Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2020; 26(40): 6163-6181
Published online Oct 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i40.6163
Published online Oct 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i40.6163
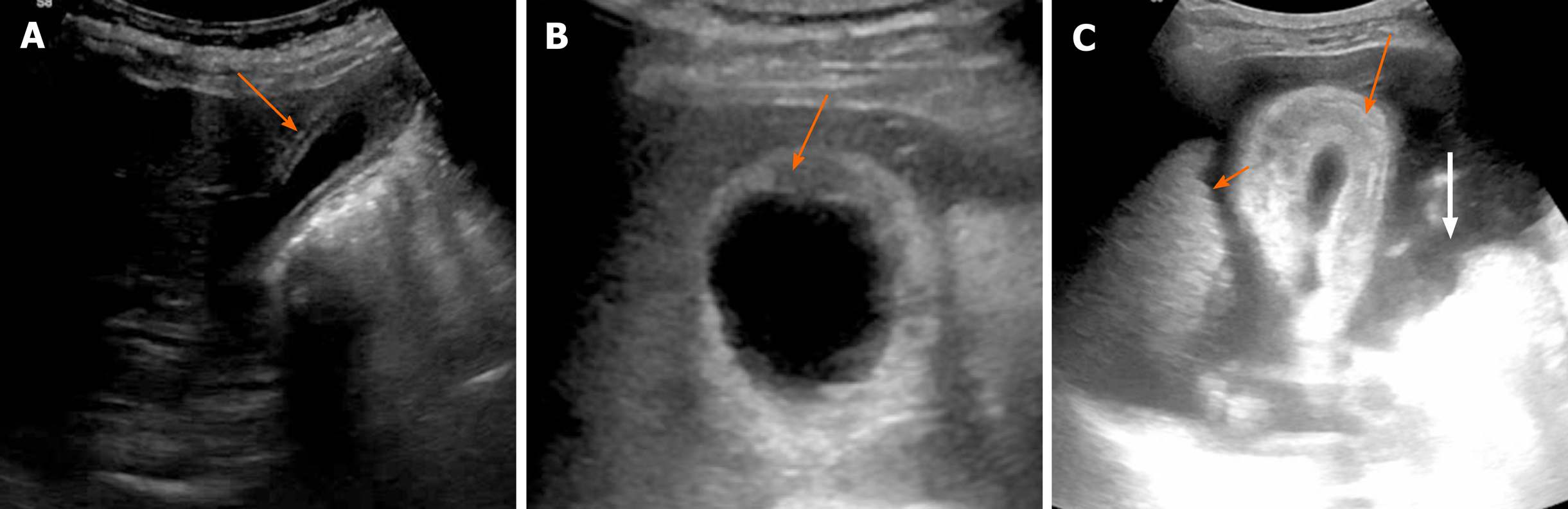
Figure 1 Ultrasound features of benign and malignant gallbladder wall thickening.
A: Mild symmetrical mural thickening with clearly defined layers (arrow) suggestive of benign thickening; B: Asymmetrical mural thickening with foal discontinuity of mucosa (arrow) suggestive of malignant thickening; C: Marked circumferential mural thickening with mesh like architecture (arrow) is seen. Also note the nodular outline of liver (short arrow) and ascites (white arrow) suggestive of decompensated ascites as the underlying cause.
