Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2021; 27(30): 4963-4984
Published online Aug 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i30.4963
Published online Aug 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i30.4963
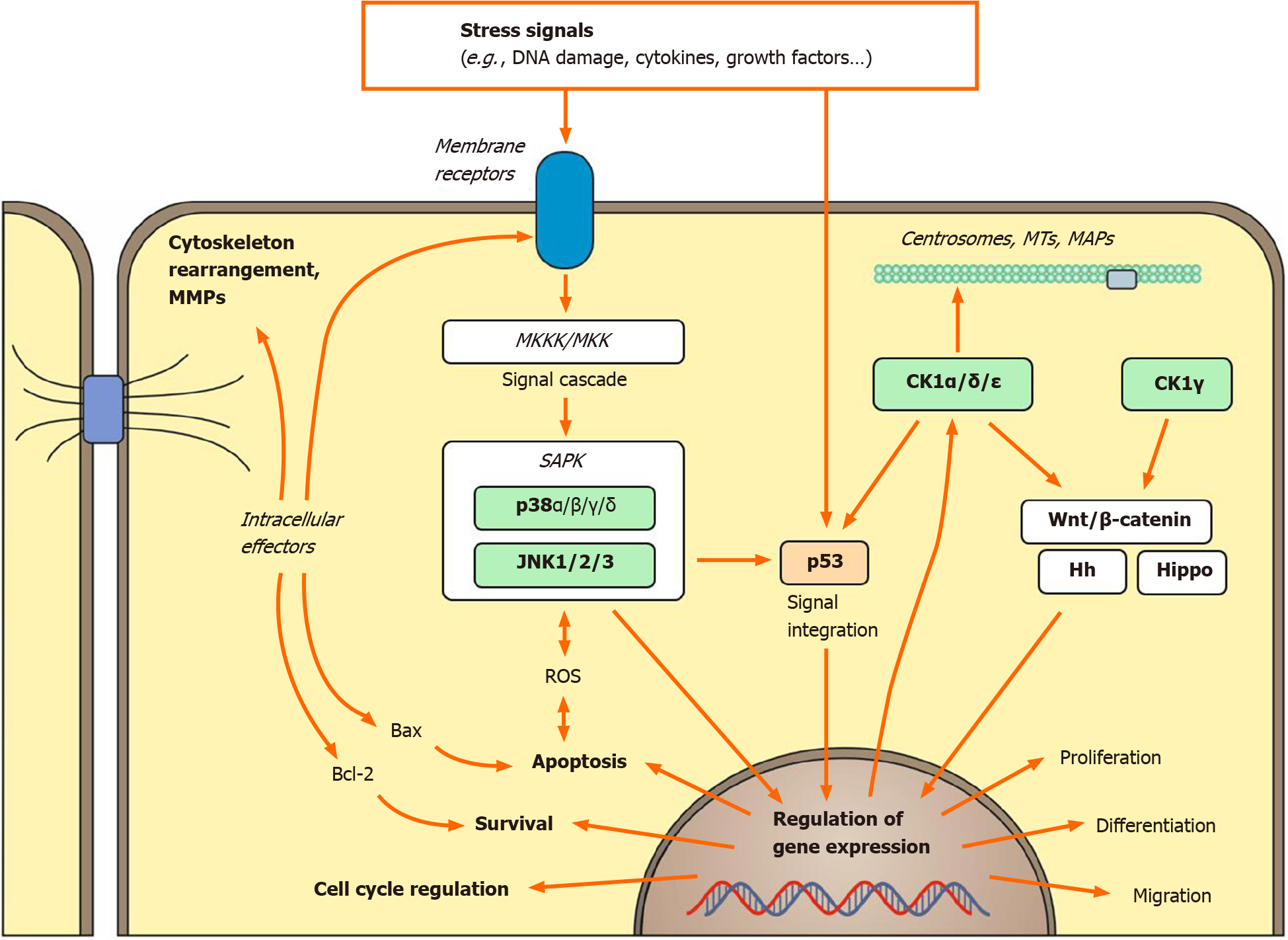
Figure 1 Signal integration mediated by stress-activated protein kinases.
The stress-activated protein kinases (SAPKs) c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 as well as the protein kinases of the casein kinase 1 (CK1) family are activated in response to endogenous and exogenous stress stimuli. Therefore, JNK and p38 are either activated directly or through upstream signaling cascades [mitogen-associated protein kinase kinase kinases (MKKKs), mitogen-associated protein kinase kinases (MKKs)] and subsequently exercise their functions through intracellular signal integrating effectors such as the transcription factors JNK, p53, c-myc, or β-catenin. In response to certain stress stimuli, the kinases of the CK1 family also take key functions in regulatory effects mediated via p53 or through various signal transduction pathways like the Wnt/β-catenin, Hedgehog (Hh), or Hippo pathway. Finally, cellular stress response including regulation of proliferation, differentiation, migration, cell cycle progression, survival, and apoptosis is initiated by modulation of gene expression. MAP: Microtubule-associated protein; MMP: matrix metalloproteinase; MT: Microtubule; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: Traub B, Roth A, Kornmann M, Knippschild U, Bischof J. Stress-activated kinases as therapeutic targets in pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(30): 4963-4984
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i30/4963.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i30.4963