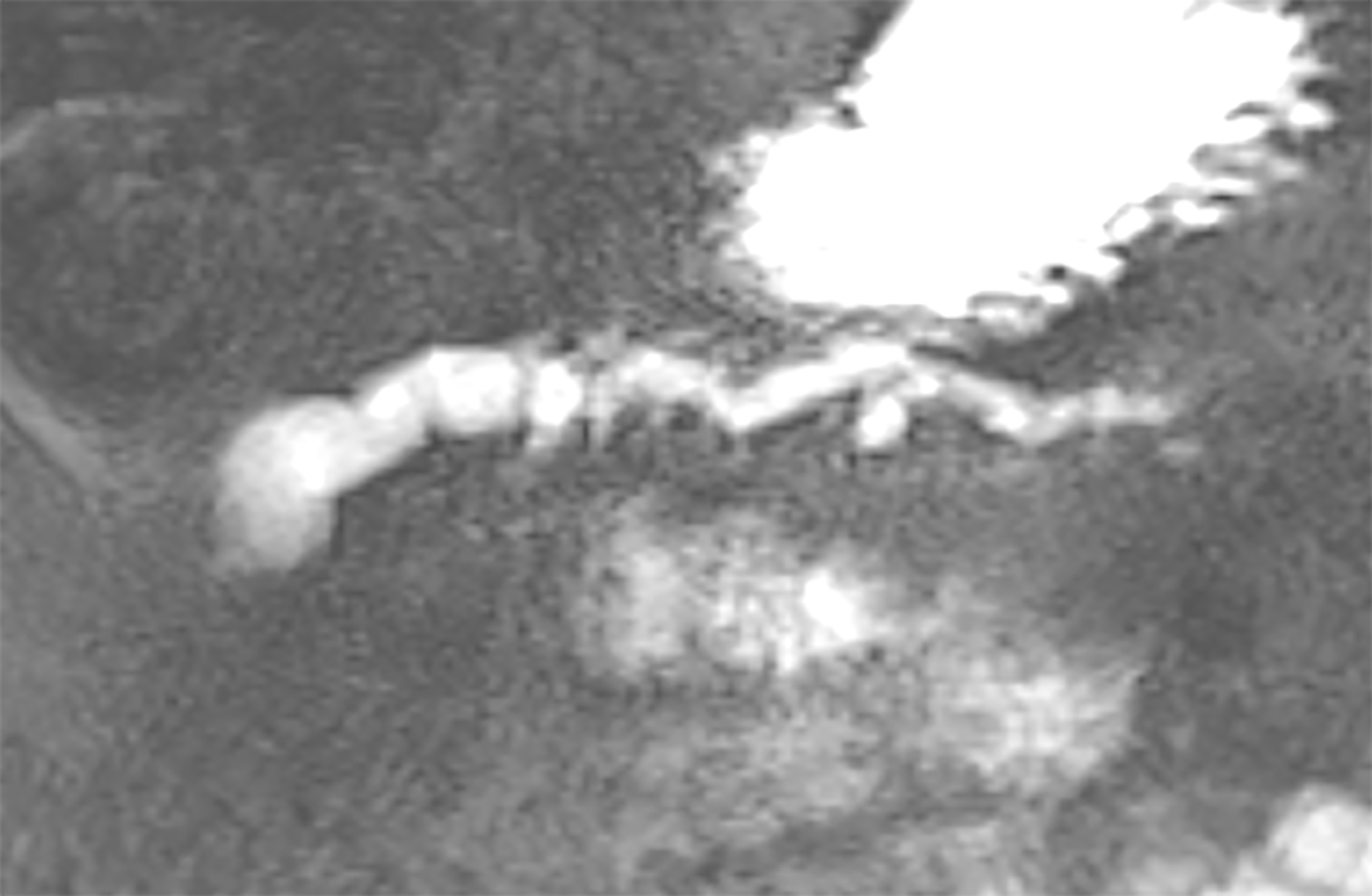
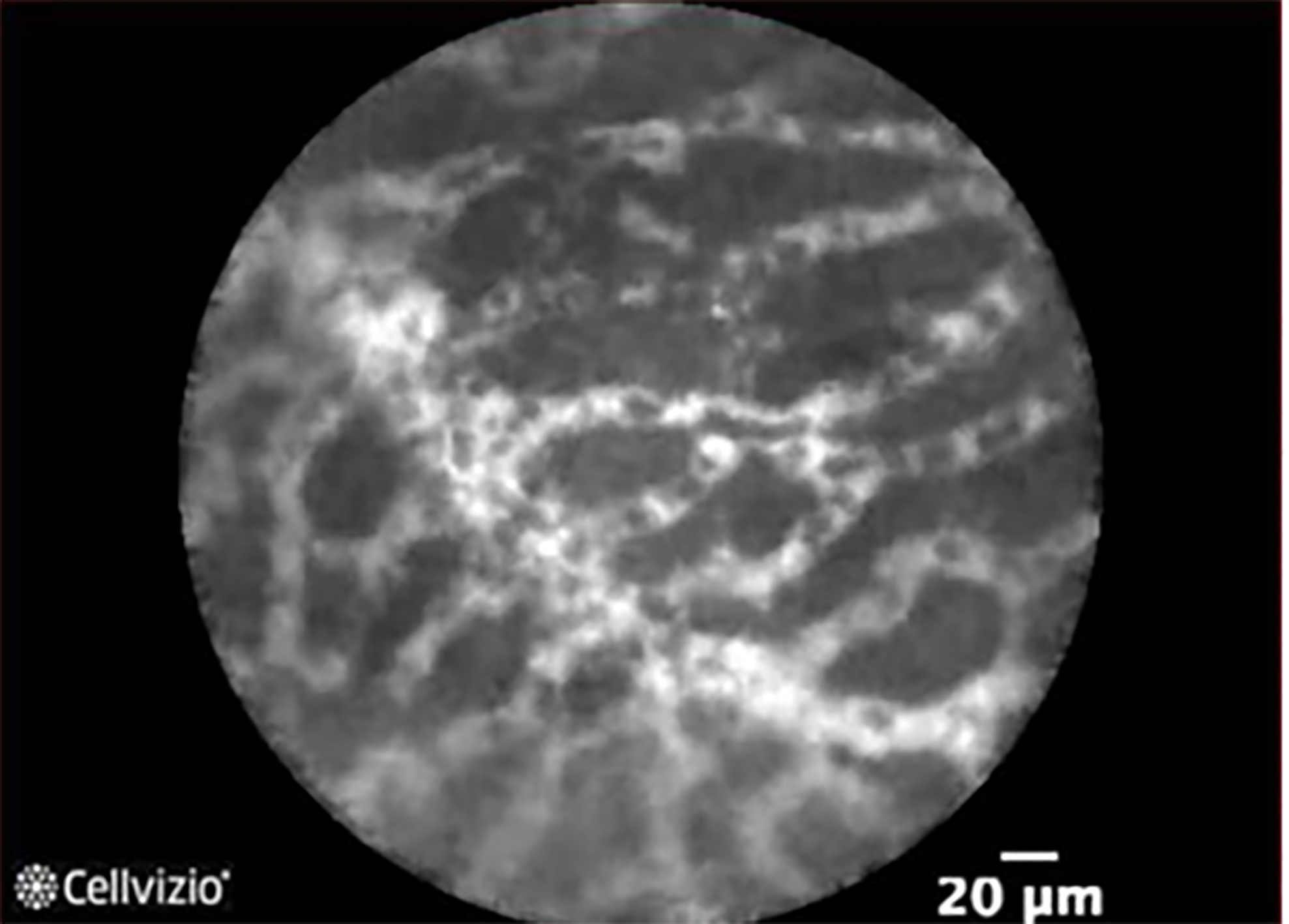
Figure 7 Superficial vascular network in serous cystadenoma.
Courtesy of Mauna Kea Technologies.
