Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2020; 26(1): 21-34
Published online Jan 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i1.21
Published online Jan 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i1.21
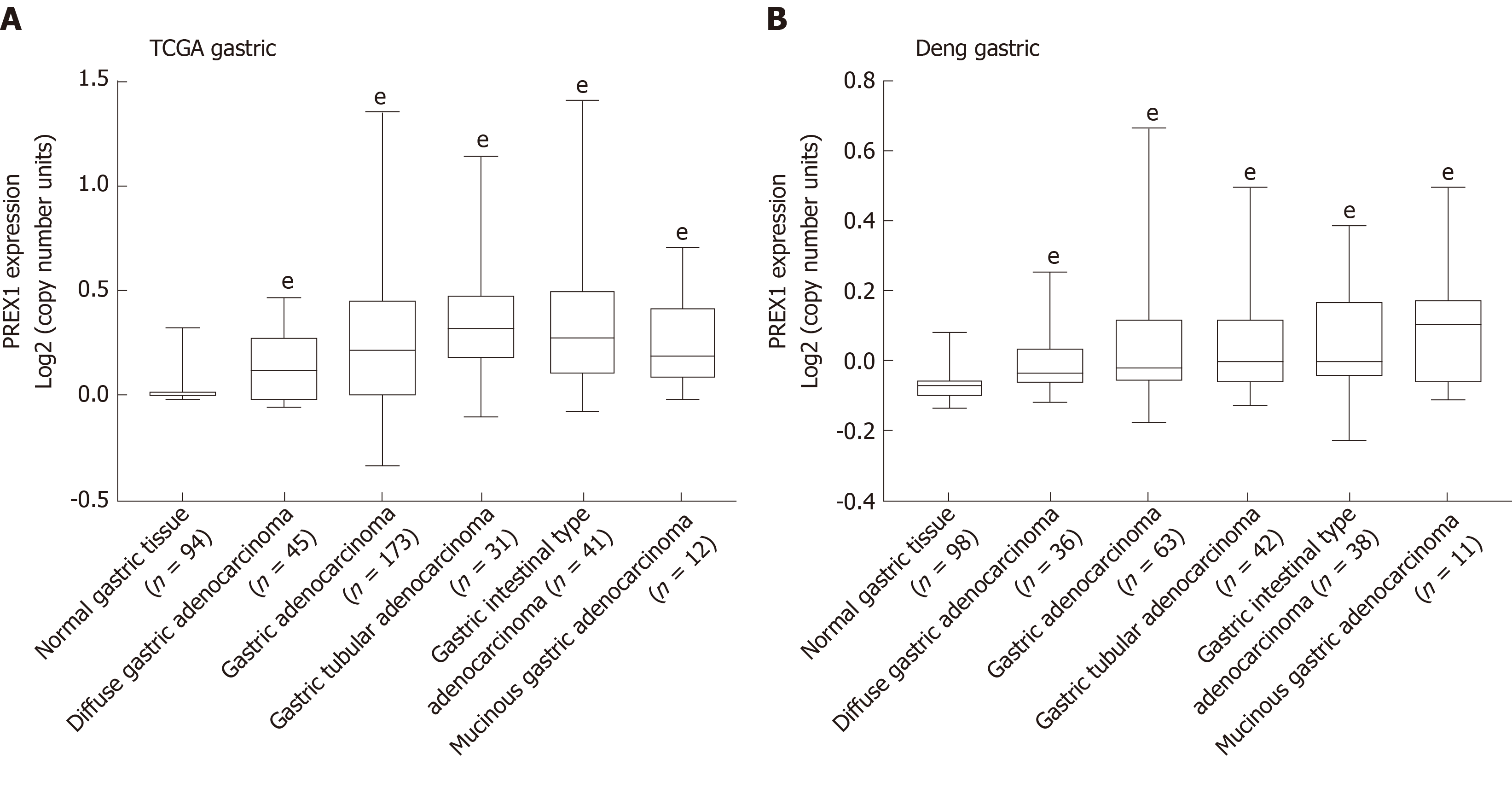
Figure 1 The expression of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1 was evaluated in the Oncomine portal.