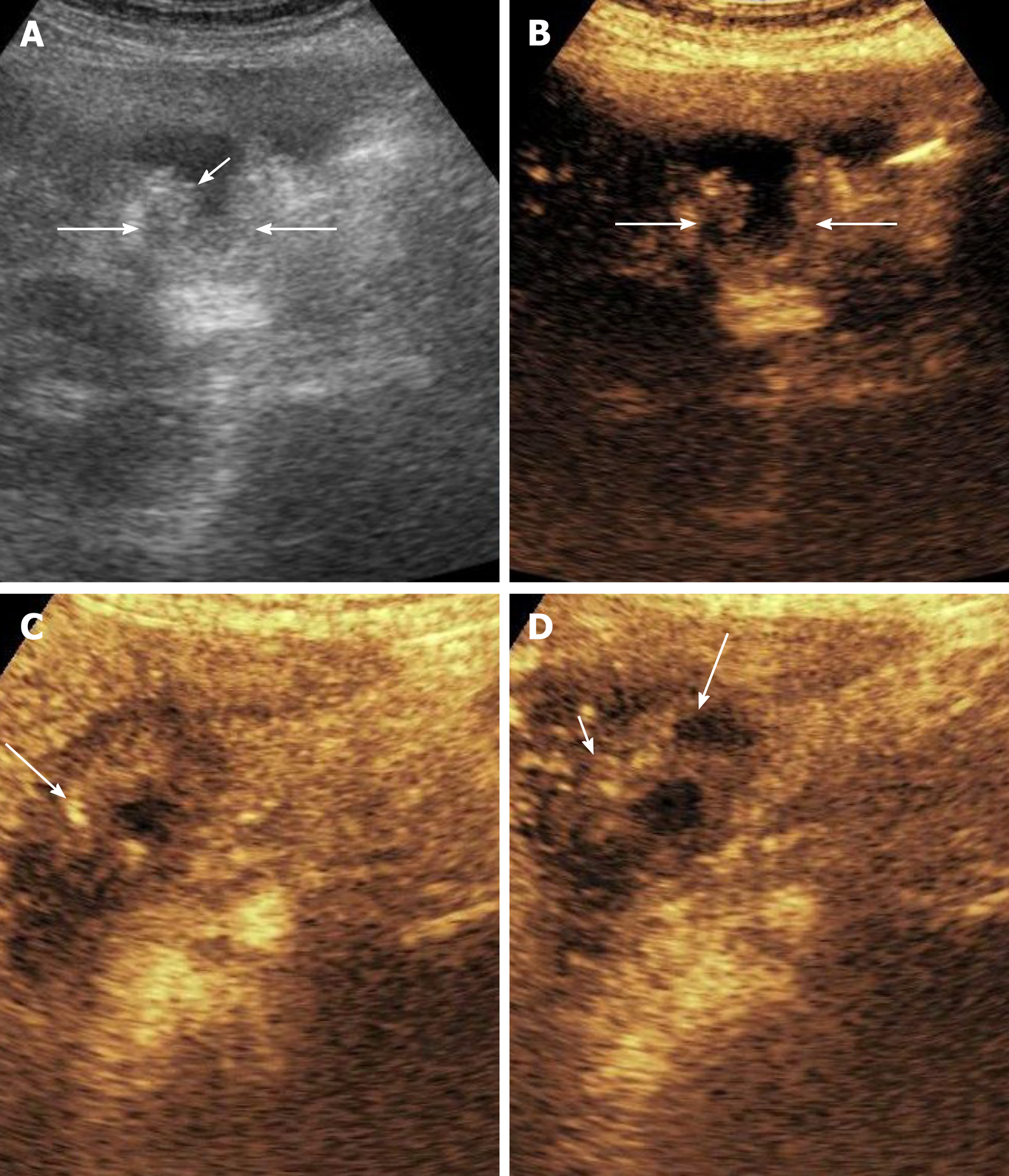
Figure 2 Contrast enhanced ultrasound in gallbladder wall thickening.
A: Grey scale image shows asymmetrical mural thickening in the neck and body of gallbladder (arrows), short arrow shows the lumen of gallbladder; B: Image before contrast injection shows the baseline status of the gallbladder (arrows show the wall); C: Image at 17 s after contrast injection shows heterogenous mural enhancement (arrow); D: Image at 35 s shows washout (arrow). The infiltration of adjacent liver (short arrow) is well visualized on this image.
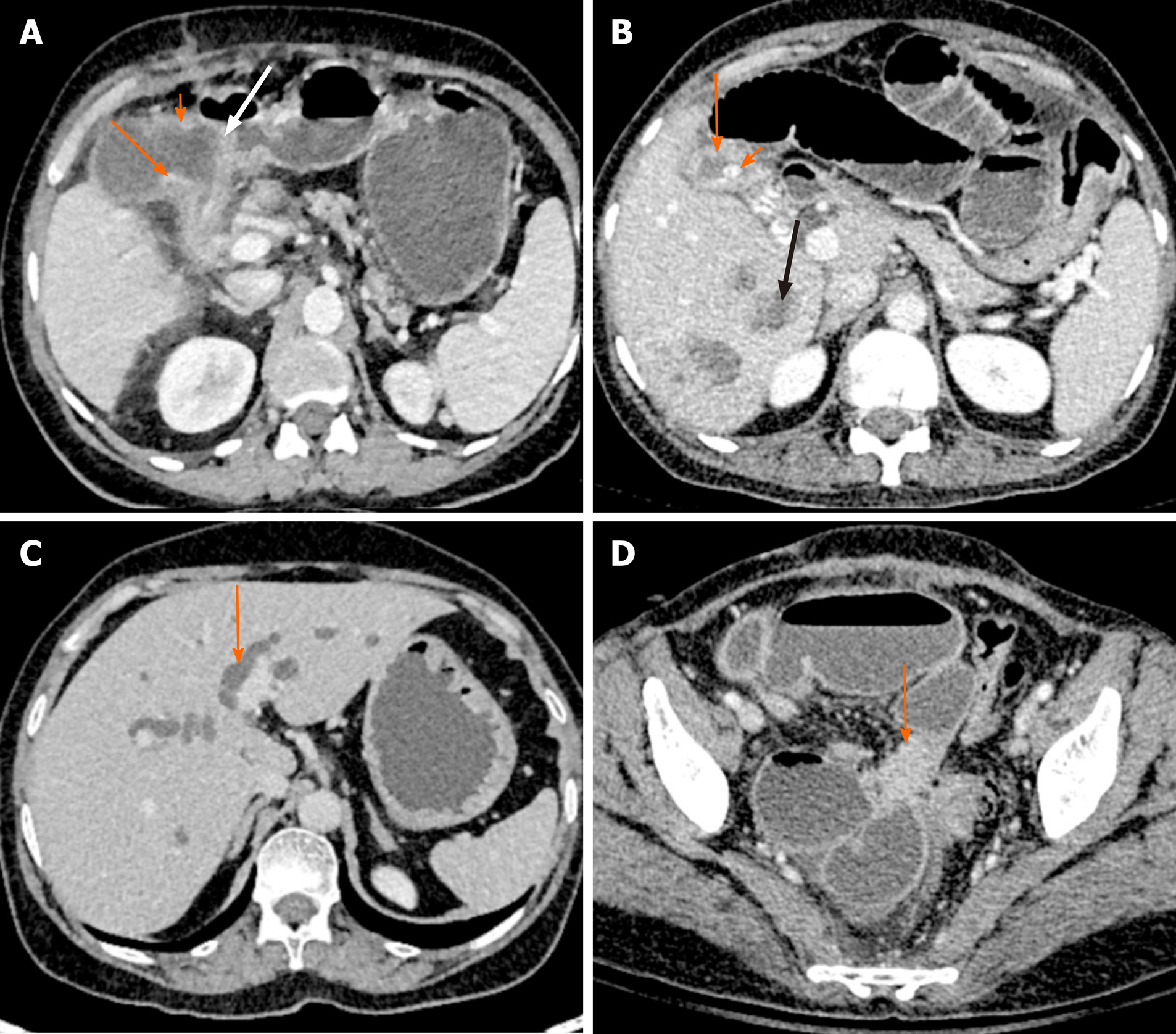
Figure 3 Direct and indirect findings of malignant gallbladder wall thickening on computed tomography.
