Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2021; 27(15): 1569-1577
Published online Apr 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i15.1569
Published online Apr 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i15.1569
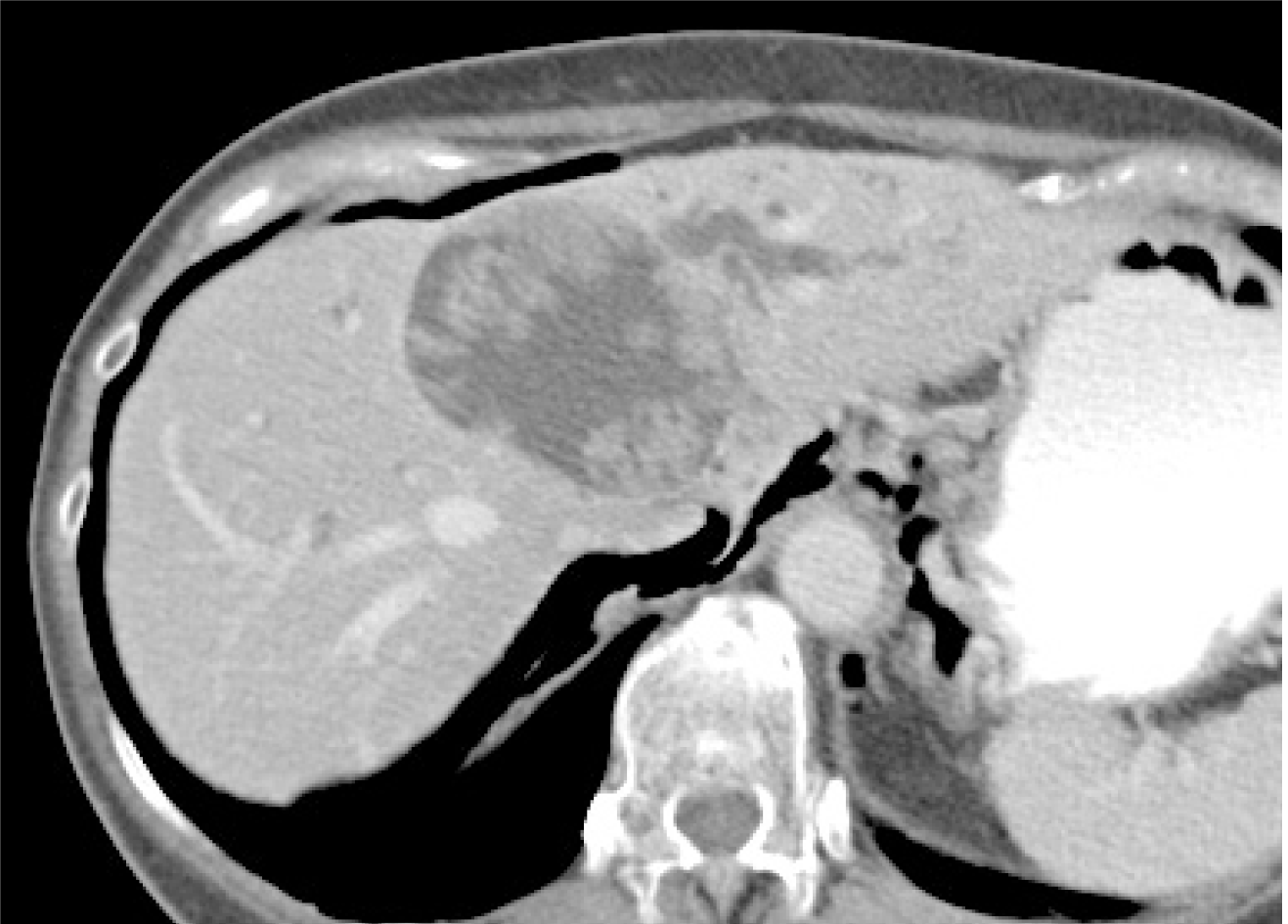
Figure 1 Contrast computed tomography revealed a 70-mm cystic lesion with a papillary bump in the lumen of left hepatic lobe.
