Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2021; 27(24): 3568-3580
Published online Jun 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3568
Published online Jun 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3568
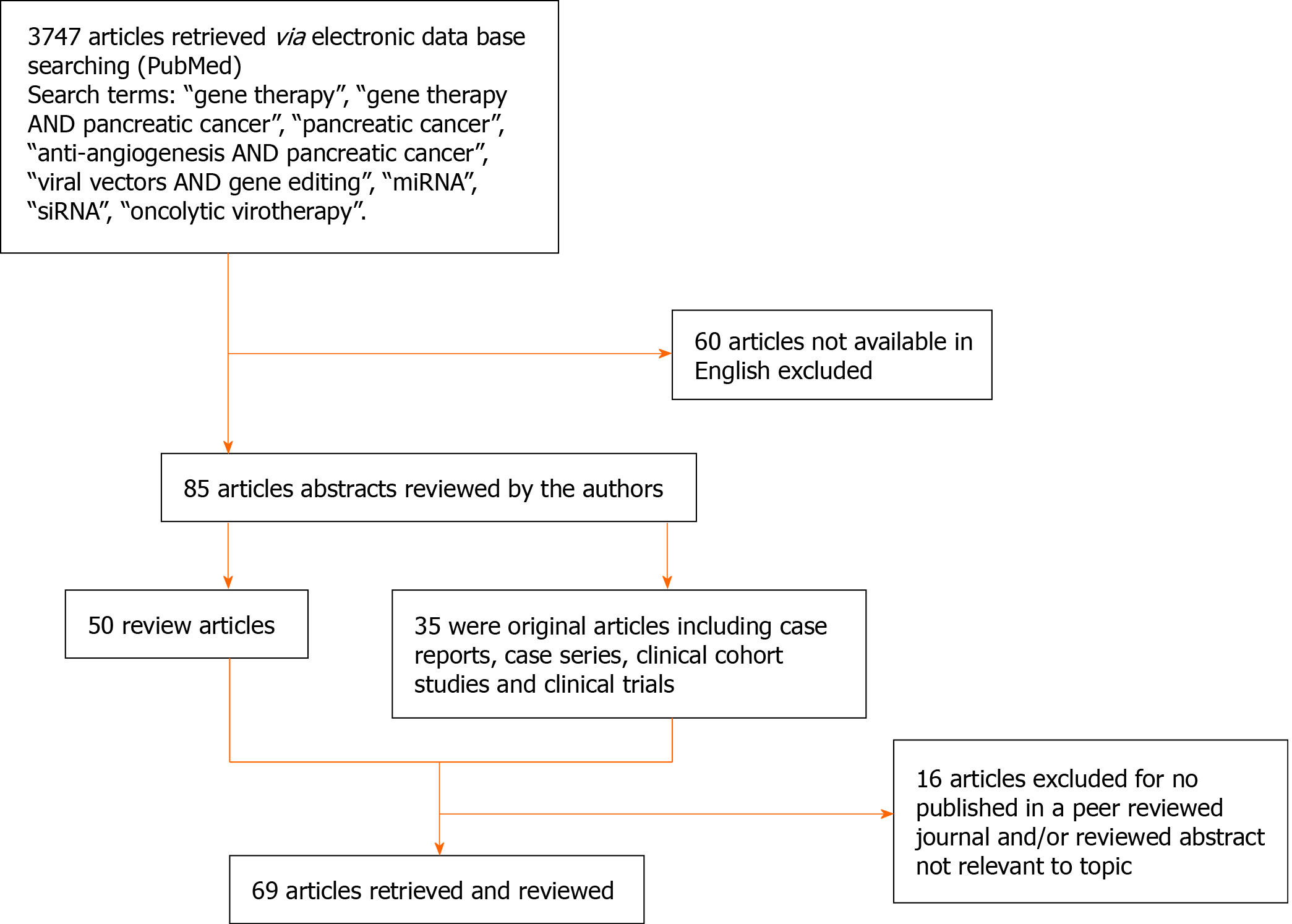
Figure 1 Decision tree for literature research strategy.