A: There is asymmetrical mural thickening of the gallbladder neck (arrow). Also note the nodularity of the gallbladder wall in the body (short arrow) and loss of fat plane with the antropyloric region of stomach (white arrow); B: Gallbladder wall is thickened and heterogeneous (arrow). There is a calculus at the neck (short arrow). Multiple hypodense lesions are seen in right lobe (black arrow). Fine needle aspiration cytology from one of these lesions revealed metastasis; C: There is bilobar intrahepatic biliary radicle dilatation in a patient with gallbladder cancer (arrow); D: A soft tissue deposit is seen in subserosal location in pelvis causing bowel obstruction (arrow).
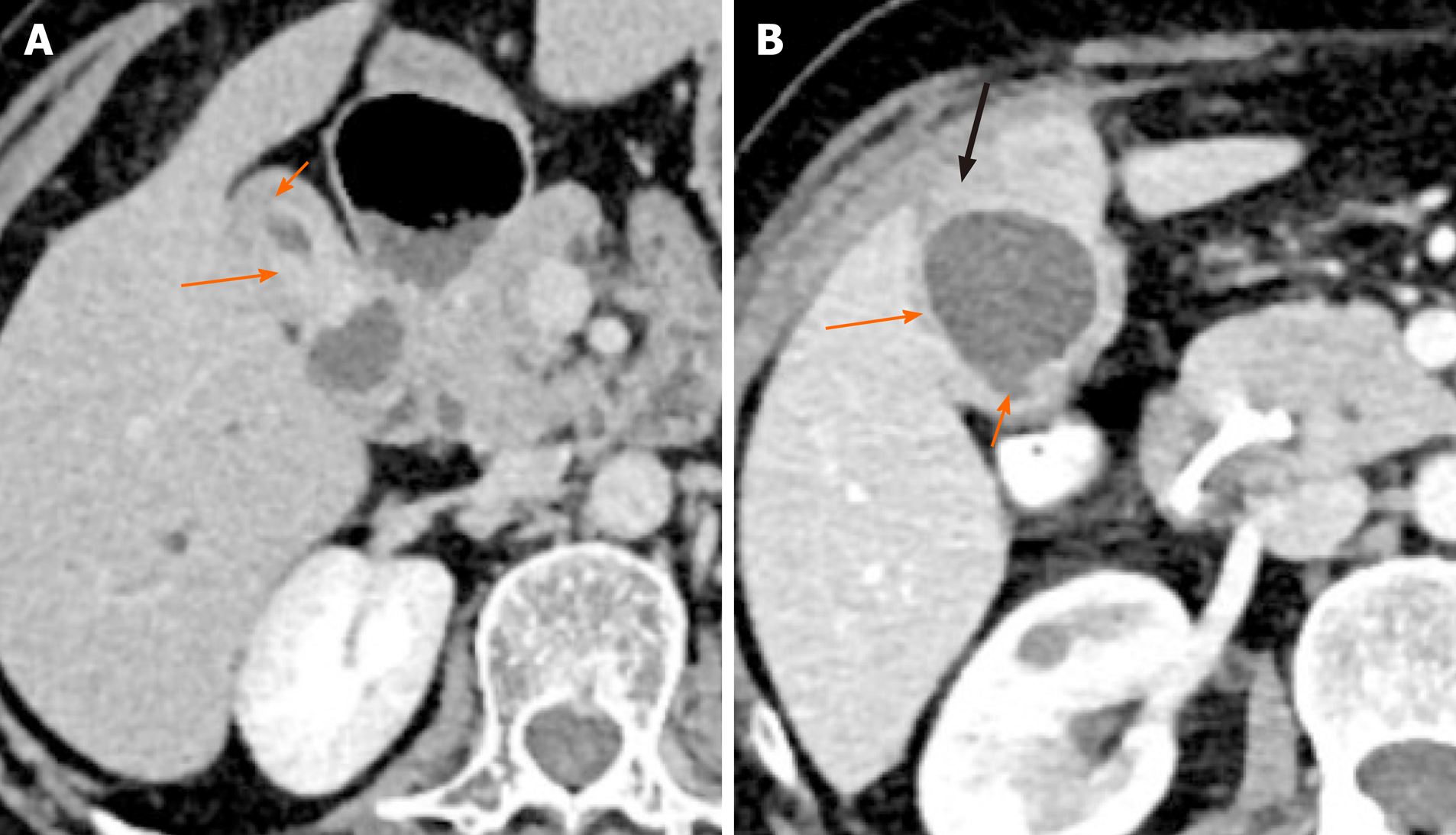
Figure 4 Patterns of malignant gallbladder wall thickening on computed tomography.
