Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2020; 26(38): 5884-5895
Published online Oct 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i38.5884
Published online Oct 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i38.5884
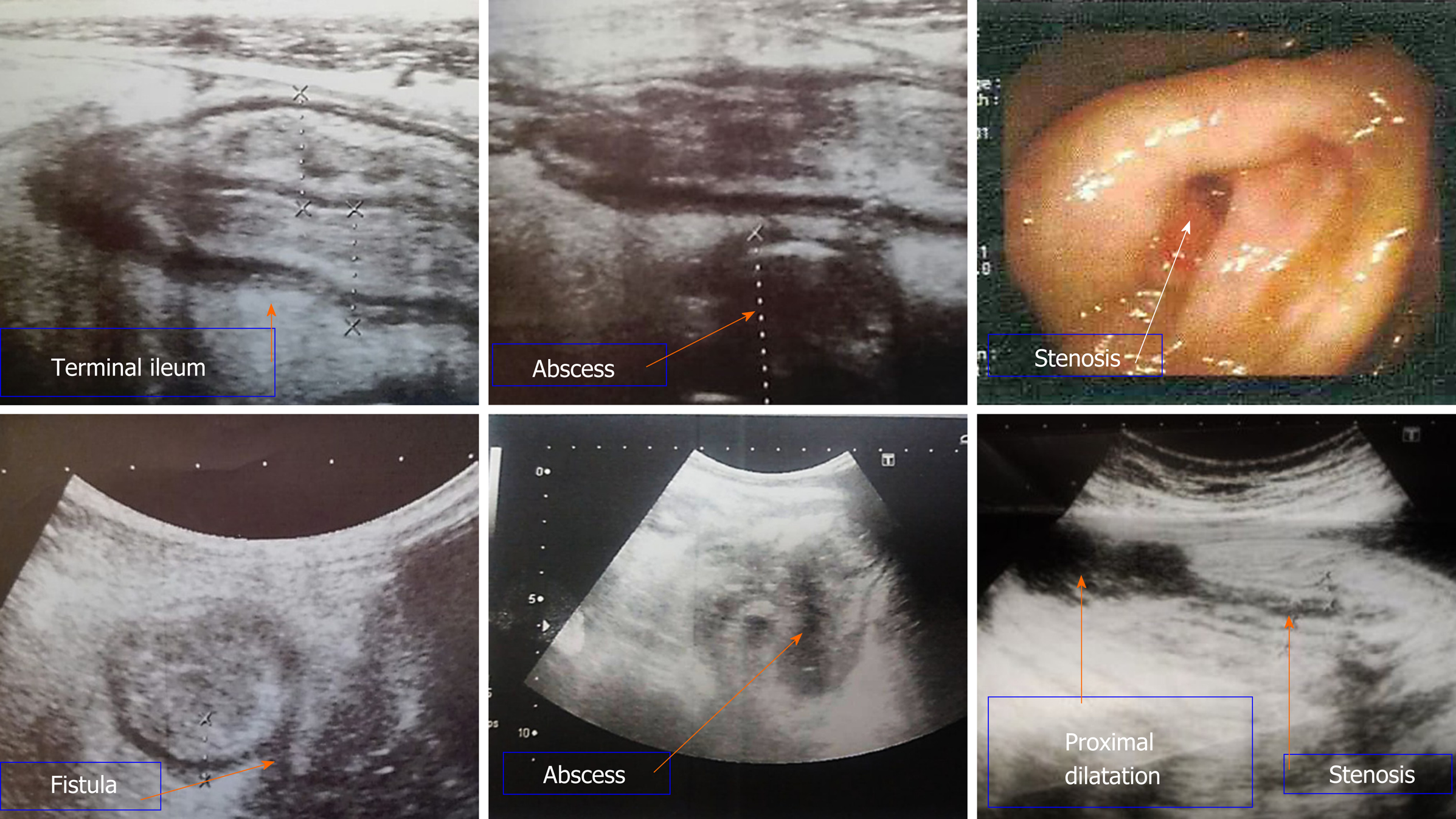
Figure 1 Bowel ultrasound and colonoscopy images.
Bowel ultrasound demonstrates diffuse terminal ileal wall thickening likely of inflammatory nature with sonographic evidence of fistulization with mesenteric abscess formation. Stenosis which was detected during colonoscopy was seen by bowel ultrasound with proximal dilatation.
