Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2019; 25(36): 5483-5493
Published online Sep 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i36.5483
Published online Sep 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i36.5483
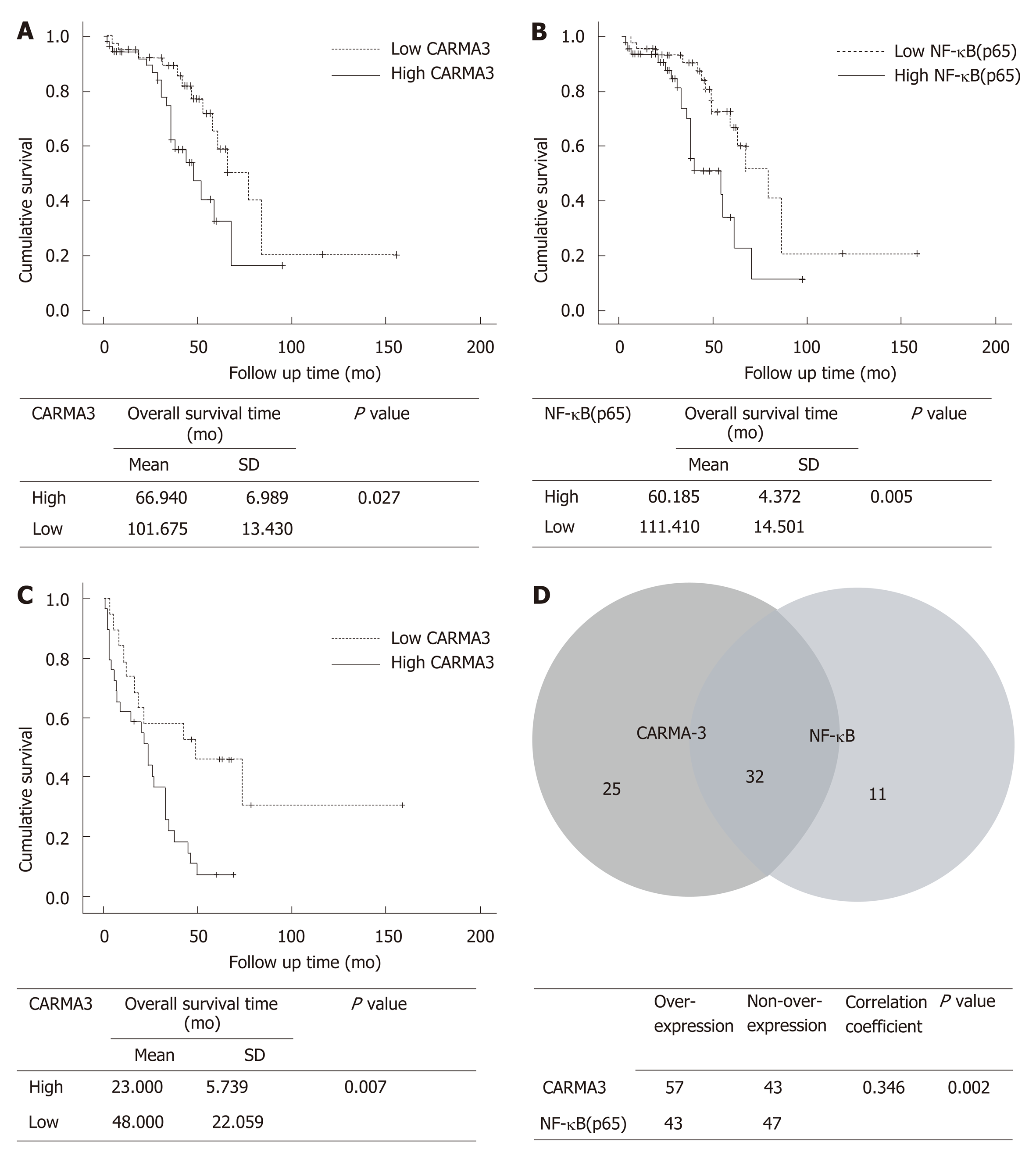
Figure 1 CARMA3 and nuclear factor kappa-B (p65) are correlated with clinical prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients.
A: High CARMA3 (n = 54) expression suggested shorter overall survival time (P = 0.027); B: High nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) (p65) (n = 40) expression indicated shorter postoperative overall survival (P = 0.005); C: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with high CARMA3 expression had a shorter disease free survival time than those with low CARMA3 expression (P = 0.007); D: Correlation between CARMA3 and NF-κB expression in HCC tissue (P = 0.002). NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-B.
