Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2020; 26(25): 3673-3685
Published online Jul 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i25.3673
Published online Jul 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i25.3673
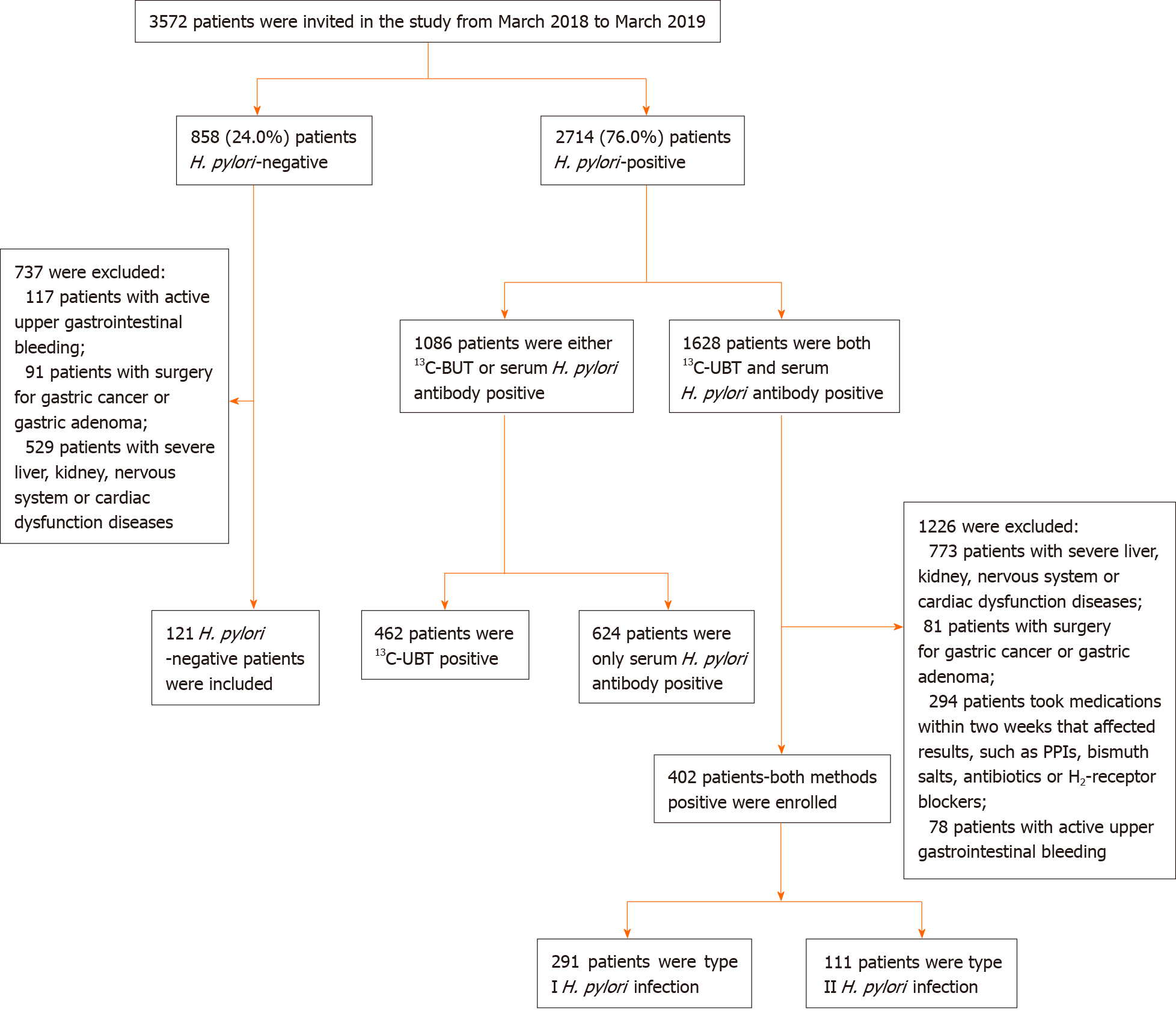
Figure 1 Flowchart of enrolled patients–screening program.
