Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2019; 25(34): 5120-5133
Published online Sep 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i34.5120
Published online Sep 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i34.5120
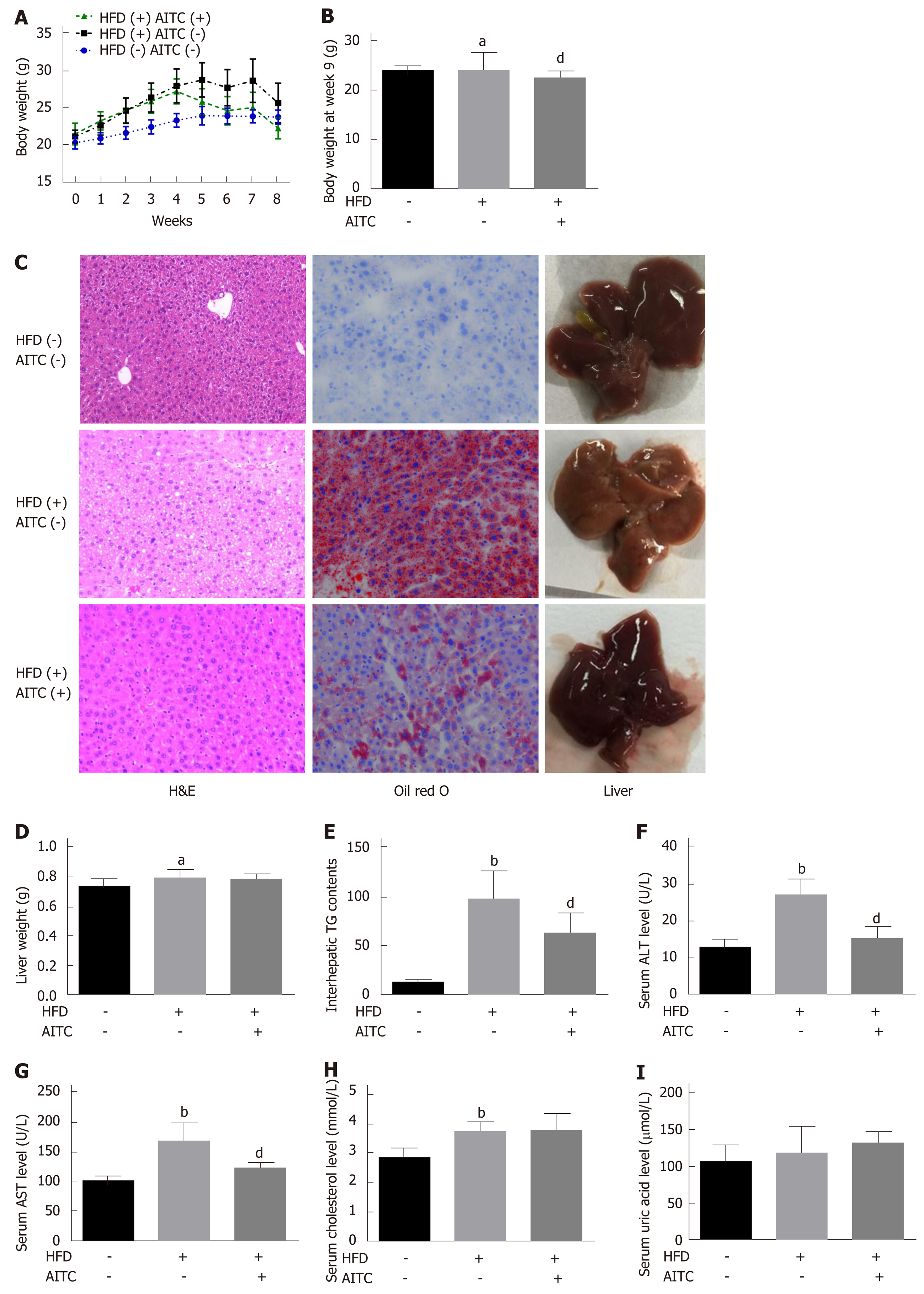
Figure 1 Allyl isothiocyanate reduces body weight, ameliorates hepatic steatosis and attenuates liver injury in high fat diet-fed mice.