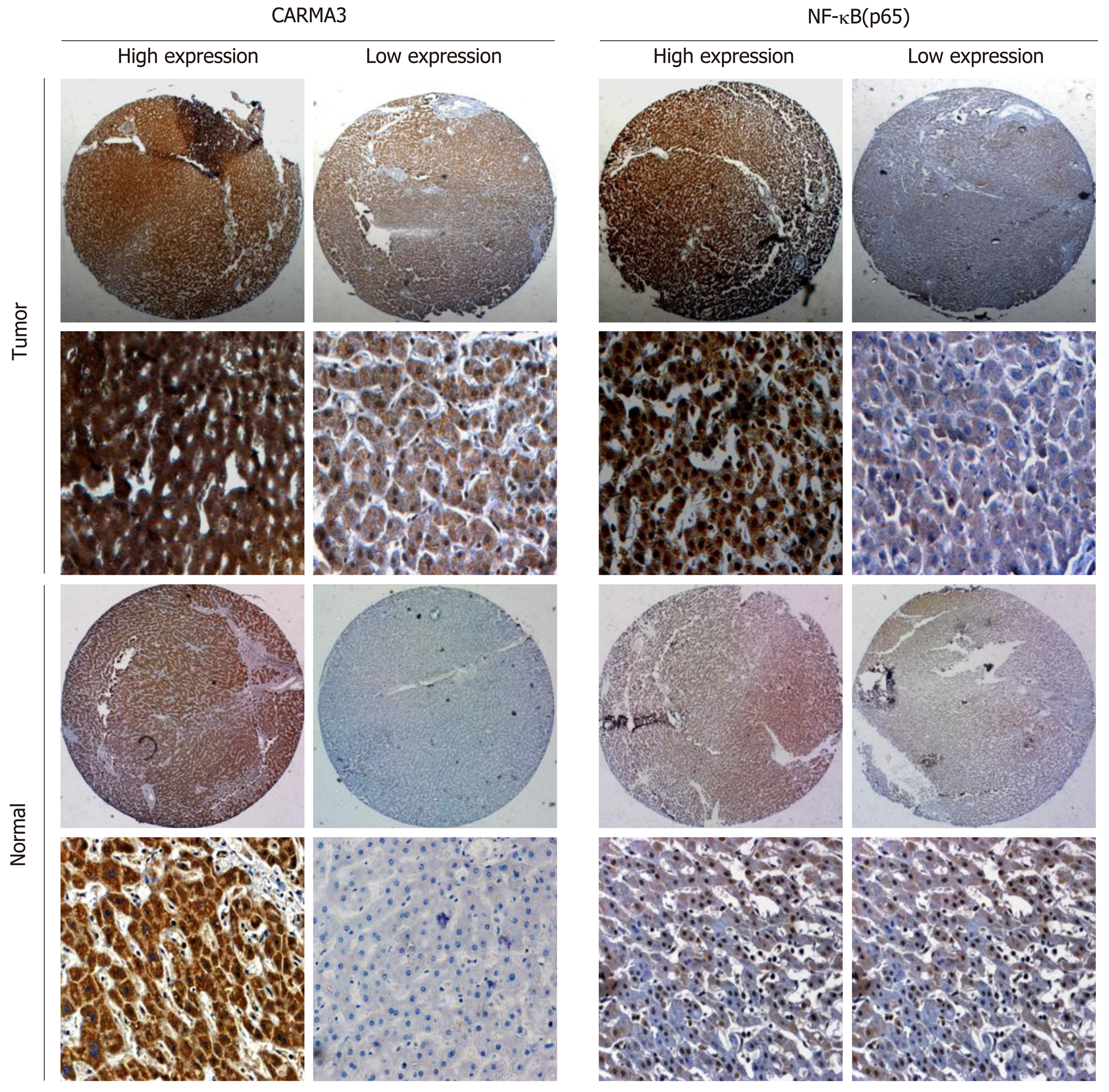
Figure 2 Expression of CARMA3 and nuclear factor kappa-B (p65) in hepatocellular carcinoma tumor tissues and the adjacent liver tissues.
Magnification, ×100. NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-B.