H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
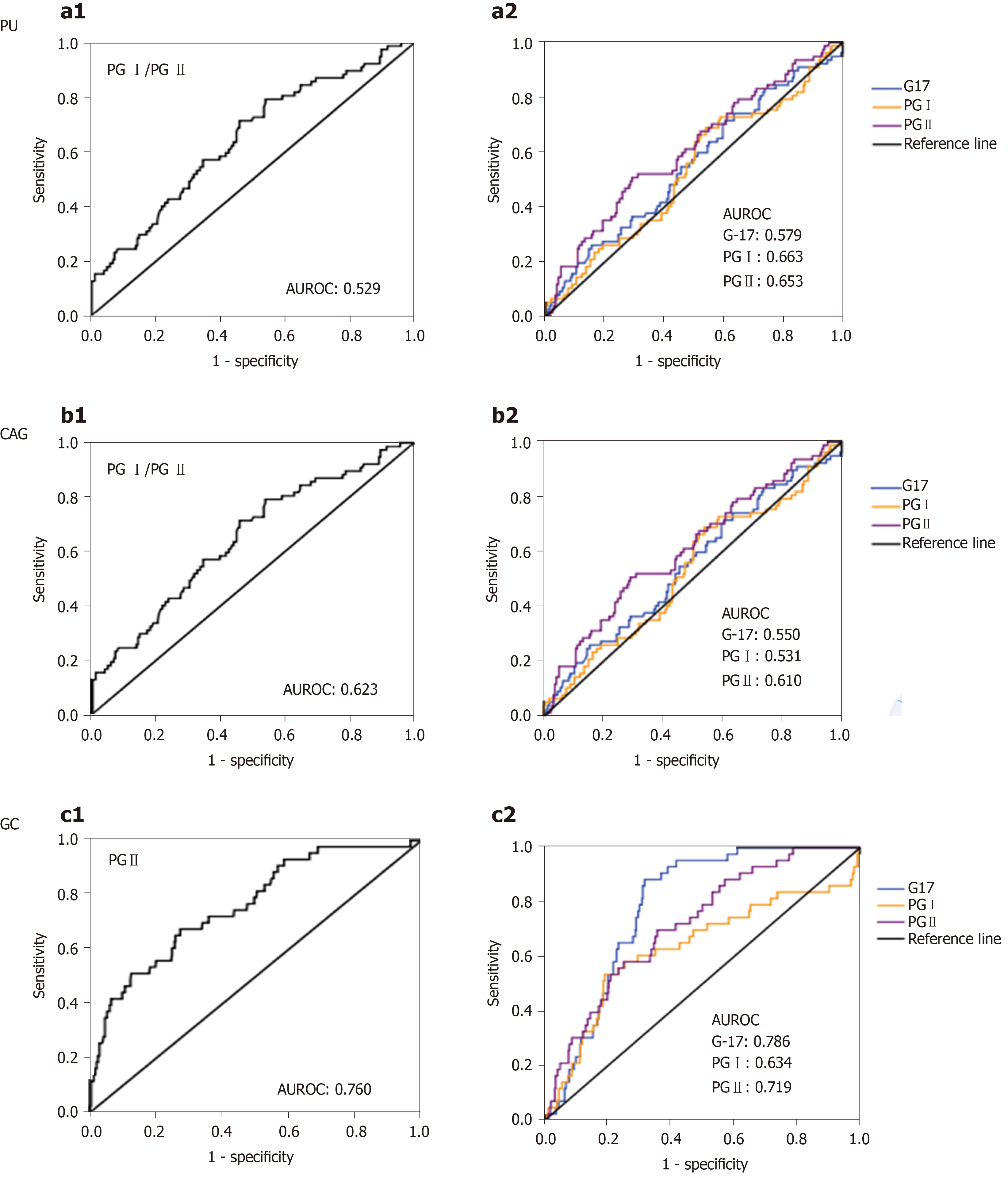
Figure 2 Receiver operating characteristic curves for gastrin-17, pepsinogen I, pepsinogen II and pepsinogen I / pepsinogen II in prediction of chronic atrophic gastritis, peptic ulcers and gastric cancer patients.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of gastrin-17 (G-17), pepsinogen (PG) I, PG II level and PG I/PG II ratio in predicting chronic atrophic gastritis (CAG), peptic ulcers (PU) and gastric cancer (GC) patients. a1-2: ROC curves of PG I/PG II ratio, G-17, PG I and PG II values for predicting PU; b1-2: ROC of PG I/PG II ratio, G-17, PG I and PG II values for predicting CAG; c1-2: ROC of PG I/PG II ratio, G-17, PG I and PG II values for predicting GC. PG: Pepsinogen; PU: Peptic ulcers; AUROC: Area under receiver operating characteristic curve; CAG: Chronic atrophic gastritis; G-17: Gastrin-17; GC: Gastric cancer.
- Citation: Yuan L, Zhao JB, Zhou YL, Qi YB, Guo QY, Zhang HH, Khan MN, Lan L, Jia CH, Zhang YR, Ding SZ. Type I and type II Helicobacter pylori infection status and their impact on gastrin and pepsinogen level in a gastric cancer prevalent area. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(25): 3673-3685
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i25/3673.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i25.3673