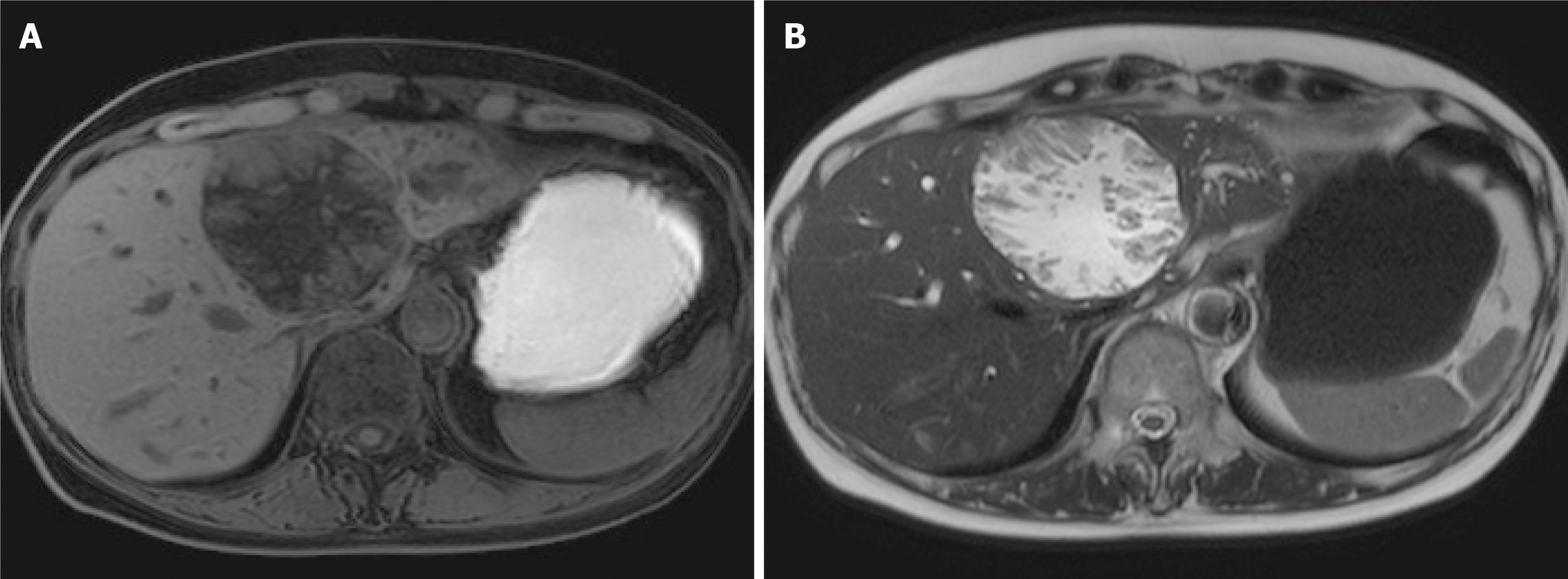
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging.
A: T1-weighted image; and B: T2-weighted image papillary solid lesion protuberating from cystic wall is noted and the cystic component showed the same signals