A: There is thick enhancing inner layer (arrow) and relatively hypoenhancing outer layer (short arrow); B: There is heterogeneously enhancing gallbladder wall (arrow) with focal disruption of mucosa (short arrow) and serosa (black arrow) at certain places.
Figure 5 Benign gallbladder wall thickening on magnetic resonance imaging.
A: T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging shows hypointense thickening of the gallbladder fundus (arrow); B: The thickening shows subtle hyperintensity on T1-weighted image (arrow); C: There is homogeneous contrast enhancement on gadolinium enhanced image (arrow).
Figure 6 Malignant gallbladder wall thickening on magnetic resonance image.
A: True fast imaging with steady state precession image shows marked thickening of the gallbladder fundus (arrow); B: Arterial phase of contrast enhancement shows early enhancement (arrow).
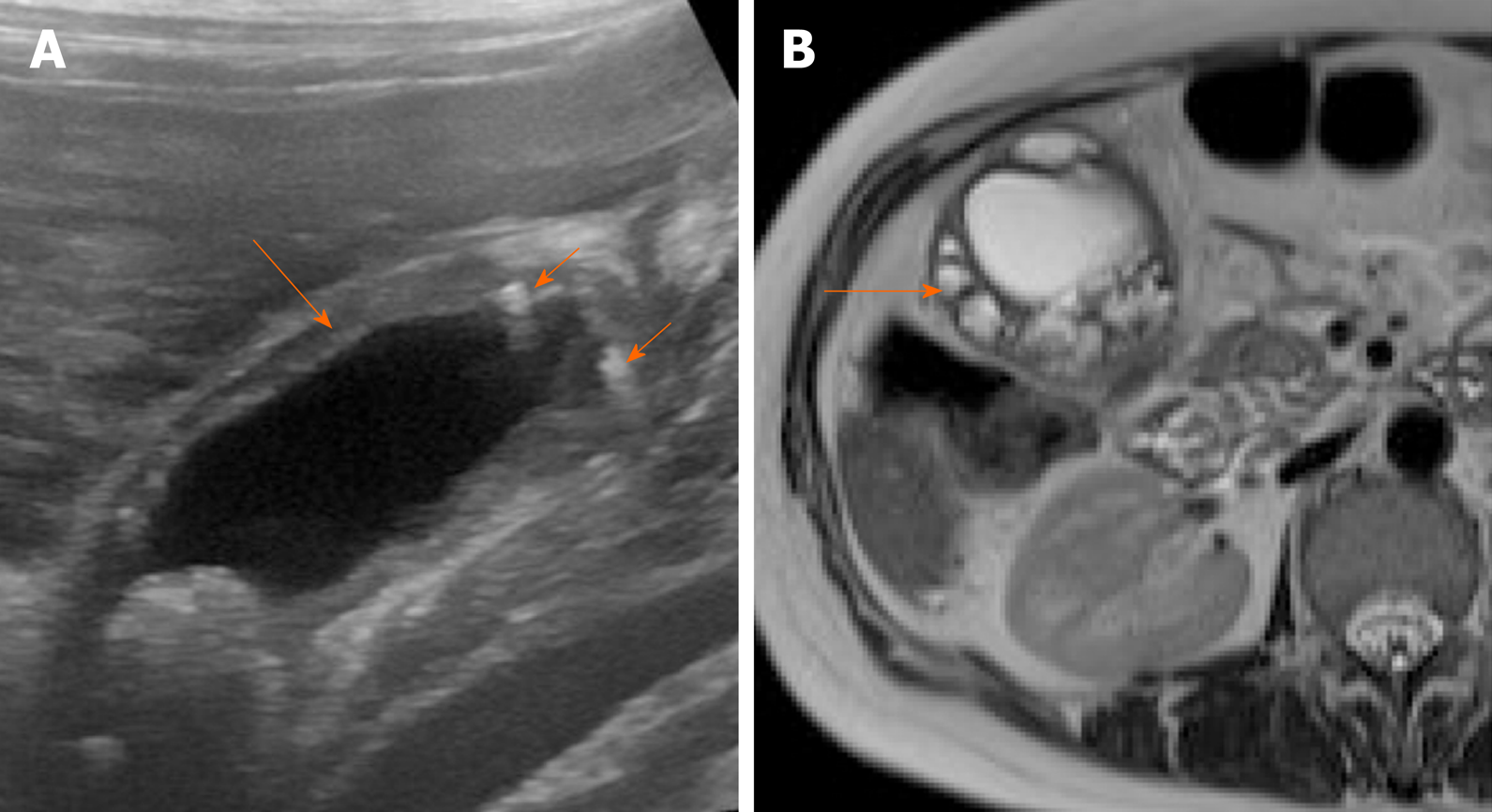
Figure 7 Imaging findings in adenomyomatosis.