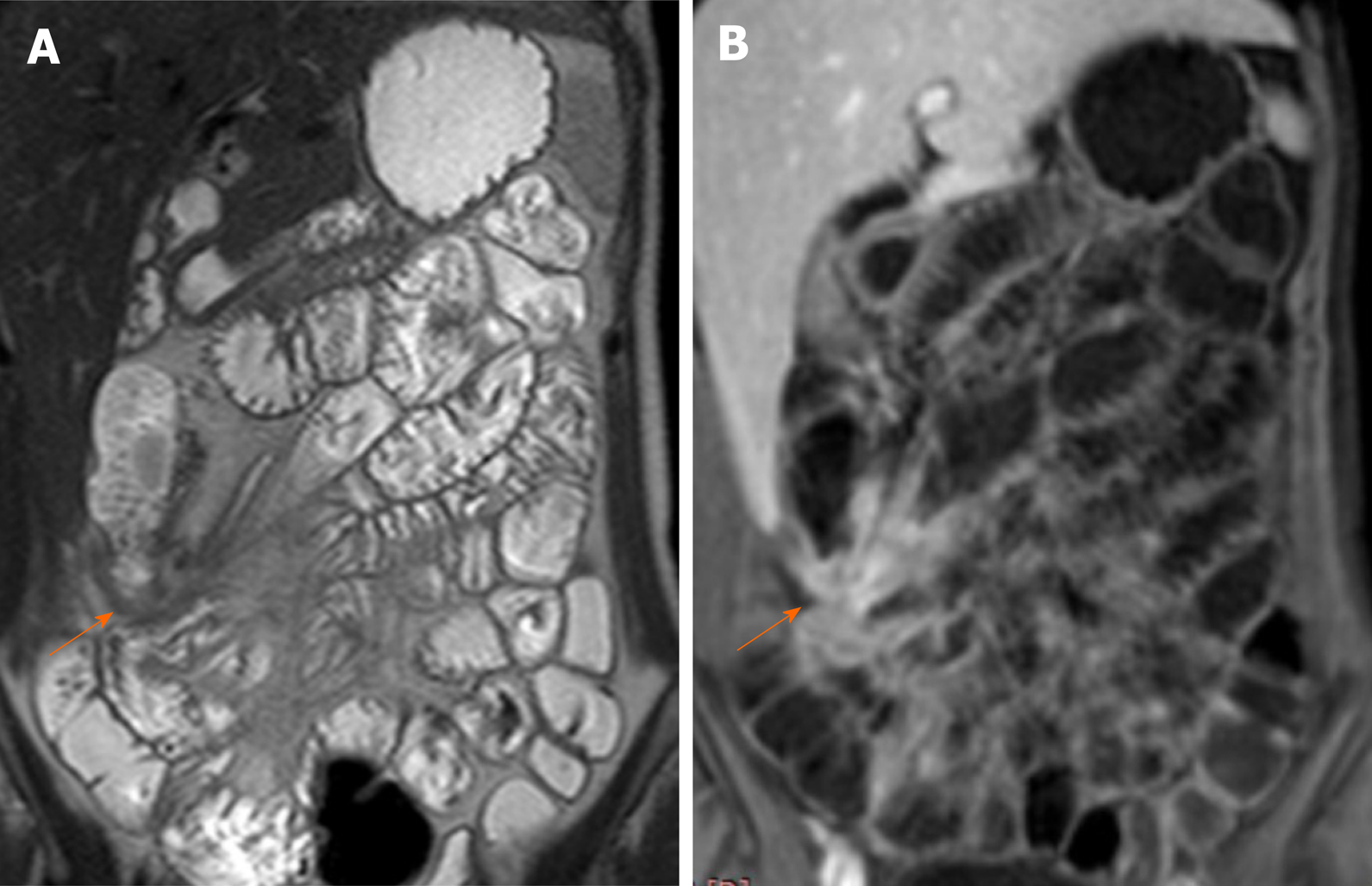
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance enterography.
A: Coronal T2WI shows enteroenteric fistula at the right iliac fossa with stellate appearance of the thickened ileal loops (white arrow); B: Coronal fat-suppressed three-dimensional gradient echo postcontrast T1WI shows accentuated star-like enhancement at the right iliac fossa denoting fistulizing crohn’s disease.