as water. Transportation between the cyst and the root of left hepatic duct is noted.
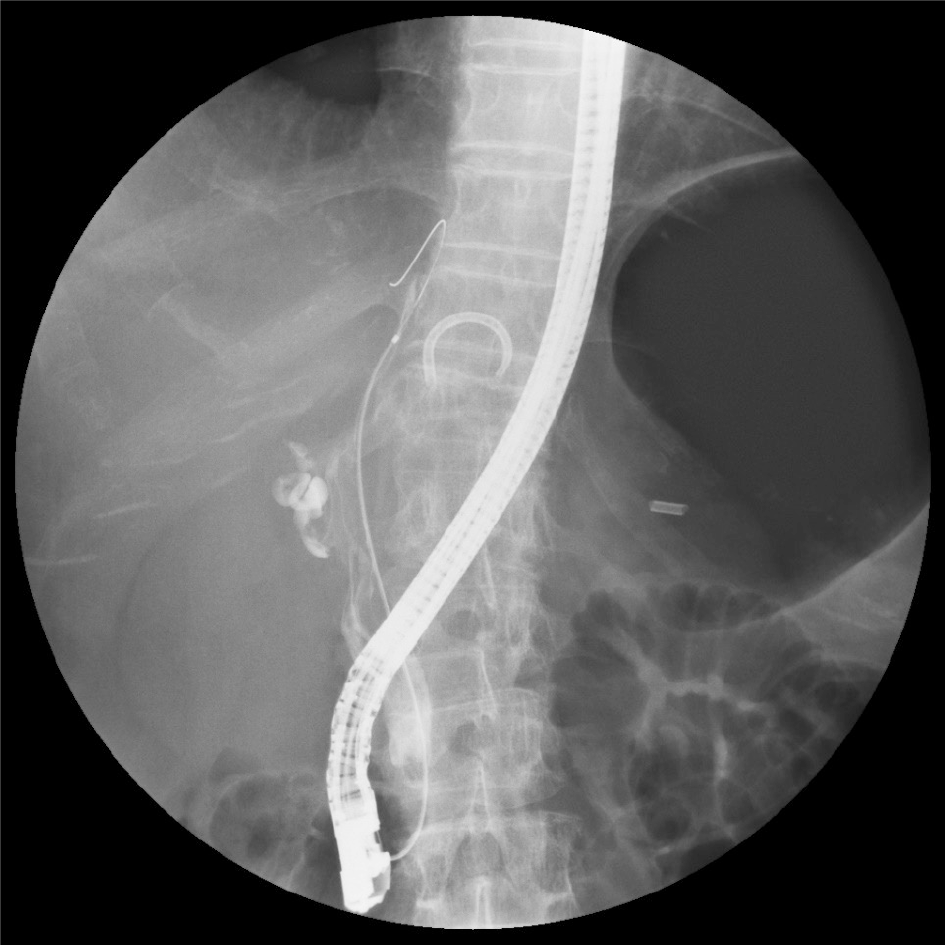
Figure 3 Translucency caused by mucus is noted from hepatic portal region to lower bile duct.
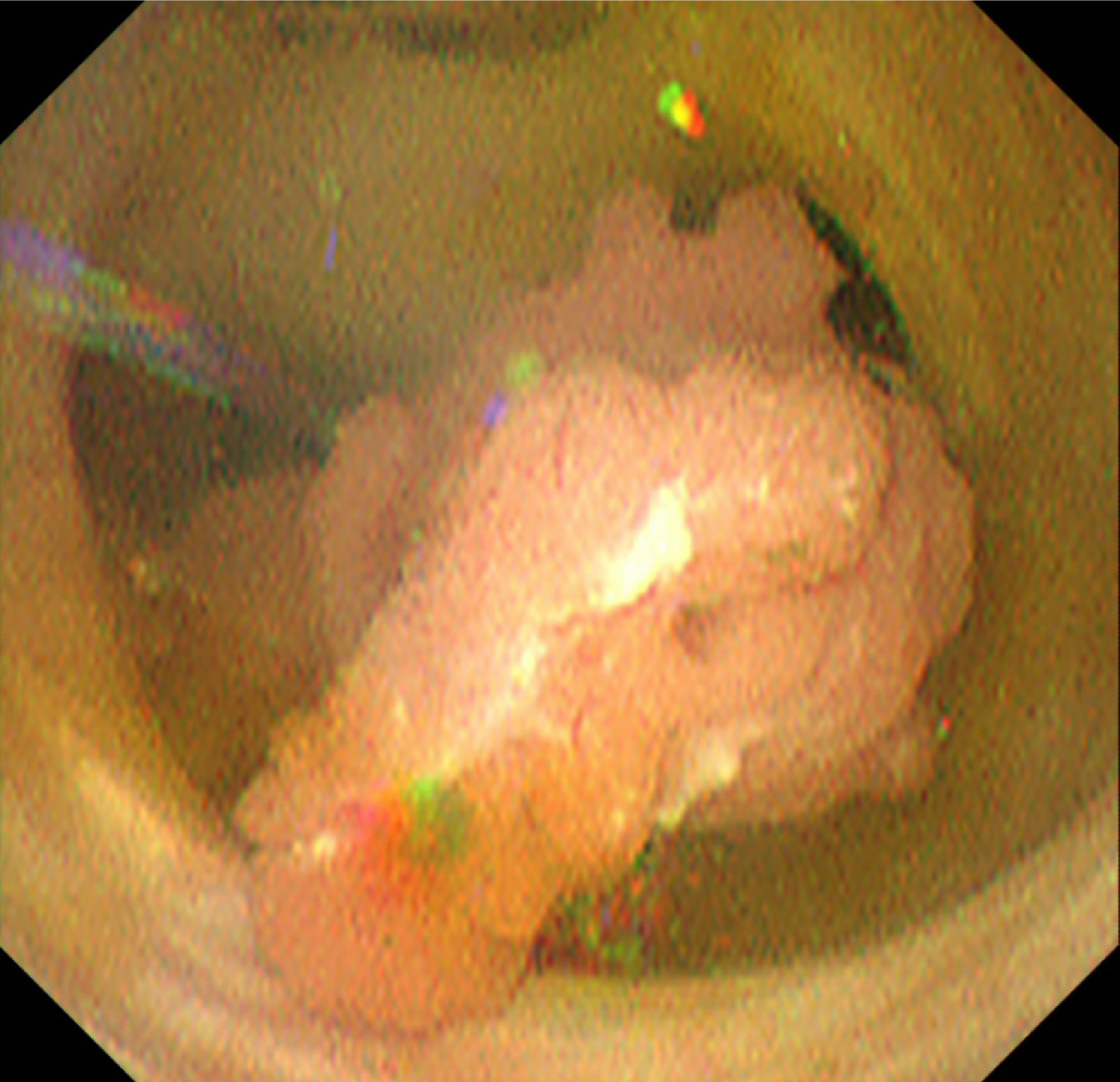