A: The expression of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1 in the cancer genome atlas gastric cancer database was conducted; B: Deng’s gastric tissues from Oncomine portal[32] were selected to evaluate the phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1 mRNA levels in different histology types of gastric cancer, the data was evaluated by high-resolution single nucleotide polymorphism arrays. Statistical significance is expressed as eP < 0.001 vs normal gastric tissue. PREX1: Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1; TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas.
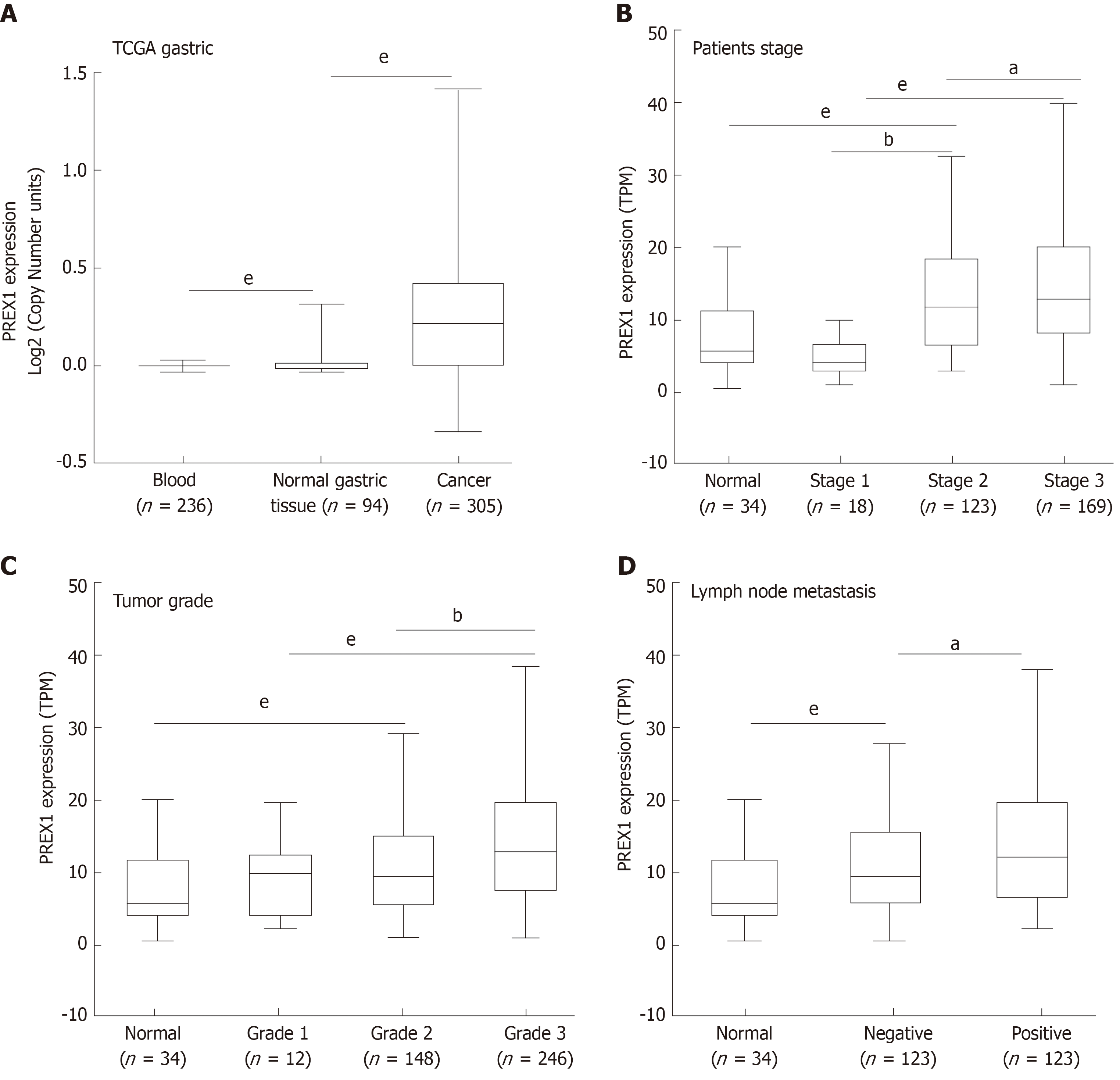
Figure 2 The association between phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1 expression and clinical features.