A: Body weight evaluated weekly; B: Body weight at week 8; C: Representative liver sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) (left panel) or oil red O (middle panel) and macroscopic pictures of livers (right panel). D: Liver weight; E: Intrahepatic triglyceride (TG) content. Liver function was evaluated by detecting serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) (F), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (G), total cholesterol (H) and uric acid (I). Scale bar in panel represents 100 μm. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs HFD(-) AITC(-), dP < 0.01 vs HFD(+) AITC(-). HFD: High fat diet; AITC: Allyl isothiocyanate; TG: Triglyceride; H&E: Hematoxylin and eosin; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase.
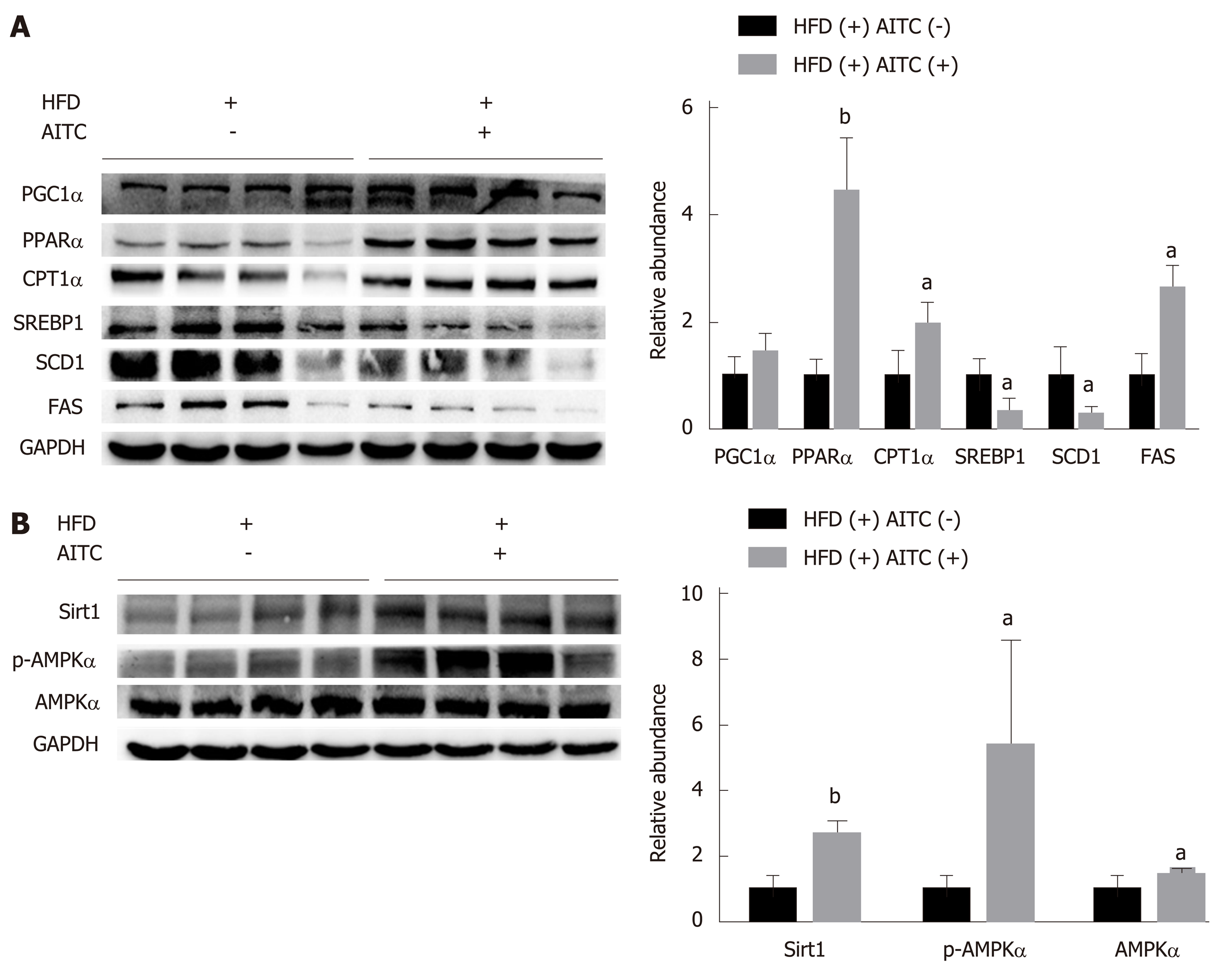
Figure 2 Allyl isothiocyanate upregulates the expression of proteins involved in fatty acid β-oxidation, downregulates the protein levels of lipogenesis genes, and activates the Sirtuin 1/AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in the liver tissues of high fat diet-fed mice.