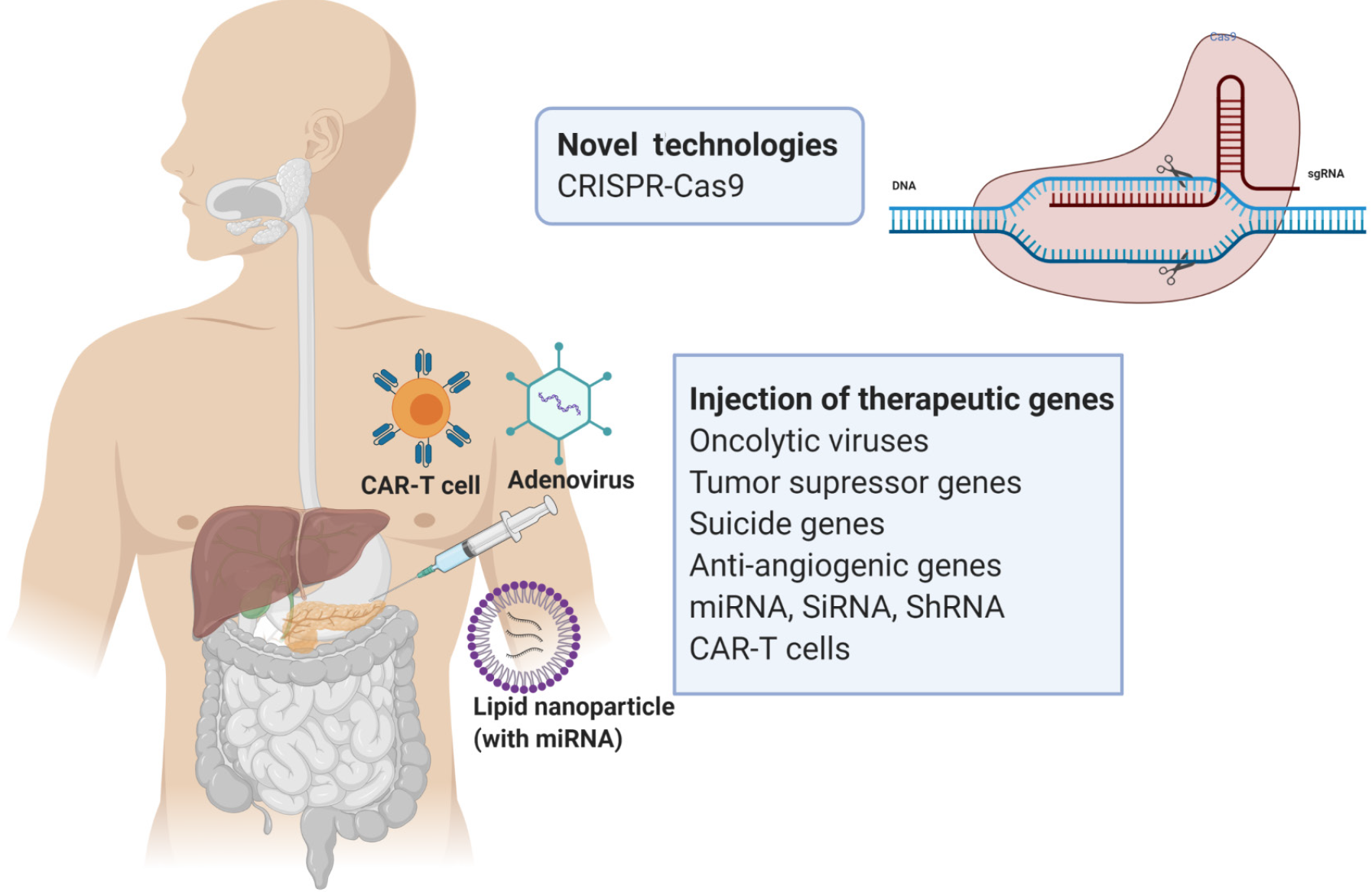
Figure 2 Summary of the therapeutic strategies of gene therapy for pancreatic cancer.
The above diagram was created with Biorender.com. CAR-T: Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell; CRISPR-Cas9: Clustered regularly interspaced palindromic repeats-Cas9.