Figure 4 The lesion originates from the root of left hepatic duct, and pedunculated and elevated lesion protruded toward the extrahepatic bile duct, with no clear superficial spread.
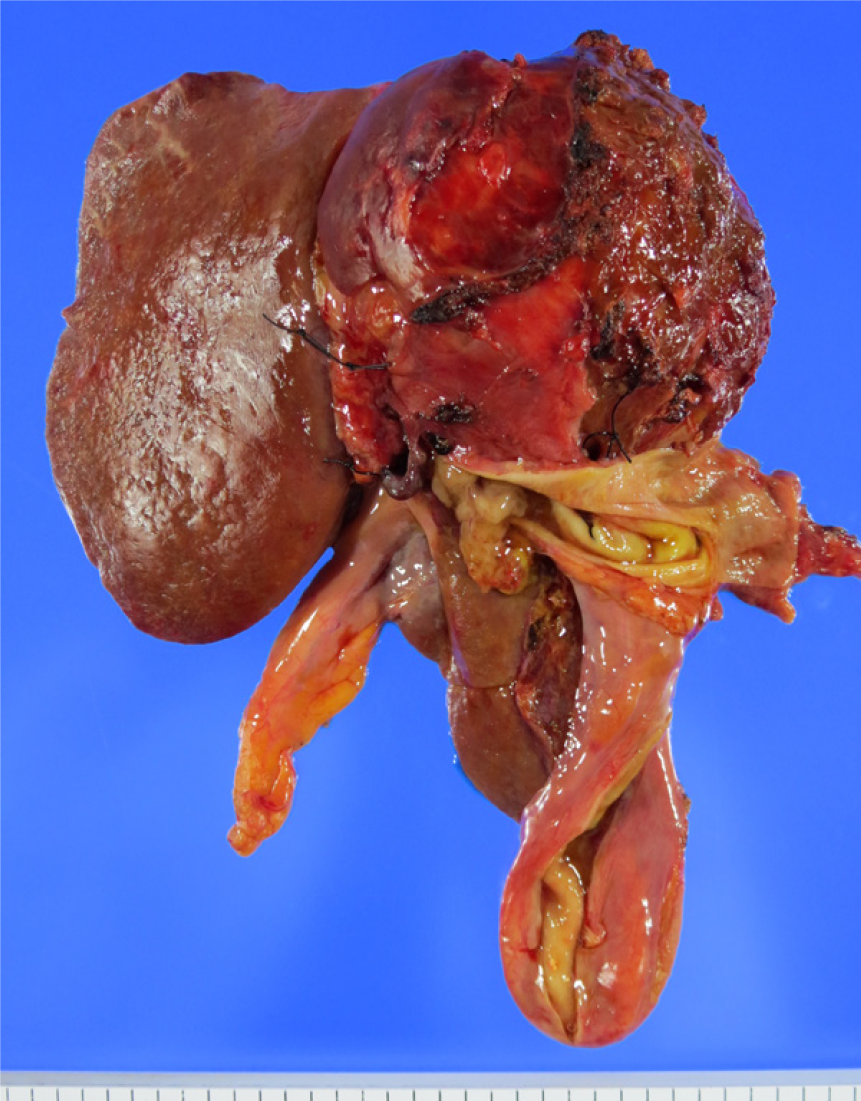
Figure 5 Resected specimen.