A: Ultrasound image shows symmetrical mural thickening (arrow) with echogenic foci showing comet tail artifacts (short arrows); B: T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging shows multiple intramural cystic lesions (arrow).
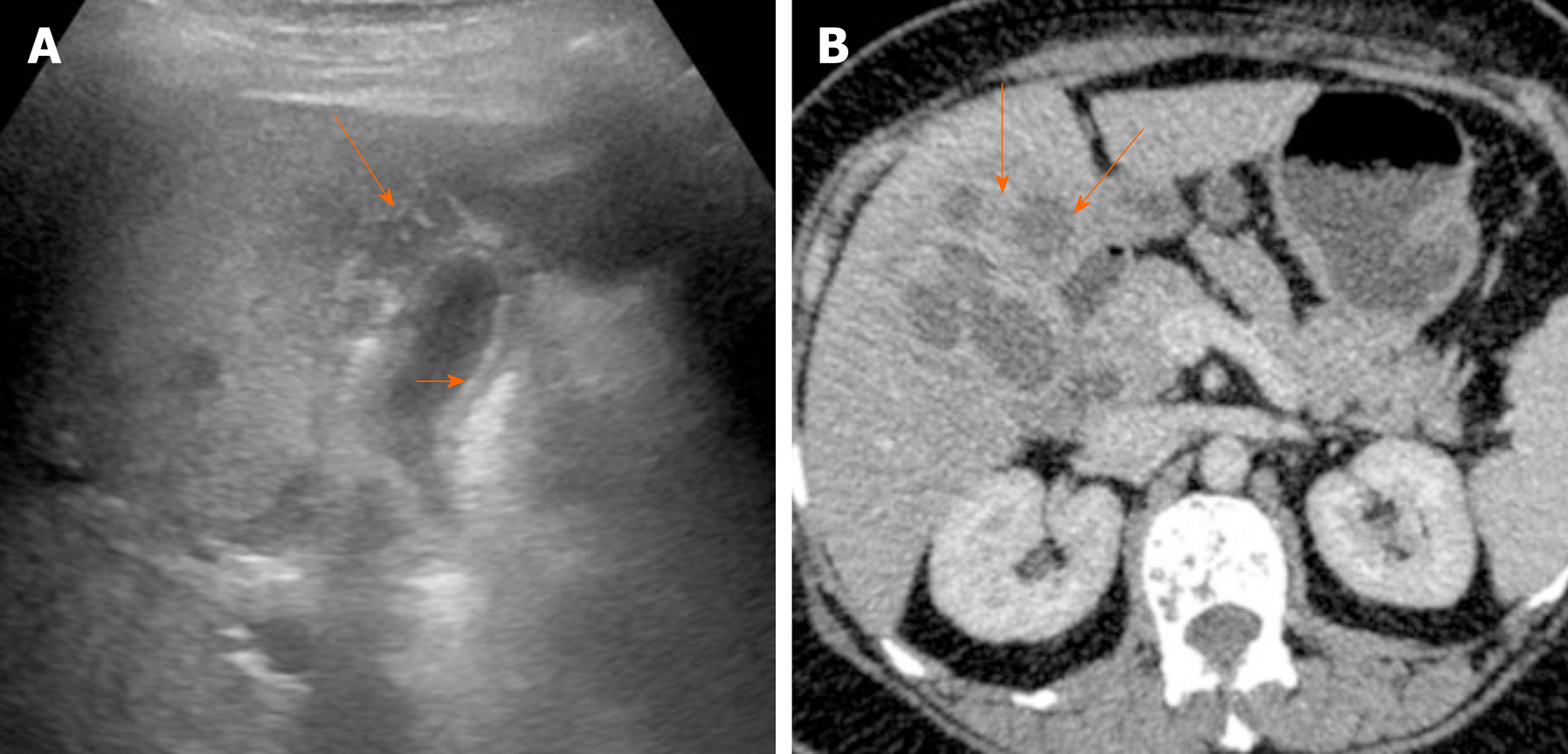
Figure 8 Imaging findings in xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis.
A: Ultrasound image shows symmetrical echogenic inner layer (short arrow) with multiple hypoechoic intramural lesions (arrow); B: Contrast enhanced computed tomography image shows multiple intramural hypodense lesions (arrows).