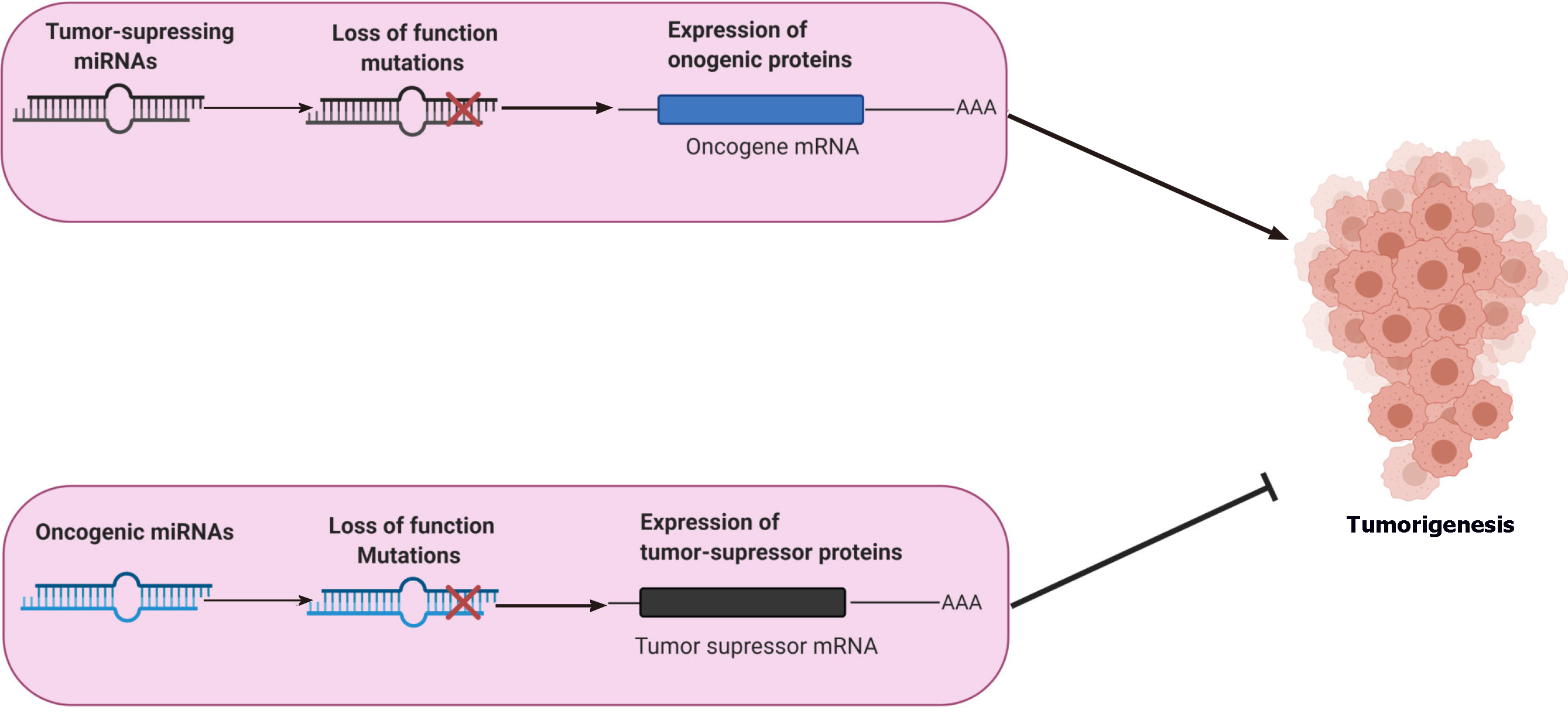
Figure 3 Roles of miRNAs in the regulation of tumorigenesis.
miRNAs are essential for the regulation of tumorigenesis. The primary role of tumor-suppressing miRNAs is to suppress the expression of oncogenes, thus inhibiting tumorigenesis whereas oncogenic miRNAs (oncoMIR) block translation of tumor suppressor genes inducing tumorigenesis and, thus tumor formation. Loss of function (mutations) in tumor-suppressing miRNAs induce tumorigenesis (increased expression of oncogenic proteins). However, loss of function (mutations) in oncogenic miRNAs (increased expression of tumor-suppressor mRNA) results in the suppression of tumorigenesis. The above diagram was created with Biorender.com.