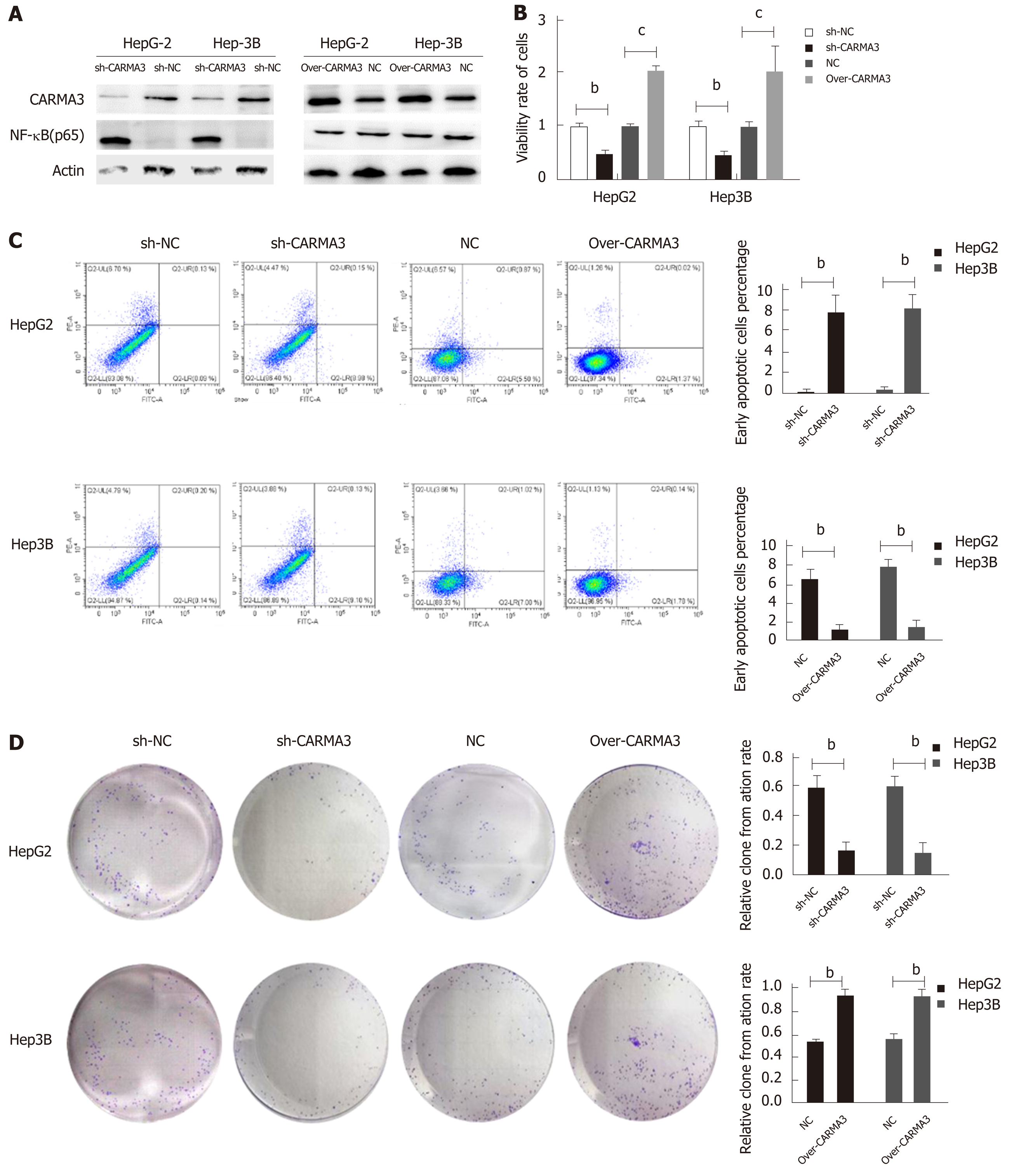
Figure 3 Regulation of CARMA3 expression has effects on capacities of proliferation, colony formation, and apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
A: CARMA3 regulated the expression of nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) (p65) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells; B: MTT assay showed that overexpression of CARMA3 promoted proliferation, while reducing CARMA3 expression suppressed proliferation in HCC cells; C: Flow cytometry analysis showed that increasing CARMA3 inhibited early apoptosis in HCC cells, while downregulation of CARMA3 enhanced early apoptosis; D: Colony formation assay showed that CARMA3 increased colony formation number, while CARMA3 knockdown decreased colony formation number (bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs control).
Figure 4 Sodium aescinate inhibits the proliferation and colony formation and induces early apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
A: Sodium aescinate (SA) significantly inhibited the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells but had no effects on liver cells; B: Cell viability of HCC cells treated at different doses of SA and for different durations; C: SA induced early apoptosis in HCC cells; D: SA suppressed colony formation capacity in HCC cells (aP < 0.05, cP < 0.001 vs control).