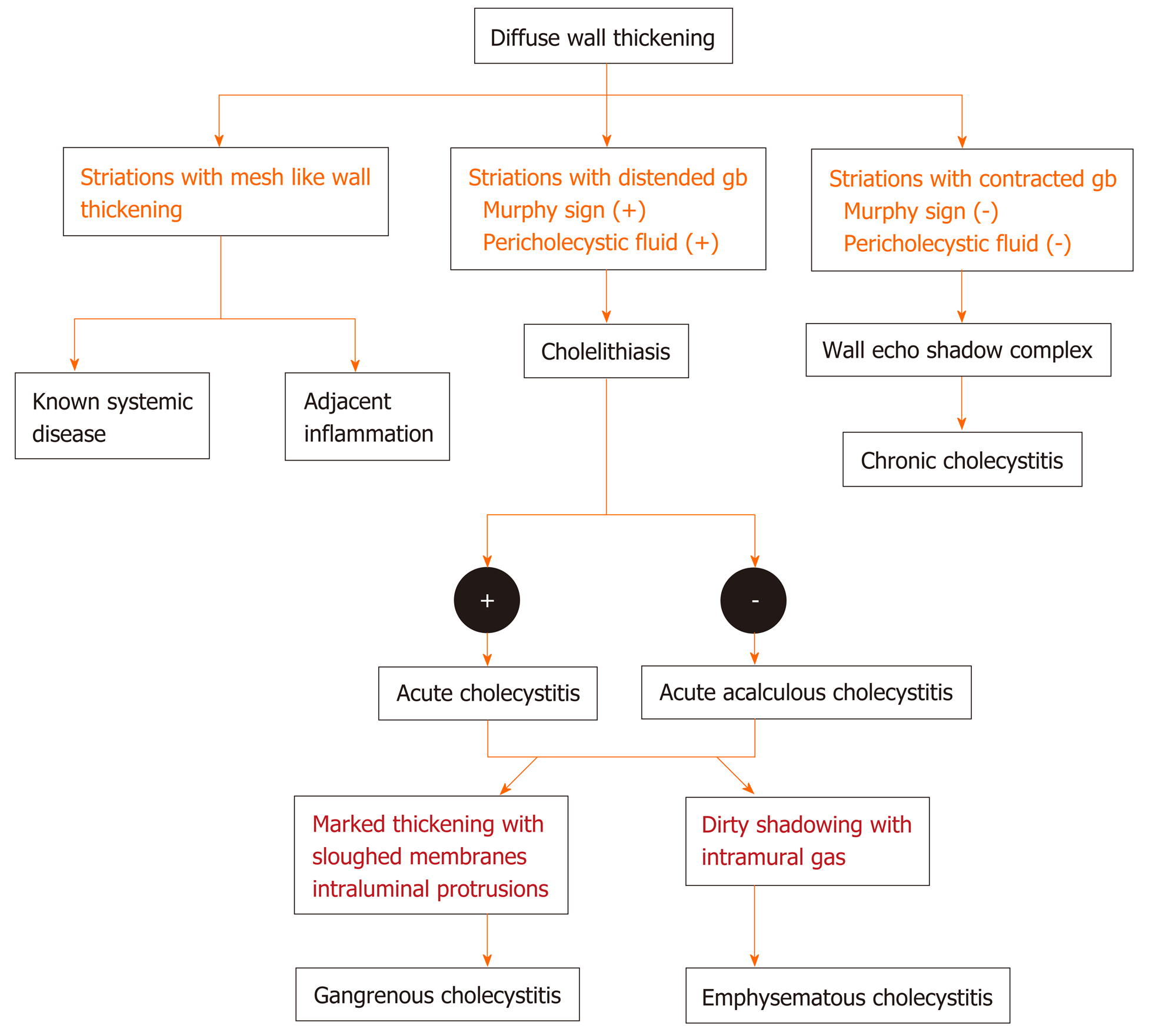
Figure 9 Flow diagram of the algorithmic approach to diagnose diffuse gallbladder wall thickening.
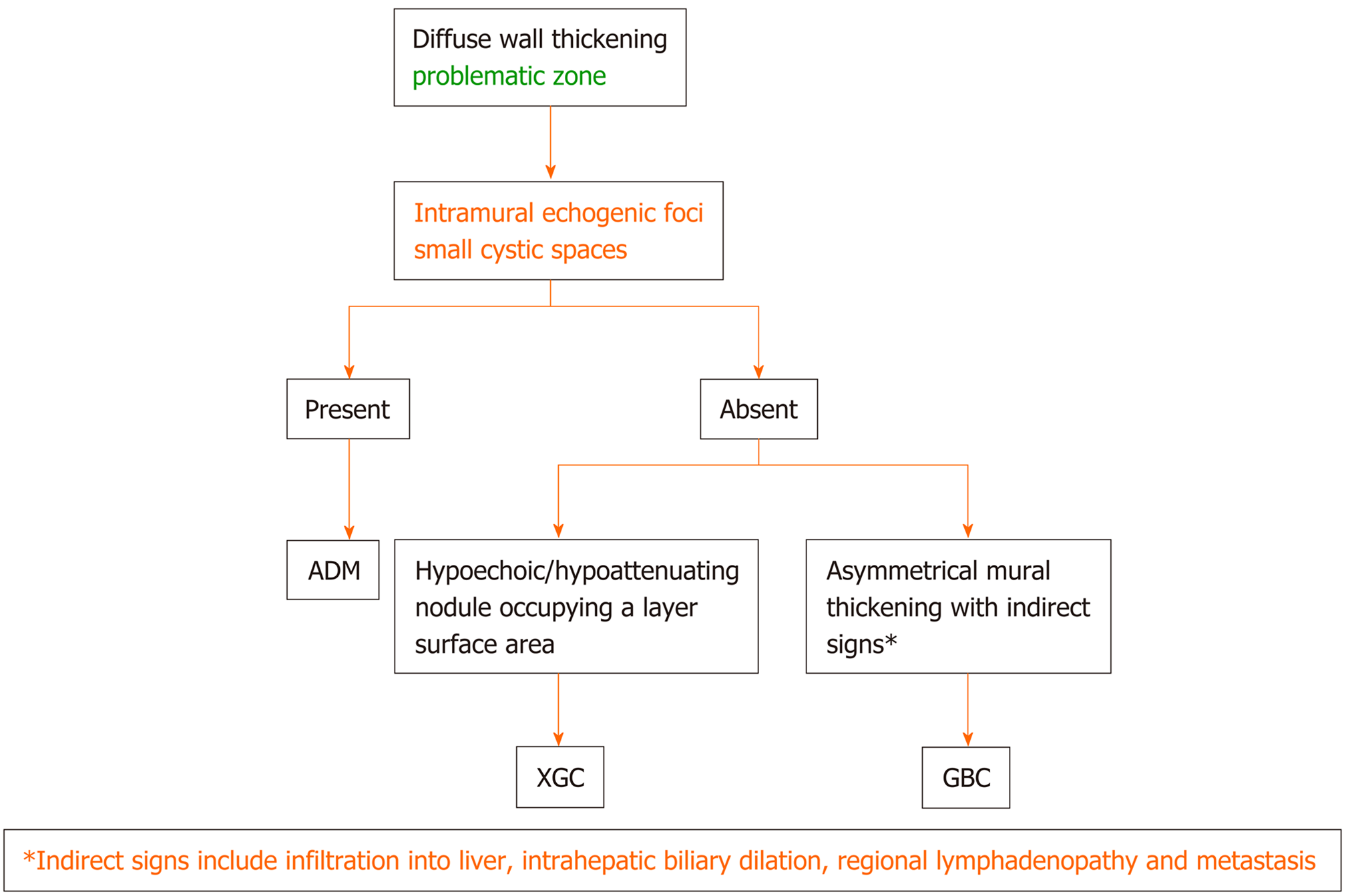
Figure 10 Flow diagram of the algorithmic approach to diagnose diffuse gallbladder wall thickening: adenomyomatosis vs xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis vs gallbladder carcinoma.
ADM: Adenomyomatosis; XGC: Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis; GBC: Gallbladder carcinoma.
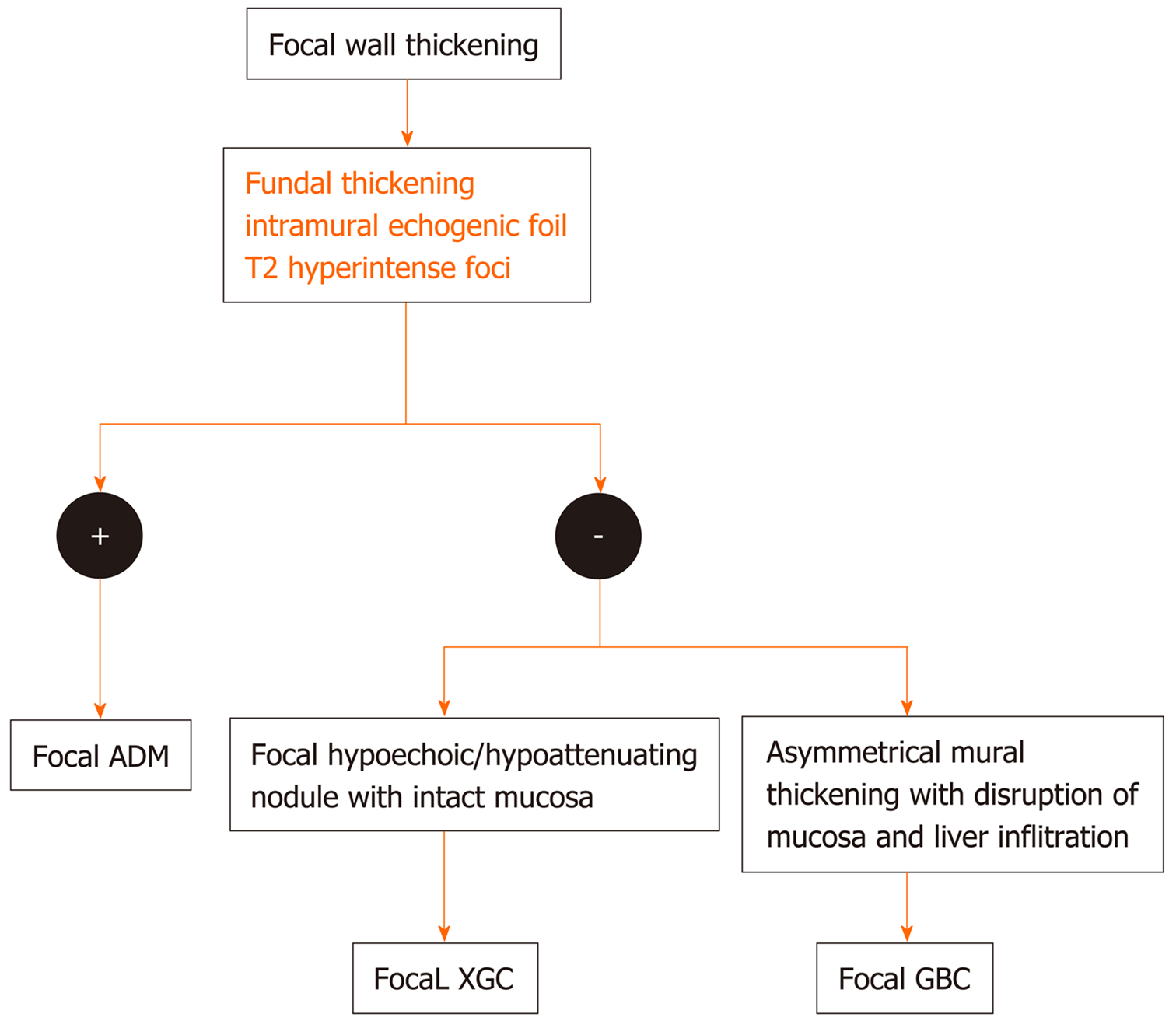
Figure 11 Flow diagram of the algorithmic approach to diagnose focal gallbladder wall thickening.
