Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2021; 27(17): 1883-1904
Published online May 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i17.1883
Published online May 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i17.1883
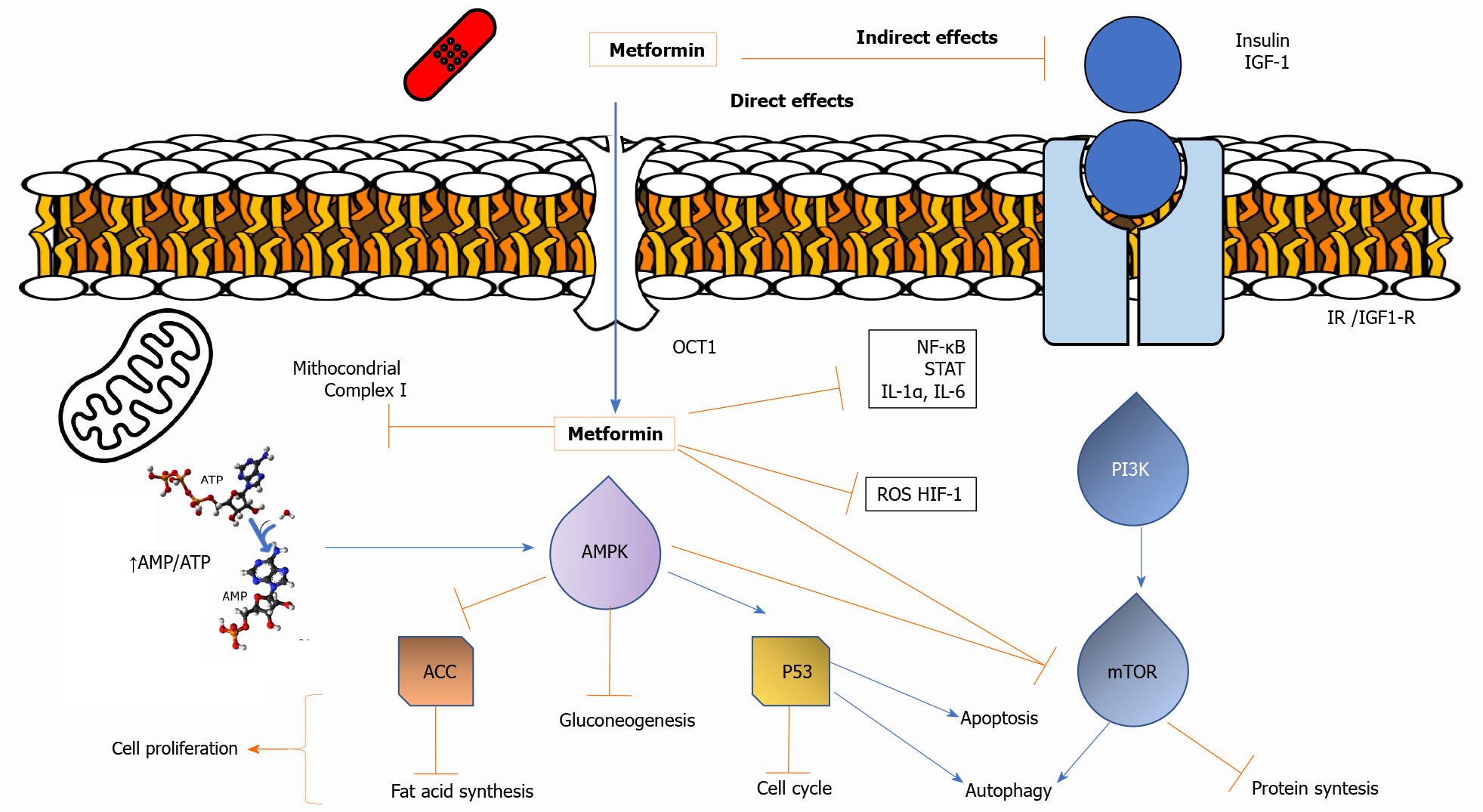
Figure 1 Overview of cellular mechanisms of metformin in cancer.
Metformin inhibits mitochondria complex I, stimulates the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase signaling pathway, and/or inhibits the insulin signaling pathway. Blue lines represent activated pathways while red lines represent inhibitory pathways. AMPK: Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha; IGF: Insulin growth factor; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor-1; IGF-1R: Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor; IR: Insulin receptor; IL-1: Interleukin 1; IL-6: Interleukin-6; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa; OCT1: Organic cation transporter 1; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; AMP: Adenosine monophosphate; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin.
- Citation: Cunha Júnior AD, Bragagnoli AC, Costa FO, Carvalheira JBC. Repurposing metformin for the treatment of gastrointestinal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(17): 1883-1904
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i17/1883.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i17.1883