Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2021; 27(27): 4371-4382
Published online Jul 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i27.4371
Published online Jul 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i27.4371
Figure 1 Pathogenesis of chronic pancreatitis and chronic pancreatitis-related pancreatic cancer.
CASC: Calcium-sensing receptor gene; CFTR: Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene; CP: Chronic pancreatitis; CTR: Chymotrypsin C gene; PRSS1: Protease serine 1 gene; SPINK 1: Serine peptidase inhibitor Kazal type 1 gene.
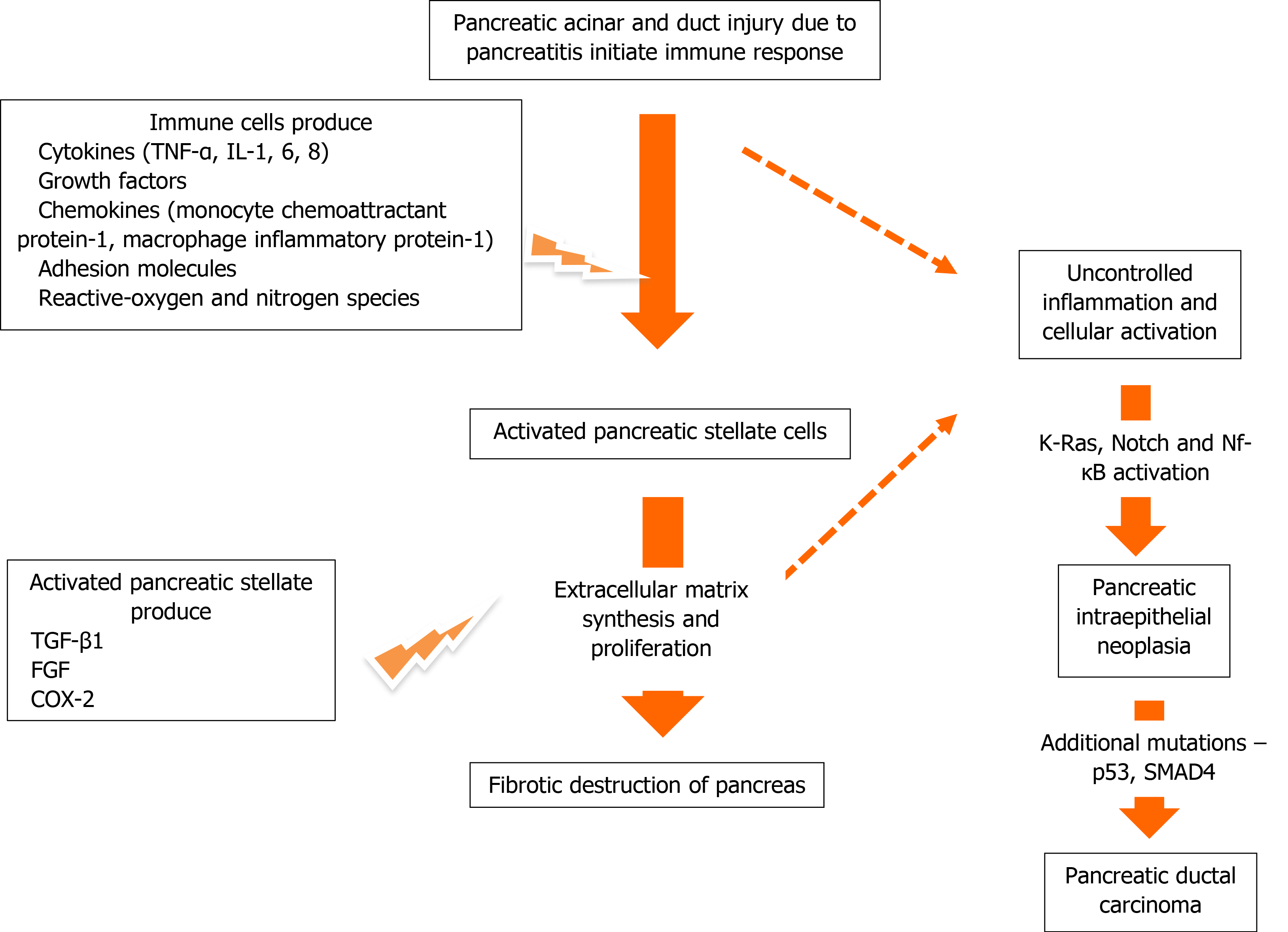
Figure 2 Mechanisms linking chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer.
COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor; IL: Interleukin. TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor β1; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
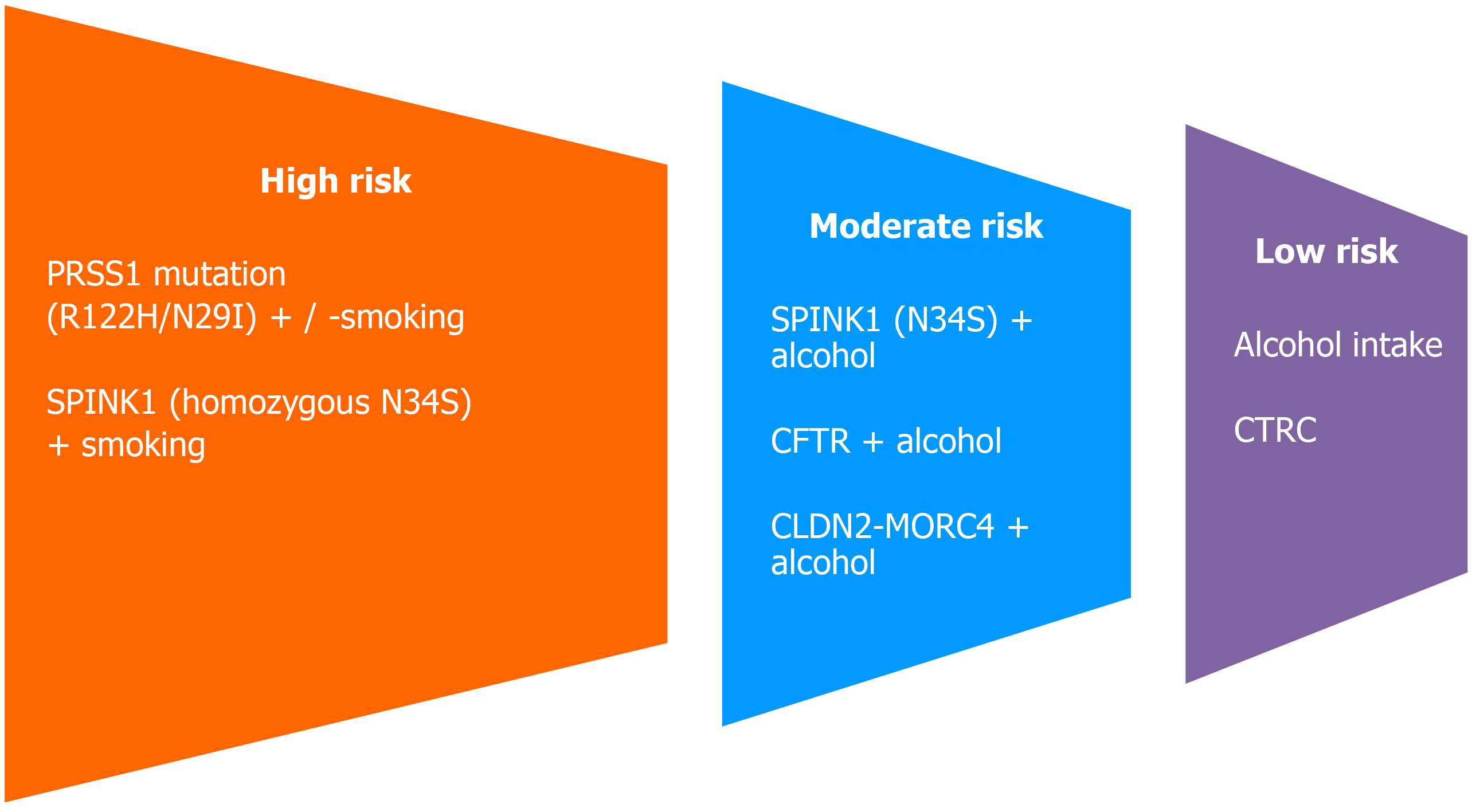
Figure 3 Proposed risk stratification of chronic pancreatitis patients.
CFTR: Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; CLDN2: Tight-junction protein claudin-2; CTRC: Chymotrypsin C; PRSS 1: Protease serine 1; SPINK 1: Serine peptidase inhibitor Kazal type 1.
- Citation: Kalayarasan R, Narayanan S, Sahoo J, Mohan P. Impact of surgery for chronic pancreatitis on the risk of pancreatic cancer: Untying the Gordian knot. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(27): 4371-4382
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i27/4371.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i27.4371