A: The expression of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1 (PREX1) in blood samples of gastric cancer patients, normal gastric tissues, and gastric tumor tissues; B: The expression of PREX1 was examined in gastric cancer patients with the different patient stage; C: The level of PREX1 was assessed in gastric cancer patients with different tumor grade; D: The level of PREX1 was examined in those gastric cancer patients with lymph node metastasis or not. Statistical significance is expressed as aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, eP < 0.001. TPM: Transcript per million; PREX1: Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1; TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas.
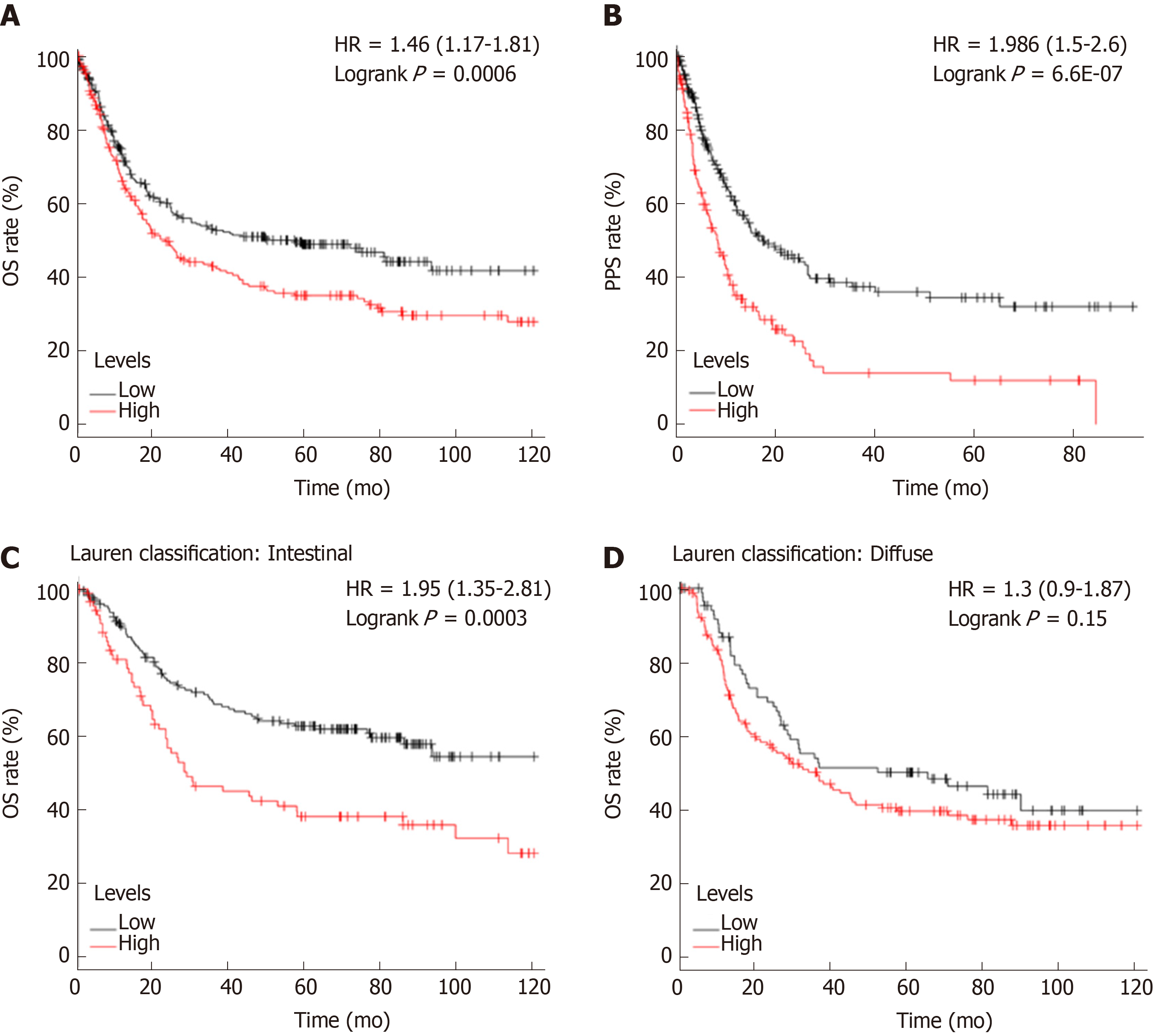
Figure 3 The survival analysis between high and low phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1 expression cohorts.
