Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2021; 27(23): 3182-3207
Published online Jun 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i23.3182
Published online Jun 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i23.3182
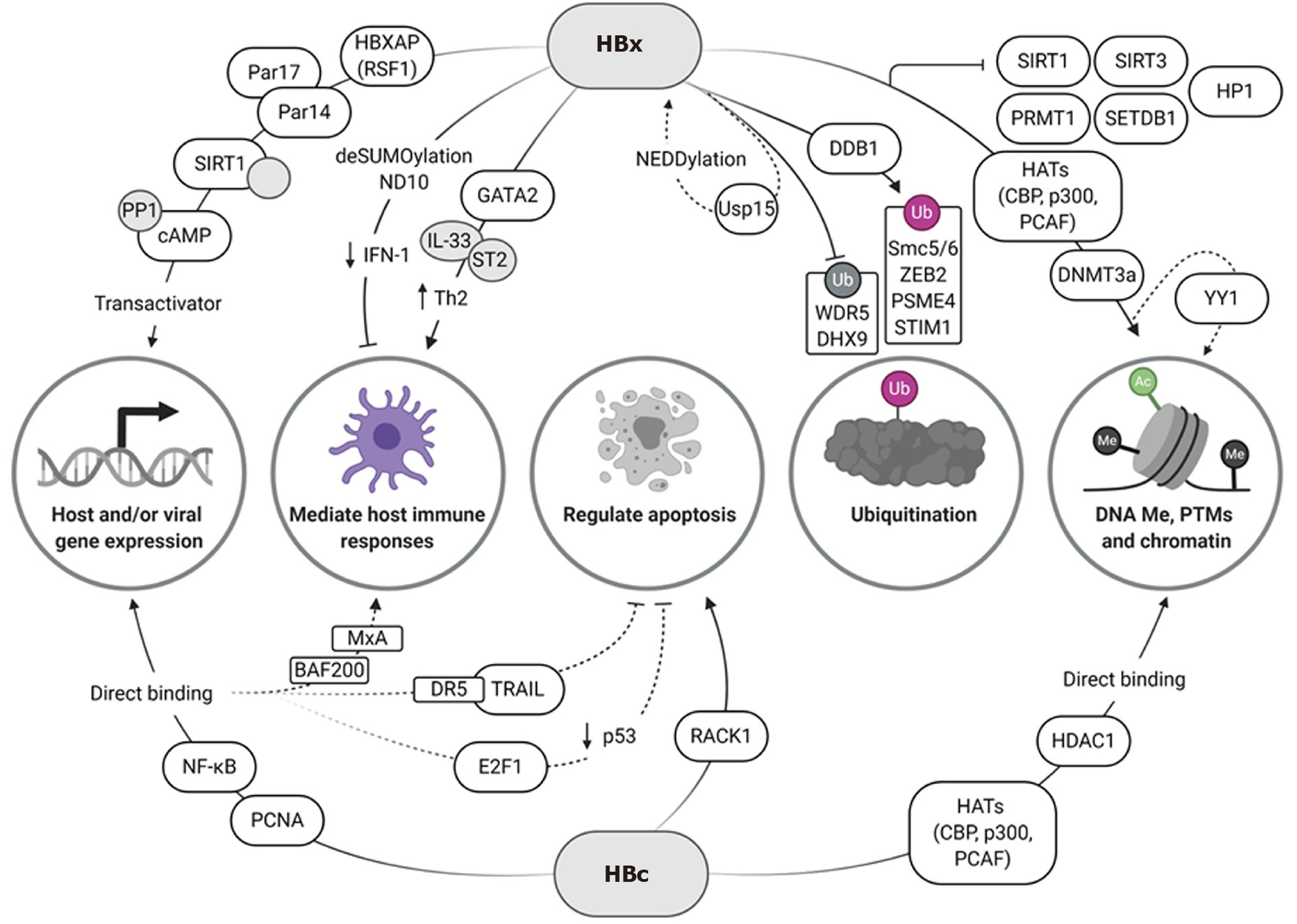
Figure 1 Hepatitis B virus proteins X and core act on multiple host cell pathways to promote viral persistence.
An intricate epigenetic regulatory network is established during Hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B virus proteins X and core contribute to this by either directly or indirectly controlling gene expression, modifying chromatin structure or location, mediating host immune responses, regulating apoptosis, and promoting or preventing ubiquitination. Pathways discussed in ‘Viral factors as epigenetic regulators’ are depicted here. Created with BioRender.com. HBx: Hepatitis B virus X protein; HBc: Hepatitis B virus core protein; IFN: Interferon; IL: Interleukin; NF-κB: nuclear factor-κappa B; PTM: Post-translational modifications; SIRT1: Sirtuin 1; YY1: Yin-Yang 1; HATs: Histone acetyltransferases; HDAC: Histone deacetylase; PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; HBXAP: HBx-associated protein; RSF1: Remodeling and spacing factor 1; Par14: Parvulin 14; Par17: Parvulin 17; PP1: Protein phosphatase 1; cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; ND10: Nuclear domain 10; GATA2: GATA binding protein 2; ST2: Interleukin 1 receptor-like 1; Th2: T helper cell type 2; Usp15: Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 15; DDB1: Damaged DNA-binding protein 1; Smc5/6: Structural maintenance of chromosomes 5/6; ZEB2: Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 2; PSME4: Proteasome activator subunit 4; STIM1: Stromal interaction molecule 1; WDR5: tryptophan-aspartic acid (WD) repeat domain 5 protein; DHX9: DExH-box RNA helicase 9; ub: Ubiquitination; SIRT3: Sirtuin 3; PRMT1: Protein arginine methyltransferase 1; SETDB1: SET domain bifurcated histone lysine methyltransferase 1; HP1: Heterochromatin protein 1 factors; CBP: CREB-binding protein; PCAF: p300/CBP-associated factor; DNMT3a: DNA methyltransferase 3a; MxA: Myxovirus resistance gene A; DR5: Death receptor 5; TRAIL: Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; E2F1: E2F transcription factor 1; RACK1: Receptor for activated protein kinase C 1.