Left lobectomy, caudal lobectomy, resection of extrahepatic bile duct, and choledochojejunostomy were performed.
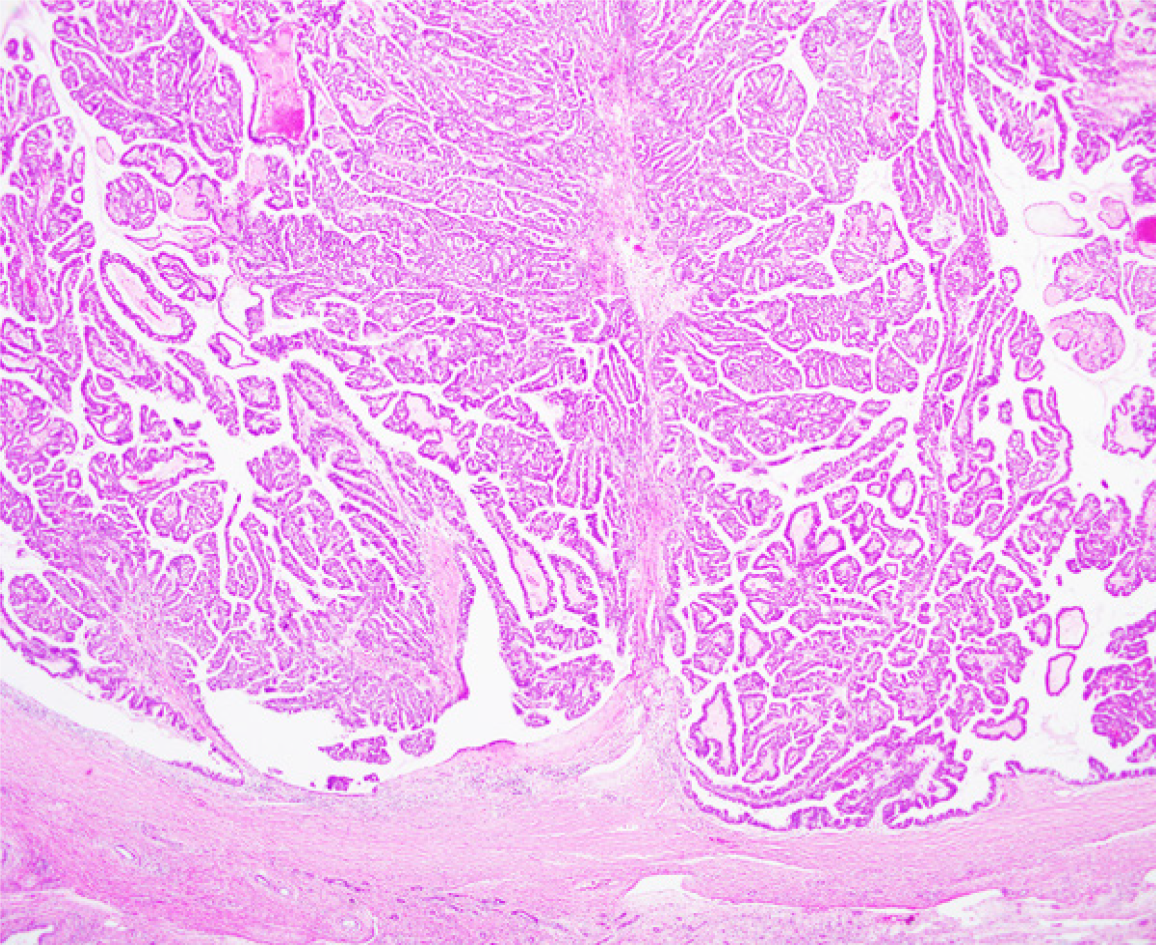
Figure 6 Pathological diagnosis is intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct with an associated invasive carcinoma (Hematoxylin-Eosin Stain) with no superficial spread.
- Citation: Sakai Y, Ohtsuka M, Sugiyama H, Mikata R, Yasui S, Ohno I, Iino Y, Kato J, Tsuyuguchi T, Kato N. Current status of diagnosis and therapy for intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(15): 1569-1577
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i15/1569.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i15.1569