A: The overall survival rate was conducted in the high and low phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1 (PREX1) expression gastric cancer patients; B: The post-progression survival analysis was conducted in the high and low PREX1 expression gastric cancer patients; C: In the intestinal gastric cancer patients; D: diffuse gastric cancer patients, the overall survival was assessed in the high and low PREX1 expression patients. OS: Overall survival; PPS: Post-progression survival; HR: Hazard ratio.
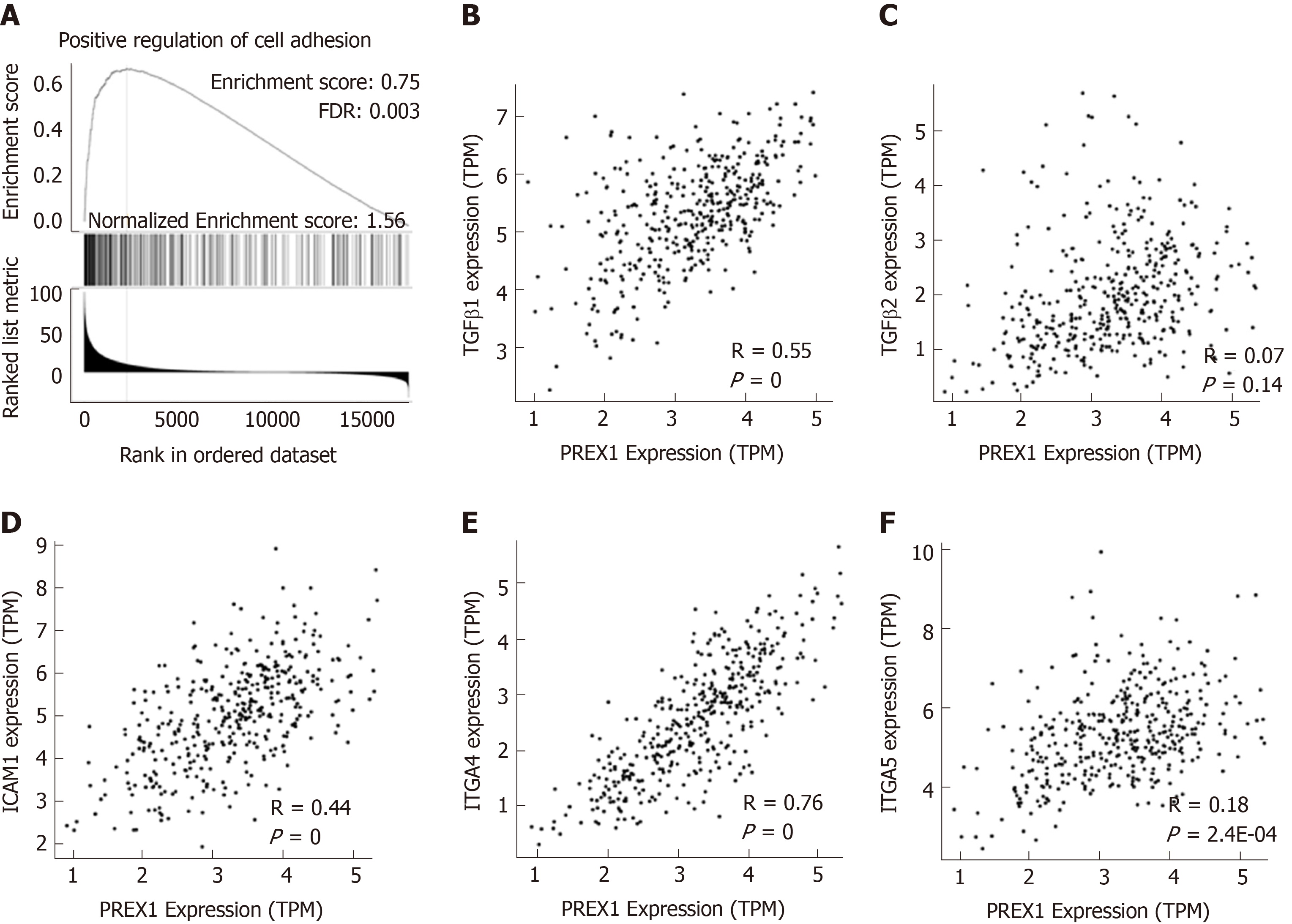
Figure 4 Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1 was closely associated with the regulation of cell adhesion.
A: The Gene Set Enrichment Analysis analysis of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1 (PREX1) and co-expression network in gastric cancer; B: The correlation between PREX1 and transforming growth factor β1 were conducted in gastric cancer; C: The correlation between PREX1 and transforming growth factor β2 were conducted in gastric cancer; D: The correlation between PREX1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 were conducted in gastric cancer; E: The correlation between PREX1 and integrin alpha 4 were conducted in gastric cancer; F: The correlation between PREX1 and integrin alpha 5 were conducted in gastric cancer. TPM: Transcript per million; FDR: False discovery rate; NES: Normalized enrichment score; TGFβ1: Transforming growth factor β1; TGFβ2: Transforming growth factor β2; ICAM1: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1; ITGA4: Integrin alpha 4; ITGA5: Integrin alpha 5; PREX1: Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1.
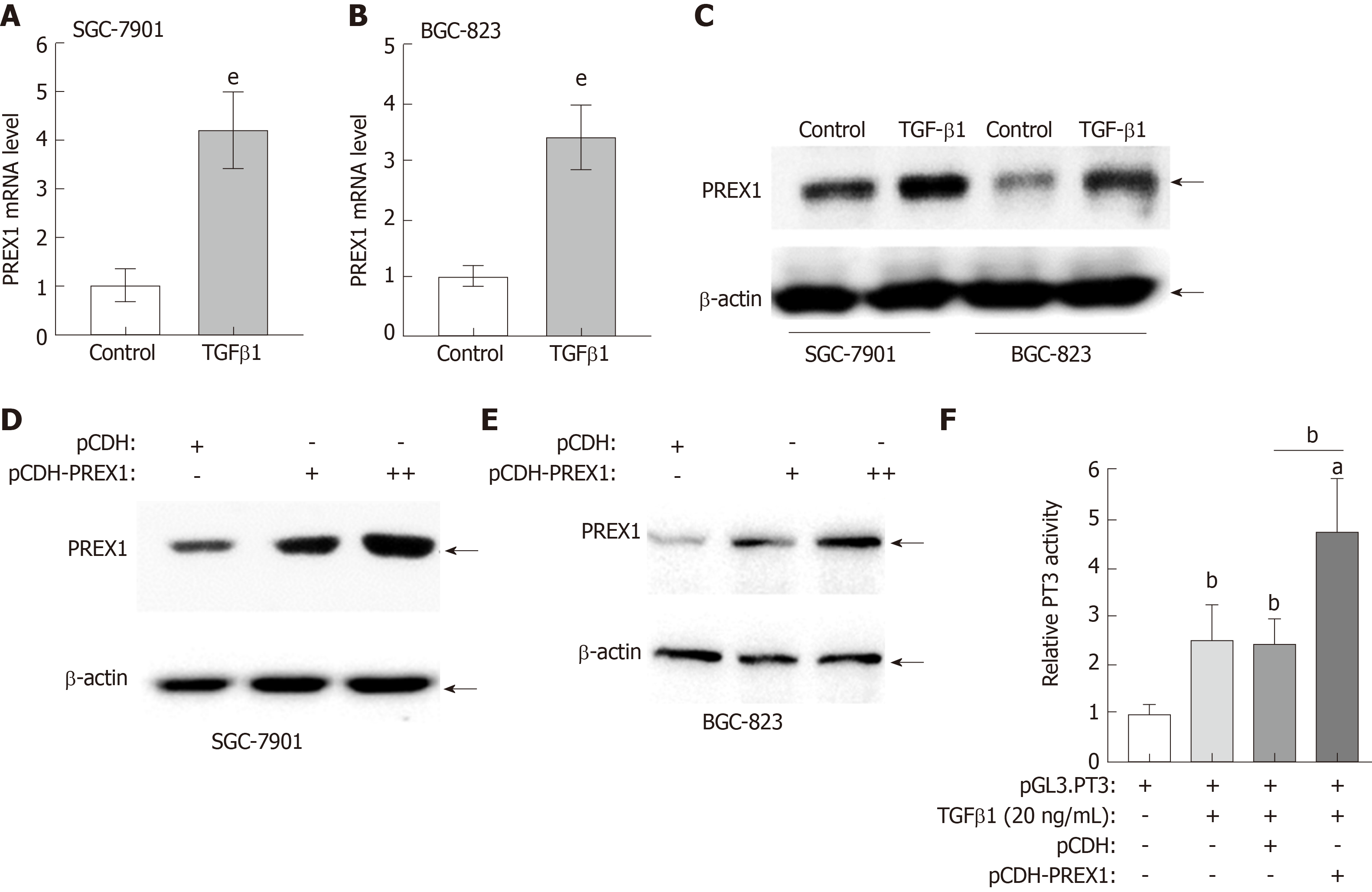
Figure 5 Feedback regulation between phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1 and transforming growth factor β1 in gastric cancer cells.
A and B: SGC-7901 cells and BGC-823 cells were treated with recombinant human transforming growth factor (TGF) β1 protein at the concentration of 20 ng/mL for 12 h, the mRNA level was assessed by reverse transcriptase quantitative polymerase chain reaction; C: SGC-7901 and BGC-823 cells were treated with recombinant human TGFβ1 protein at the concentration of 20 ng/mL for 12 h, the phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1 (PREX1) protein was examined by western blotting; D and E: SGC-7901 and BGC-823 cells were cultured with lentivirus of PREX1 overexpressing particle in dose concentration and control for 24 h, the cells were subjected to western blotting to evaluate the activation of TGFβ1; F: HEK293T cells were transfected with Luc-PT3 and Rellina plasmids, the culture medium was supplemented with lentivirus particle of PREX1 overexpression and vector control. For another 24 h culture, the cells were treated with recombinant TGFβ1 (20 ng/mL) for 6 h, then the cells were subjected to dual-luciferase reporter assay. Statistical significance is expressed as aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, eP < 0.001. PREX1: Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1; TGFβ1: Transforming growth factor β1.