A: The protein expression of sterol regulatory elementbinding protein 1 (SREBP1), its lipogenesis target genes (SCD1 and FAS), and genes involved in fatty acid β-oxidation, such as proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α (PGC1α), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) and carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 α (CPT1α), was detected by western blot analysis. B: Sirtuin 1 (Sirt1), total and phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase α (AMPKα) protein expression was detected by western blot analysis. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs HFD(+) AITC(-). PGC1α: Proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α; PPARα: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α; CPT1α: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 α; SREBP1: Sterol regulatory elementbinding protein 1; SCD1: Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase 1; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; Sirt1: Sirtuin 1; AMPKα: AMP-activated protein kinase α; p-AMPKα: Phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase α; HFD: High fat diet; AITC: Allyl isothiocyanate.
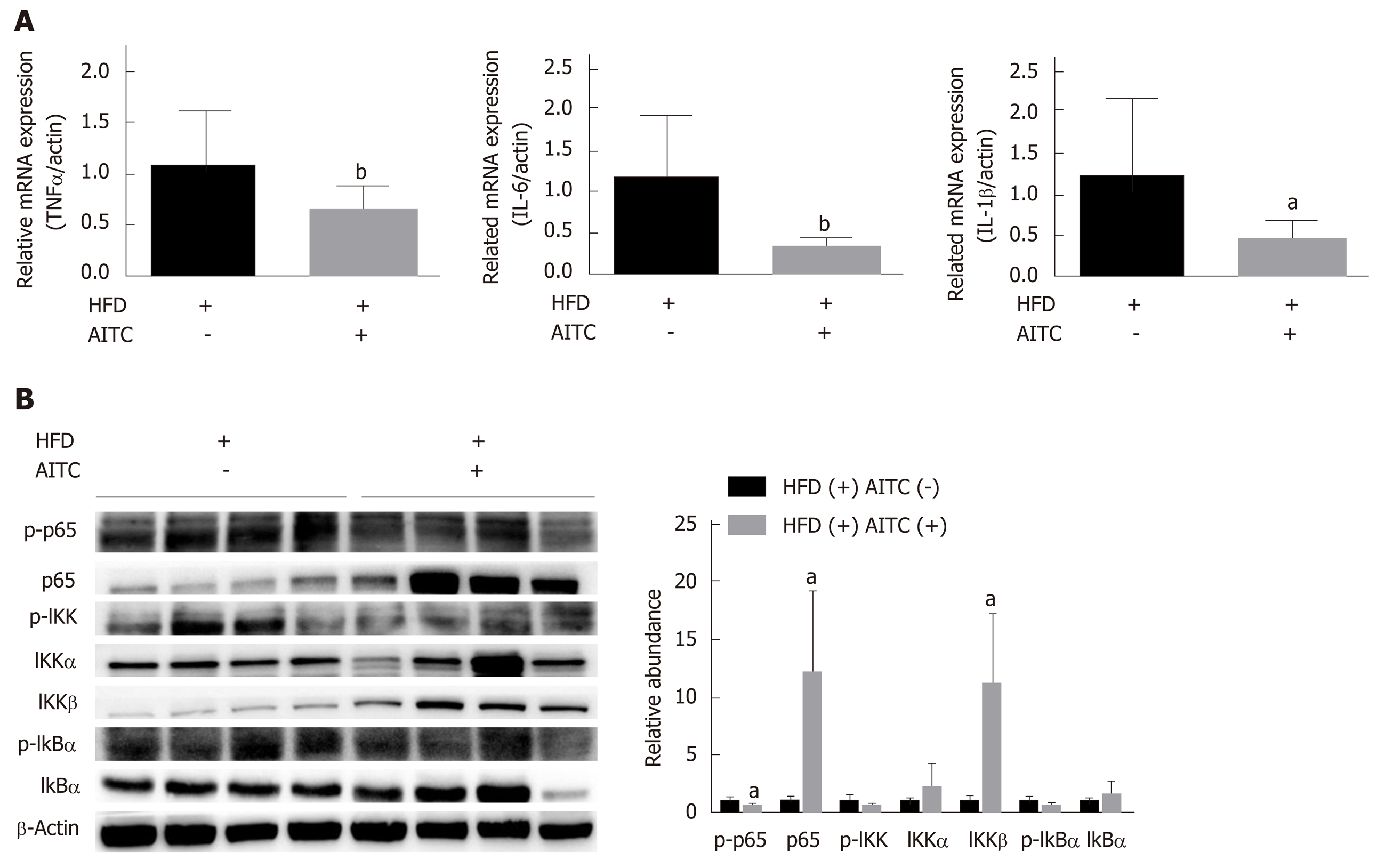
Figure 3 Allyl isothiocyanate attenuates hepatic inflammation and inhibits the IκB kinase /nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway in the liver tissues of high fat diet-fed mice.
A: The mRNA levels of proinflammatory cytokines in the liver of high fat diet (HFD)-fed control (n = 9) and HFD-fed allyl isothiocyanate (AITC)-treated mice (n = 10) were measured by quantitative real-time PCR. B: The protein expression of phosphorylated p65, p65, phosphorylated IκB kinase (IKK), IKKα, IKKβ, total and phosphorylated inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B α (IκB α) in the liver was detected by western blot analysis. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs HFD(+) AITC(-). TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor α; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; HFD: High fat diet; AITC: Allyl isothiocyanate; p-p65: Phosphorylated p65; IKK: IκB kinase; IκBα: Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B α.