ADM: Adenomyomatosis; XGC: Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis; GBC: Gallbladder carcinoma.
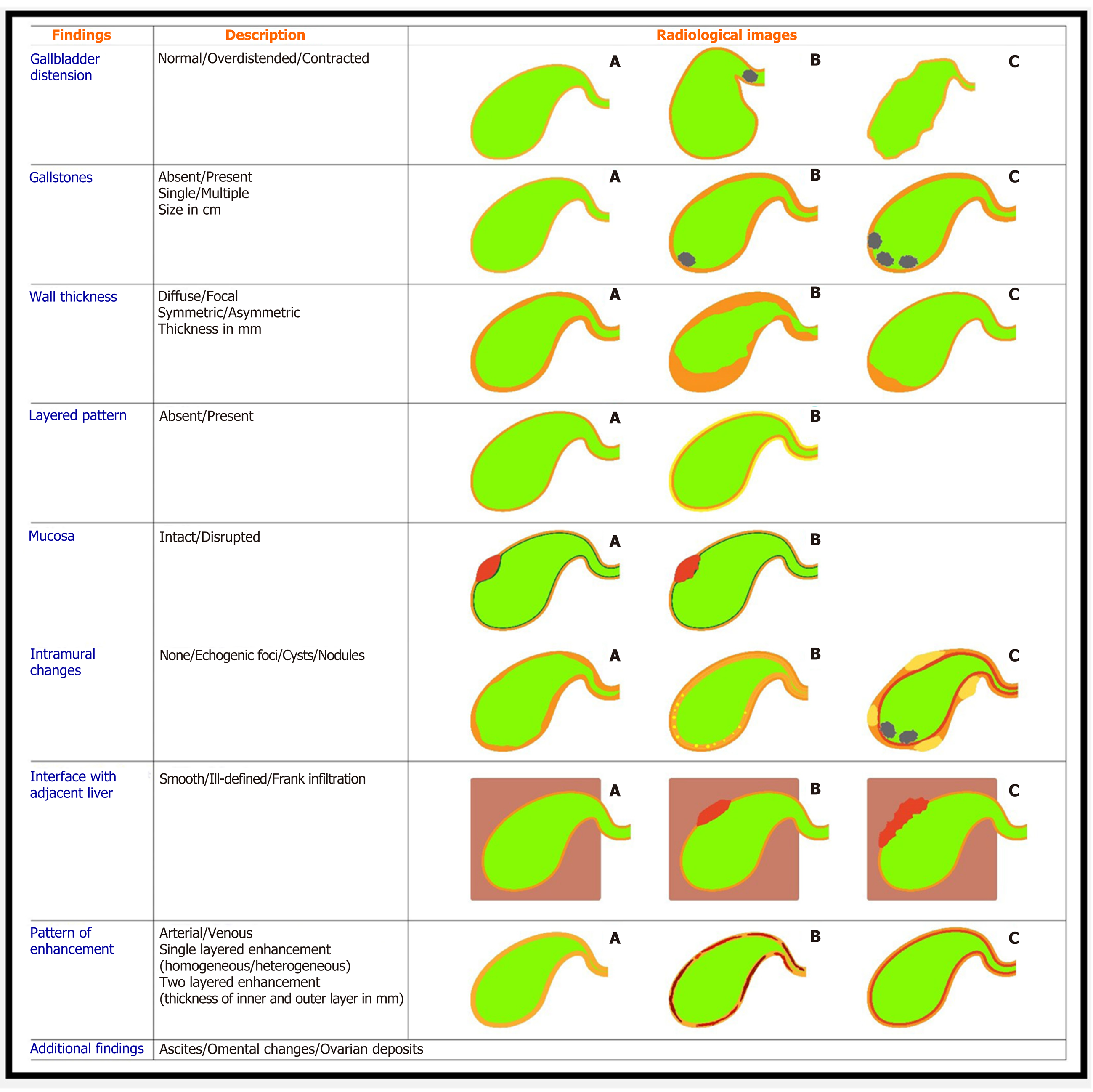
Figure 12 Reporting format of the gallbladder wall thickening.
- Citation: Gupta P, Marodia Y, Bansal A, Kalra N, Kumar-M P, Sharma V, Dutta U, Sandhu MS. Imaging-based algorithmic approach to gallbladder wall thickening. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(40): 6163-6181
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i40/6163.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i40.6163