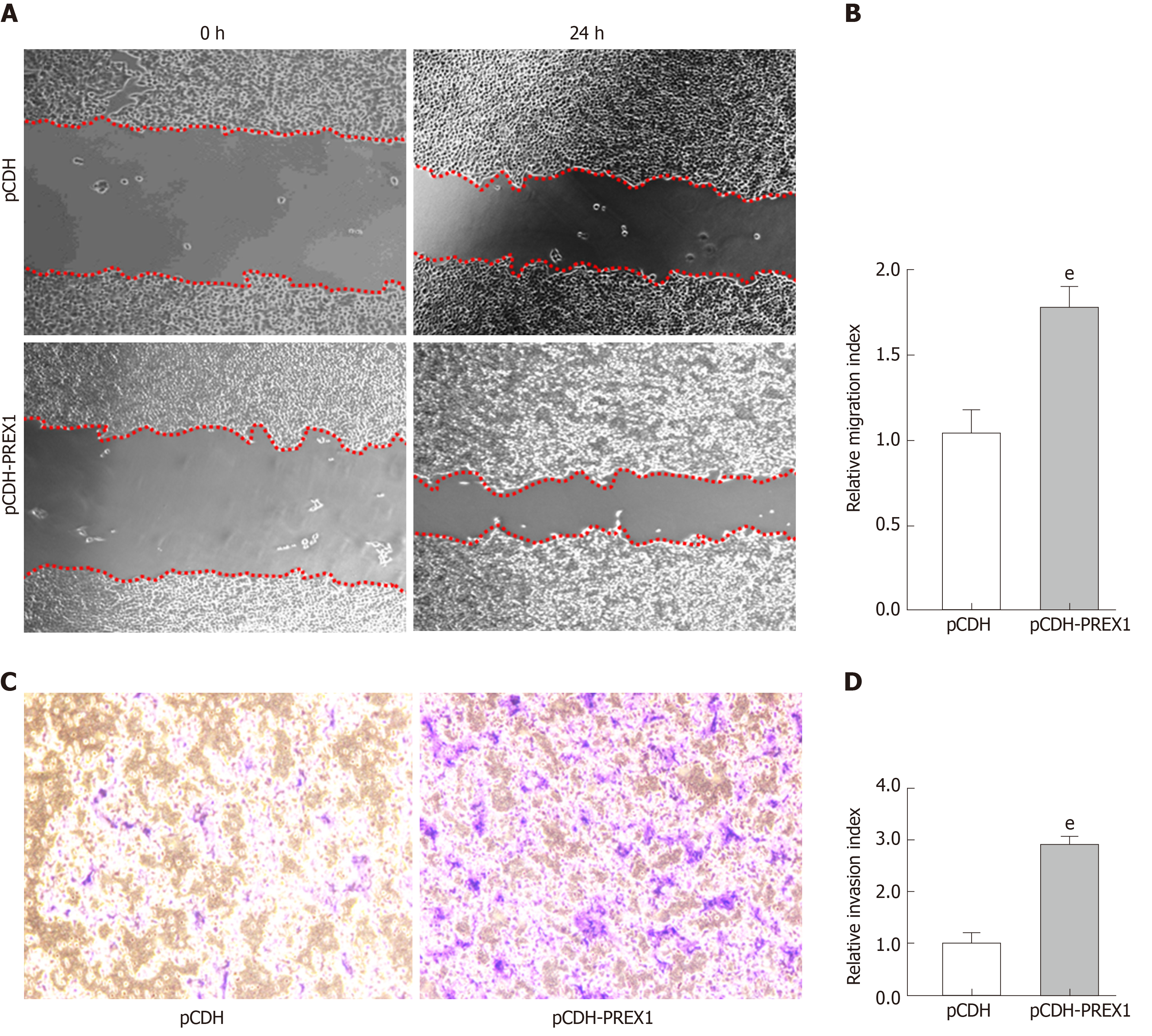
Figure 6 Overexpression of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1 could promote the metastasis of gastric cancer cells.
A: SGC-7901 cells were subjected to wound healing assay, and the cells were treated with phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1 overexpressing lentivirus and vector control lentivirus particles for 24 h; B: The relative migration index was calculated by the width of the wound scratch of panel A; C: Transwell assay was used to examine the effect of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1 in the invasion of SGC-7901 cells; D: The relative invasion index was calculated by the number of invasive cells in three different fields. eP < 0.001 vs pCDH. PREX1: Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1.
- Citation: Shao Q, Chen ZM. Feedback regulation between phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate dependent Rac exchange factor 1 and transforming growth factor β1 and prognostic value in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(1): 21-34
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i1/21.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i1.21