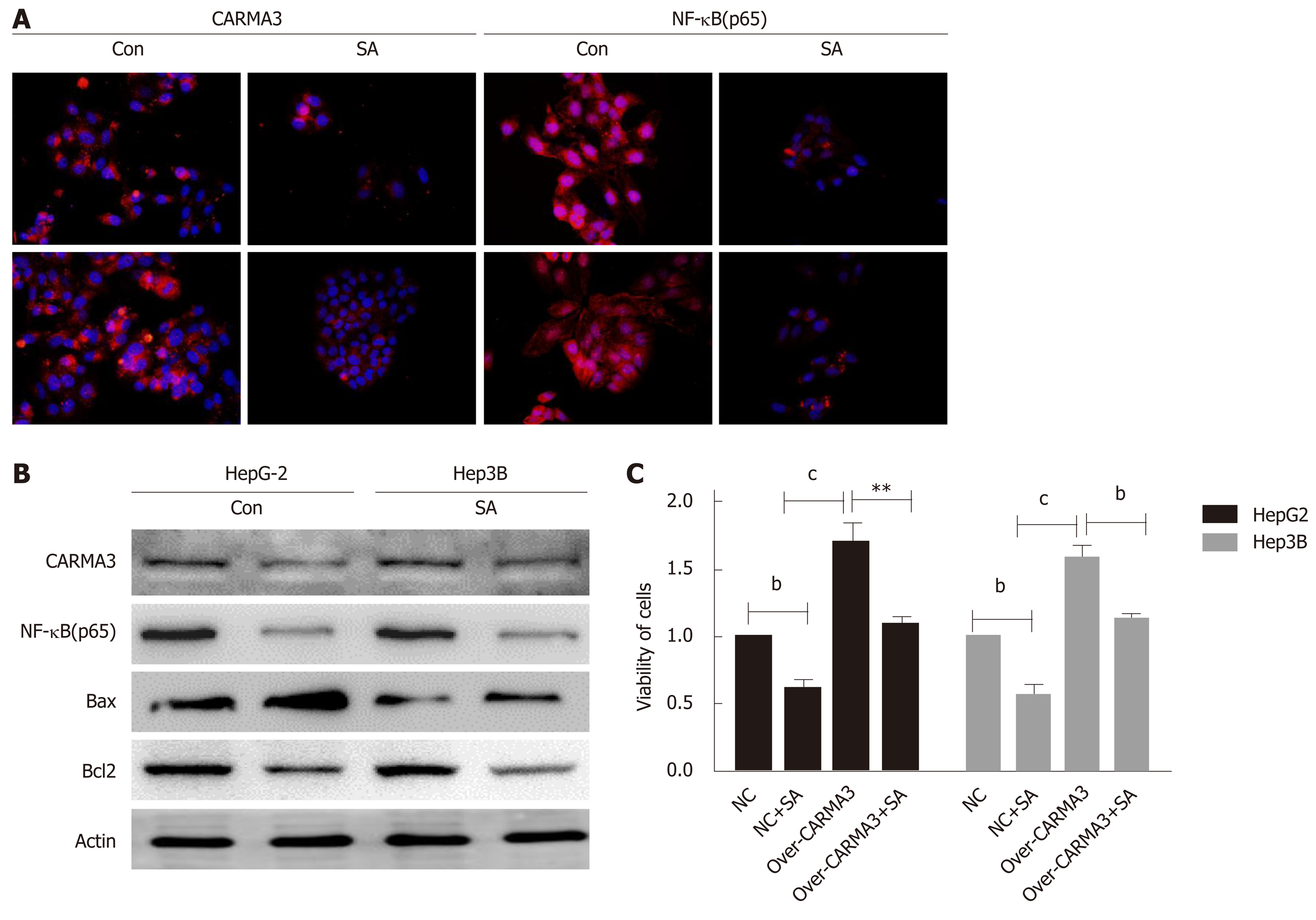
Figure 5 Sodium aescinate inhibits CARMA3/nuclear factor kappa-B signaling.
A and B: Expression of CARMA3 and NF-kB (p65) detected in HCC cells after treatment with sodium aescinate (SA) by immunofluorescence (magnification, ×400); C: Cell viability of high CARMA3 expressing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells and control HCC cells either treated with SA or saline. (bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs control).
- Citation: Hou H, Li WX, Cui X, Zhou DC, Zhang B, Geng XP. CARMA3/NF-κB signaling contributes to tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma and is inhibited by sodium aescinate. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(36): 5483-5493
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i36/5483.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i36.5483