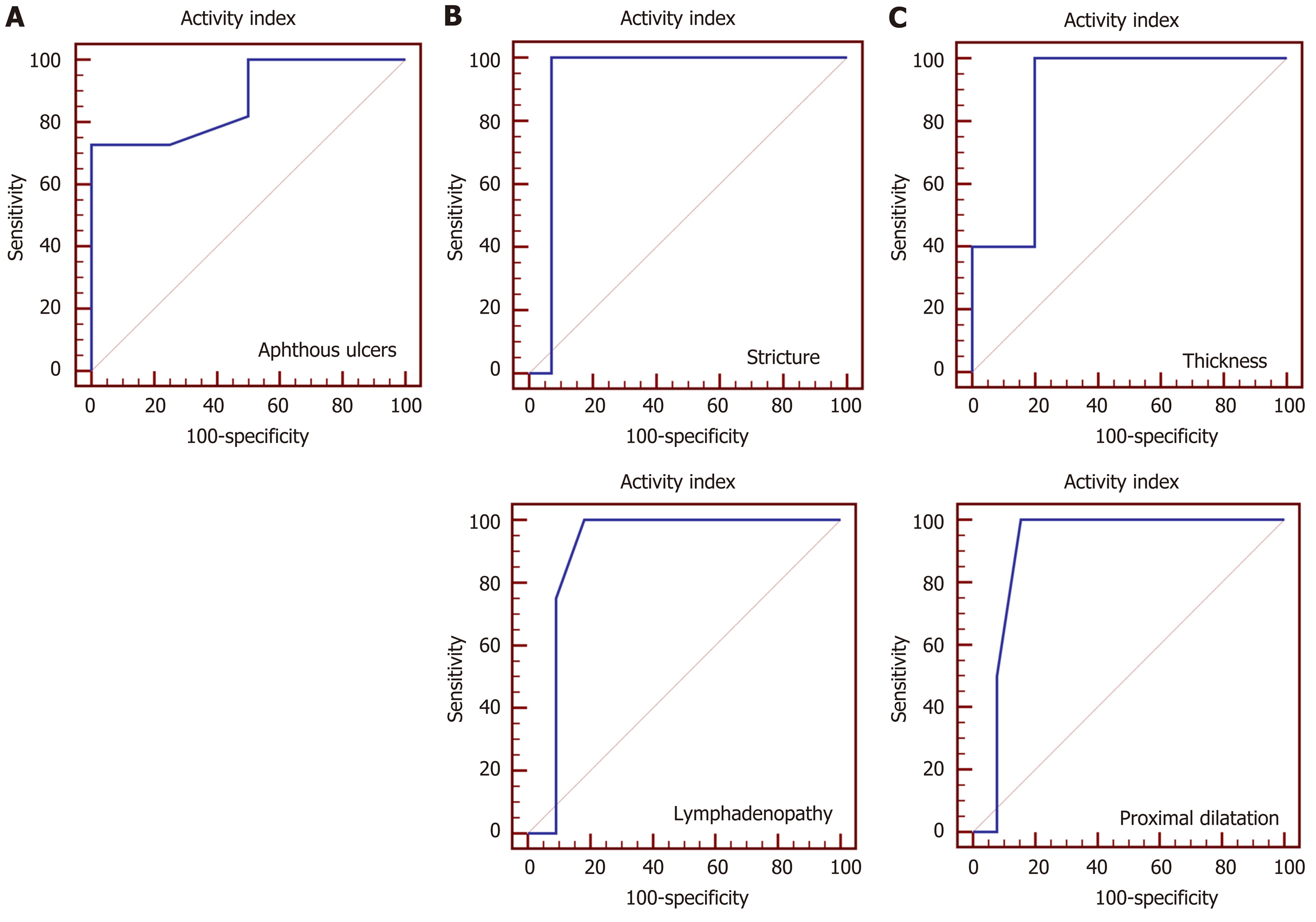
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic curve for prediction of active disease.
A: At endoscopy, aphthous ulcers mean area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was 0.875 (P < 0.001), positive likelihood ratio infinity, and negative likelihood ratio 0.28; B: Bowel ultrasound showed stricture and lymphadenopathy mean area under the ROC curve were 0.929 (P = 0.036) and 0.898 (P = 0.01) respectively, positive likelihood ratio infinity for both, and negative likelihood ratio 0.94 and 0.71 respectively; C: Magnetic resonance enterography showed thickness and proximal dilatation mean area under the ROC curve were 0.880 (P < 0.001) and 0.904 (P = 0.033) respectively, positive likelihood ratio 1.06 and infinity respectively, and negative likelihood ratio 0.88 for both.
- Citation: Kamel S, Sakr M, Hamed W, Eltabbakh M, Askar S, Bassuny A, Hussein R, Elbaz A. Comparative study between bowel ultrasound and magnetic resonance enterography among Egyptian inflammatory bowel disease patients. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(38): 5884-5895
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i38/5884.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i38.5884