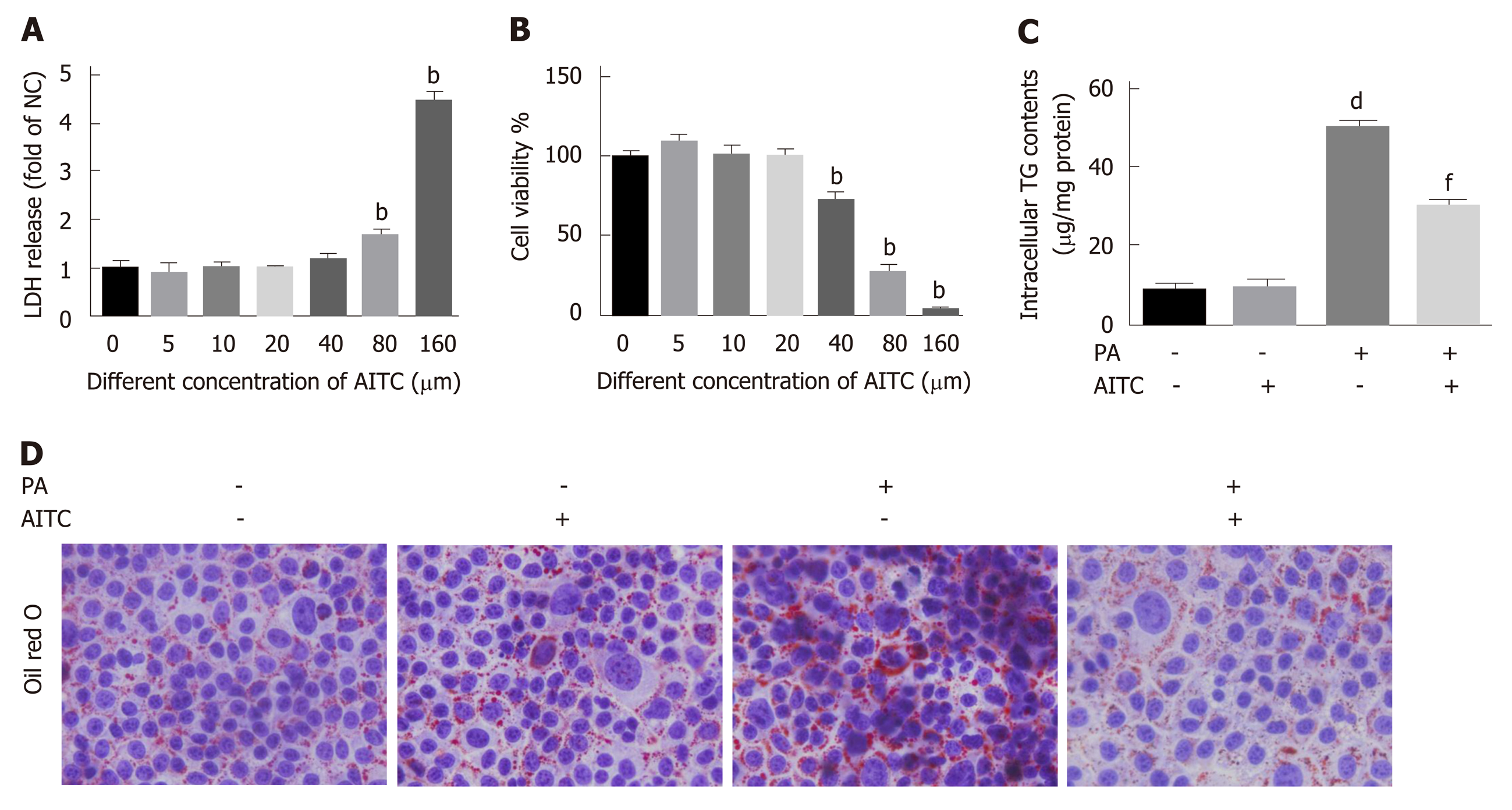
Figure 4 Allyl isothiocyanate alleviates palmitate acid-induced lipid accumulation in vitro.
Palmitate acid (200 μmo/L)-stimulated AML-12 cells were treated with allyl isothiocyanate (20 μmo/L) or dimethyl sulfoxide (vehicle) for 24 h. A: Cytotoxicity was measured by the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release method in AML-12 cells (n = 3/group). B: Cell viability was measured using the cholecystokinin-8 (CCK-8) assay in AML-12 cells (n = 3/group). C: Intracellular triglyceride (TG) content in AML-12 cells (n = 3/group). And D: Representative image of oil red O staining of AML-12 cells in different groups. Scale bar in panel represents 100 μm. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. bP < 0.01 vs 0 μmol/L AITC, dP < 0.01 vs PA(-) AITC(-), fP < 0.01 vs PA(+) AITC(-). LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase; CCK-8: Cholecystokinin-8; TG: Triglyceride; NC: Negative control; PA: Palmitate acid: AITC: Allyl isothiocyanate.
