Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2021; 27(19): 2312-2324
Published online May 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i19.2312
Published online May 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i19.2312
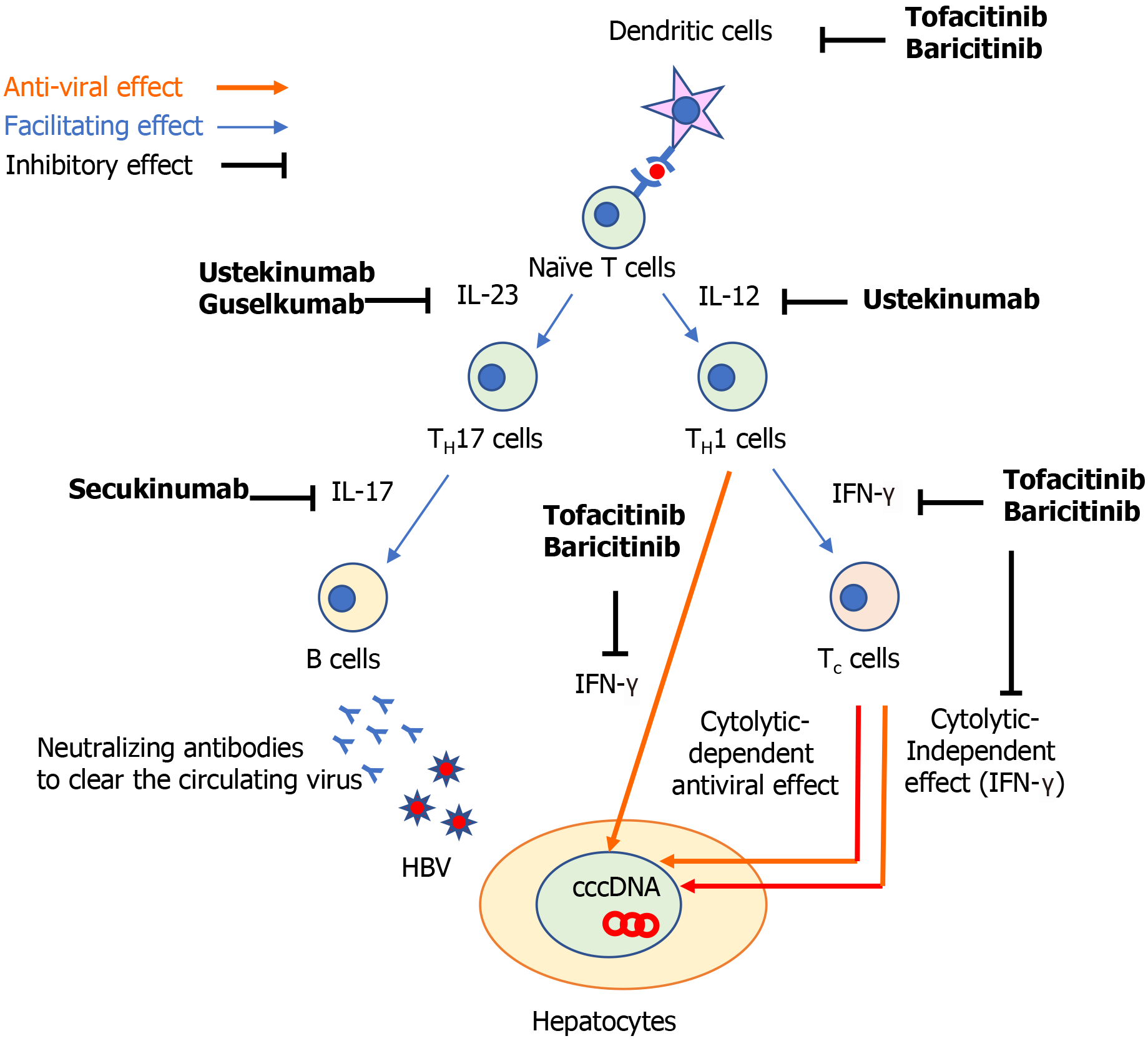
Figure 1 The possible immunological mechanism to explain how non-tumor necrosis factor-targeted biologics can induce the development of hepatitis B reactivation.
cccDNA: Covalently closed circular DNA; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; IFN: Interferon; IL: Interleukin; TH17 cells: IL-17 producing T helper cells; TH1 cells: T helper 1 cells; Tc cells: Cytotoxic T cells.
- Citation: Akiyama S, Cotter TG, Sakuraba A. Risk of hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients with autoimmune diseases undergoing non-tumor necrosis factor-targeted biologics. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(19): 2312-2324
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i19/2312.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i19.2312