Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2020; 26(23): 3201-3212
Published online Jun 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i23.3201
Published online Jun 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i23.3201
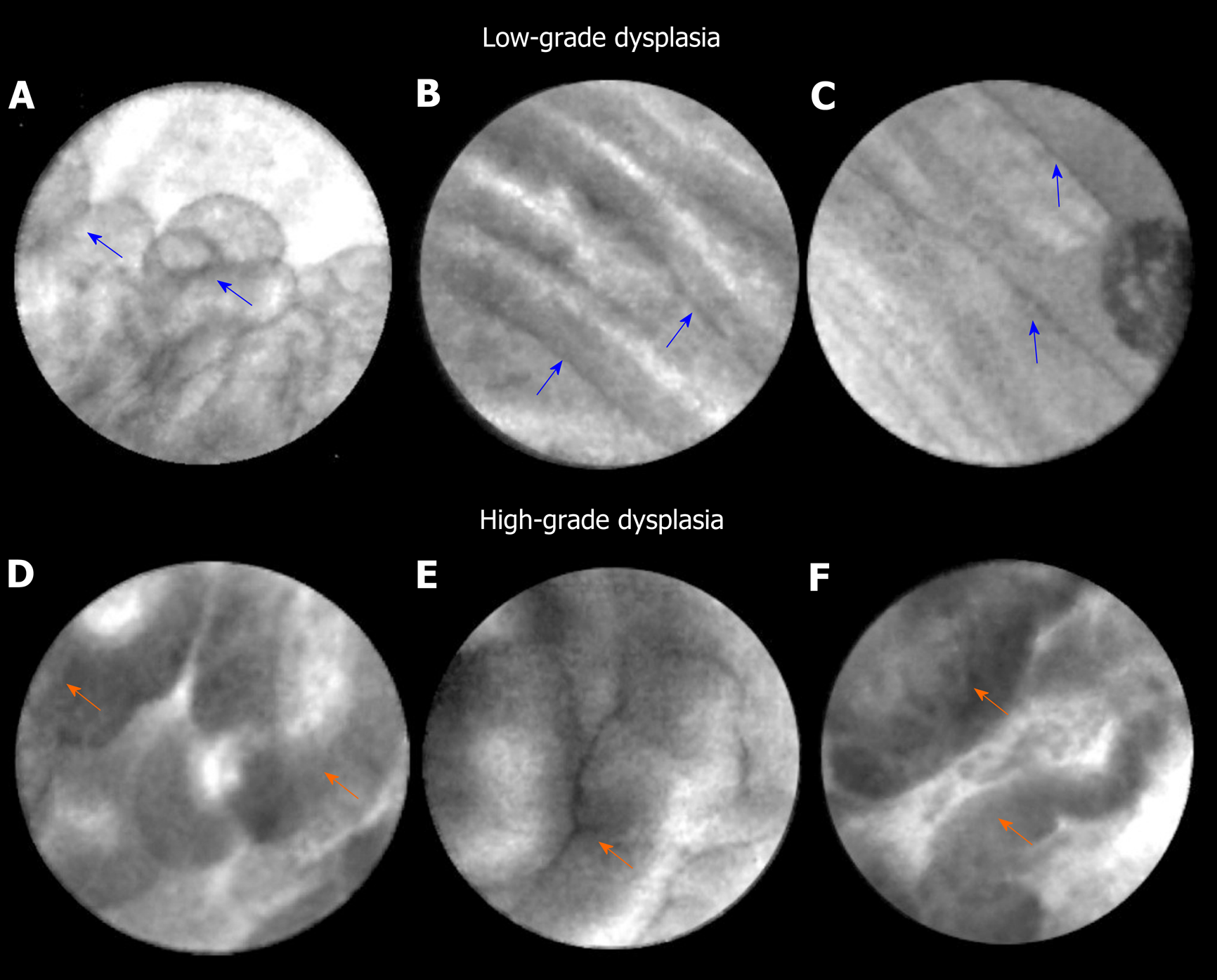
Figure 1 Endoscopic ultrasound-guided confocal endomicroscopy characteristics of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm.
A-C: Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm with low-grade dysplasia. Papillae (blue arrows) reveal thin and translucent epithelium. The papillae are small with thin epithelium in panel A. The epithelium is flat in panels B and C; D-H: Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm with high-grade dysplasia. Papillae (orange arrows) show thicker and darker epithelium. In panel D, there is higher density of papillae.
- Citation: Eiterman A, Lahooti A, Krishna SG. Endosonographic diagnosis of advanced neoplasia in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(23): 3201-3212
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i23/3201.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i23.3201