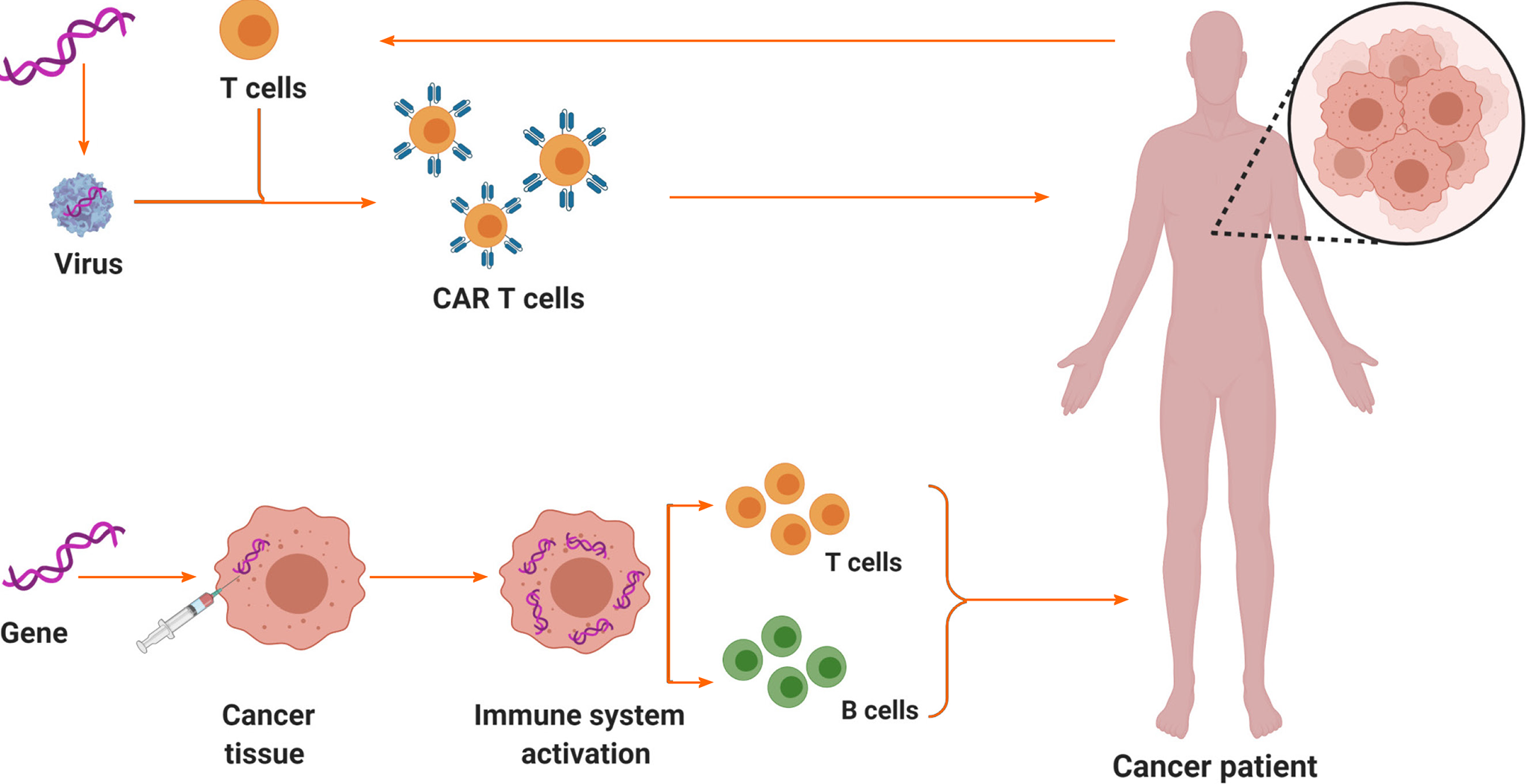
Figure 4 Schematic diagrams of two examples of immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer: chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy and immunogenic therapy (in vivo gene transfer).
The above diagram was created with Biorender.com. CAR T-cell: Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell.
- Citation: Galanopoulos M, Doukatas A, Gkeros F, Viazis N, Liatsos C. Room for improvement in the treatment of pancreatic cancer: Novel opportunities from gene targeted therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(24): 3568-3580
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i24/3568.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3568