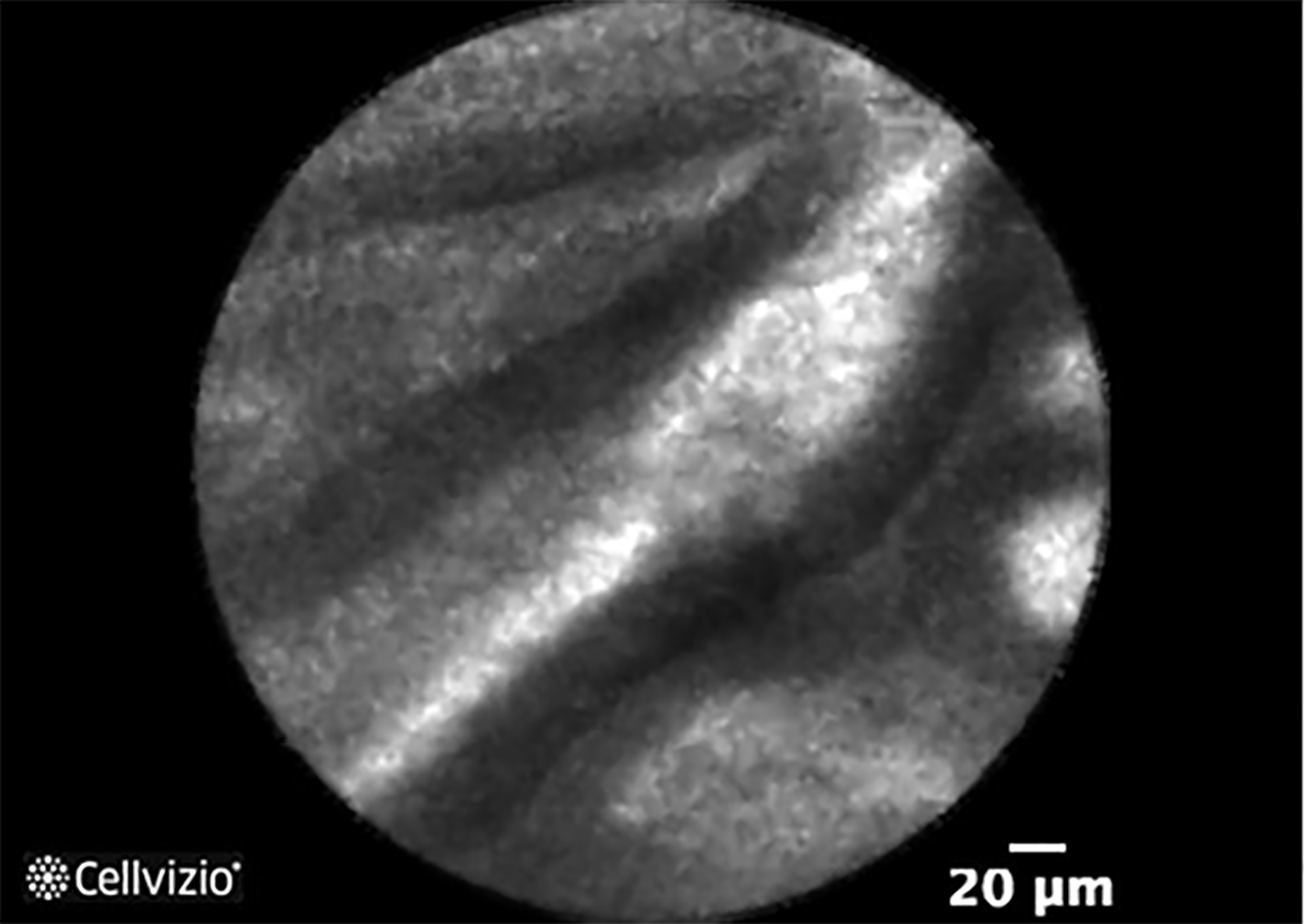
Figure 8 Papillary projections in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm.
Courtesy of Mauna Kea Technologies.
- Citation: Lee LS. Updates in diagnosis and management of pancreatic cysts. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(34): 5700-5714
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i34/5700.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i34.5700