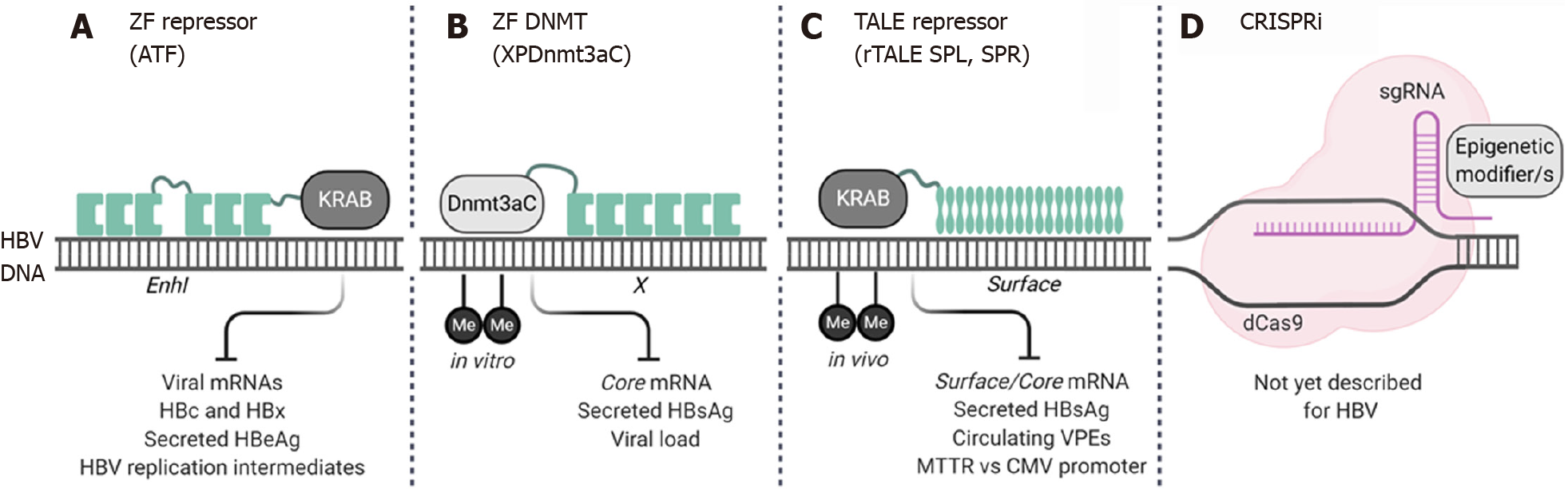
Figure 2 Novel epigenome engineering tools that target hepatitis B virus DNA.
Three different types of epigenetic editors have been designed to silence viral gene expression. The Zinc finger (ZF) repressor-based artificial transcription factors (ATF) comprise two three-finger ZF DNA binding domains (DBD) which are fused, with a C-terminal linker peptide, to the Krüppelassociated box (KRAB) repressor domain. ATFs were designed to target the EnhI region (A). A ZF-based methyltransferase (DNMT) designed to target the X region (XPDnmt3aC). The XPDnmt3aC comprises a six-finger ZF DBD fused to the catalytic domain of Dnmt3a (Dnmt3aC). Methylation of the viral DNA was achieved in vitro (B). To generate transcription activator-like effector (TALE) repressors, TALE DBDs targeting two regions of surface were fused to the KRAB repressor domain (N-terminal). In vivo, methylation of intrahepatic viral DNA was shown (C). Although not yet described for HBV, the CRISPRi epigenome editing tools provide a novel means of silencing covalently closed circular DNA. RNA guides (sgRNA) targeting the viral genome could be used to recruit a dead Cas (dCas9) with one or more epigenetic modifying domains (D). Created with BioRender.com. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; ZF: Zinc finger; ATF: Artificial transcription factor; HBx: Hepatitis B virus X protein; HBc: Hepatitis B virus core protein; HBeAg: Hepatitis B e antigen; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; TALE: Transcription activator-like effector; MTTR: Mouse transthyretin; CMV: Cytomegalovirus; VPE: Viral particle equivalent.
- Citation: Singh P, Kairuz D, Arbuthnot P, Bloom K. Silencing hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA: The potential of an epigenetic therapy approach. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(23): 3182-3207
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i23/3182.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i23.3182