Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2020; 26(16): 1962-1970
Published online Apr 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i16.1962
Published online Apr 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i16.1962
Figure 1 Flowchart of patients included in the study, presented according to the CONSORT statement.
R: Randomization; RFV: Retroflected view; SFV: Standard forward view; CRC: colorectal cancer.
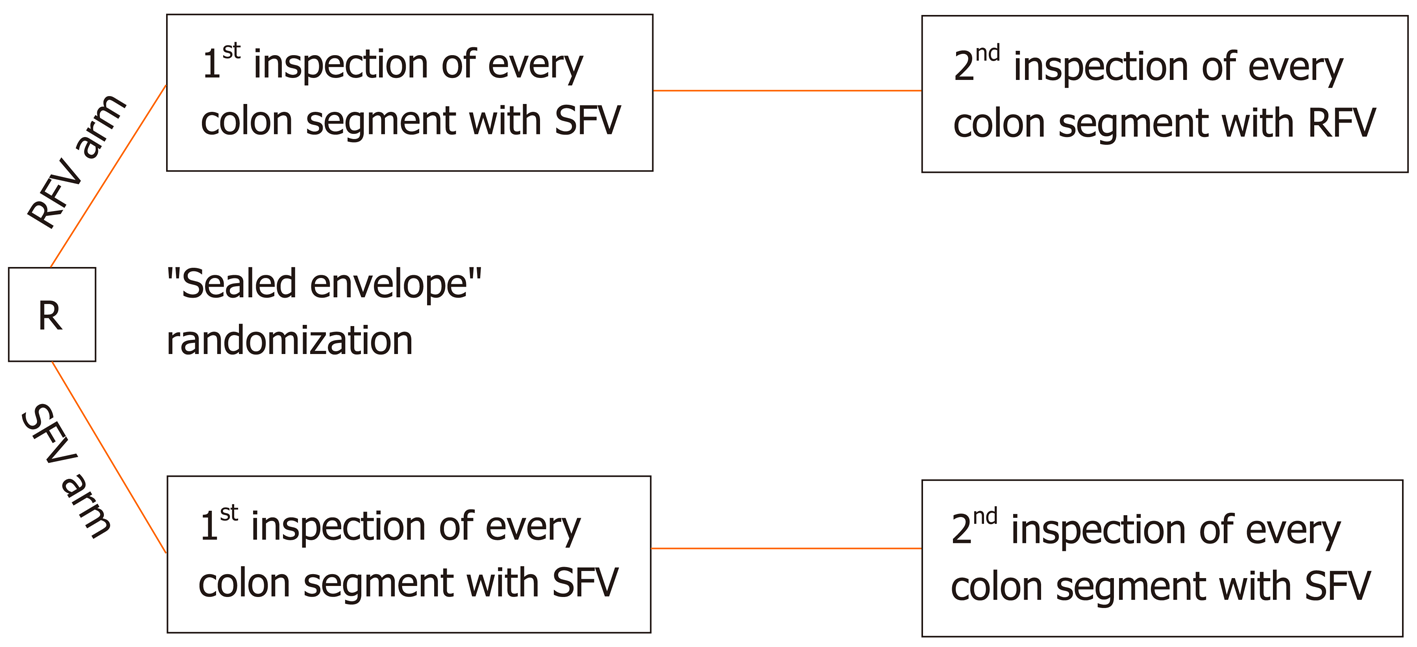
Figure 2 Randomization of the included patients and inspection modes in the retroflected view and standard forward view arm.
R: Randomization; RFV: Retroflected view; SFV: Standard forward view.
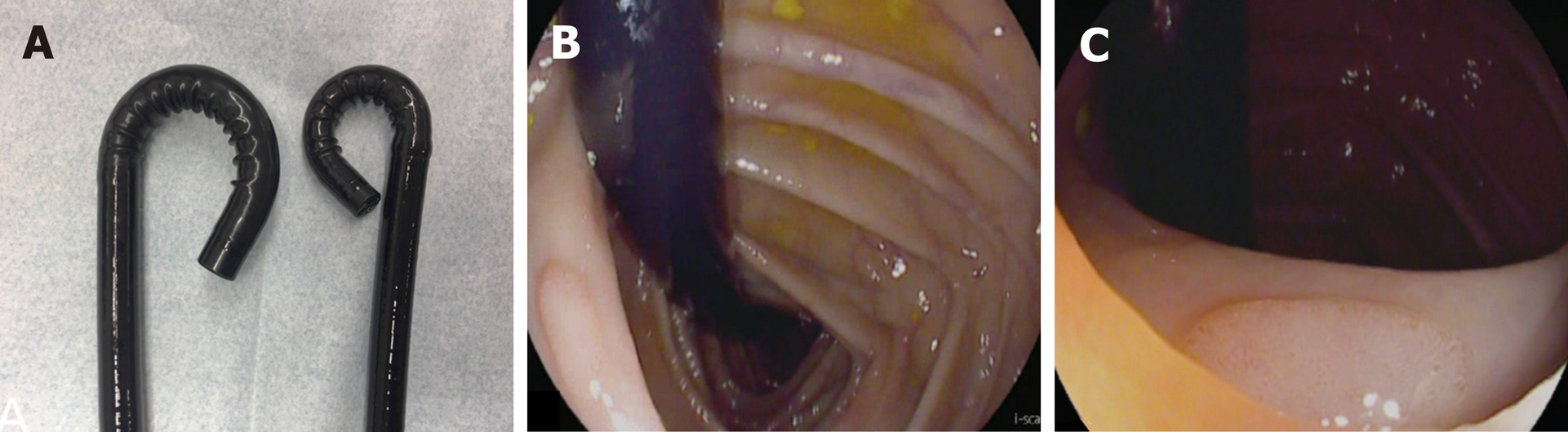
Figure 3 Retrograde inspection of the whole colon.
A: For retrograde Inspection of the whole colon, a dedicated high definition colonoscope with an outer diameter of 11.6 mm and a bending radius allowing for > 210° deflection was used (right: RetroView EC-34 i10T; left: standard colonoscope i10F2, both from Pentax Medical, Tokyo, Japan); B and C: Detection of a sessile adenoma behind a colonic fold in retroflexion in the transverse colon in the retroflected view arm.
- Citation: Rath T, Pfeifer L, Neufert C, Kremer A, Leppkes M, Hoffman A, Neurath MF, Zopf S. Retrograde inspection vs standard forward view for the detection of colorectal adenomas during colonoscopy: A back-to-back randomized clinical trial. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(16): 1962-1970
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i16/1962.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i16.1962