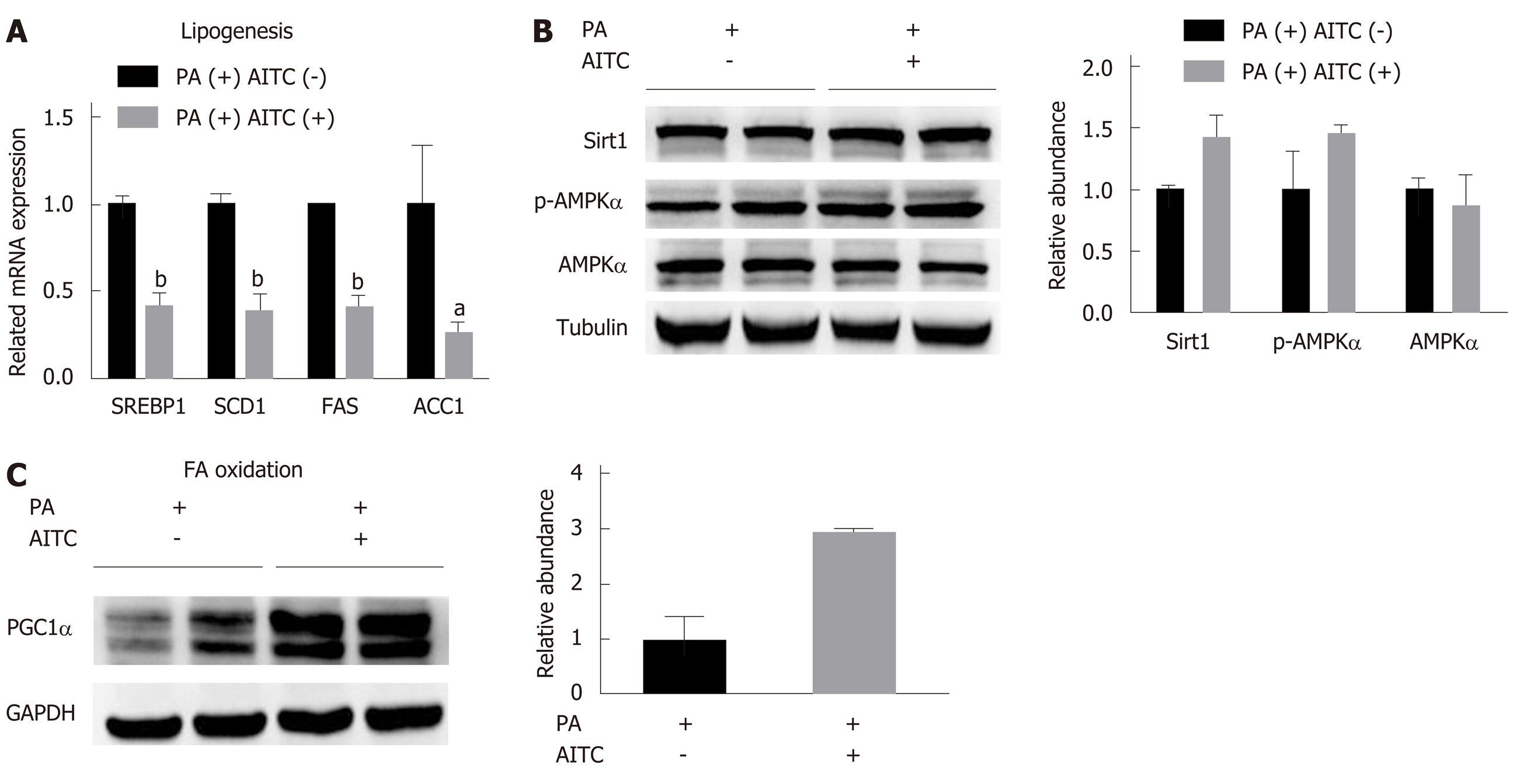
Figure 5 Allyl isothiocyanate downregulates the mRNA levels of genes involved in lipogenesis, upregulates the mRNA levels of genes involved in fatty acid β-oxidation and activates the Sirtuin 1/AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in vitro.
A: Palmitate acid (PA) (200 μmol/L)-stimulated AML-12 cells were treated with allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) (20 μmol/L) or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (vehicle) for 6 h (n = 3/group). The mRNA levels of sterol regulatory elementbinding protein 1 (SREBP1) and its lipogenesis target genes, including stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase 1 (SCD1), fatty acid synthase (FAS) and acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC1), were determined. B: PA (200 μmol/L)-stimulated AML-12 cells were treated with AITC (20 μmol/L) or DMSO (vehicle) for 24 h. The protein expression of Sirtuin 1 (Sirt1), total and phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase α (AMPKα) was detected by western blot analysis. C: PA (200 μmol/L)-stimulated AML-12 cells were treated with AITC (20 μmol/L) or DMSO (vehicle) for 24 h. The protein level of proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator1α (PGC1α), which is involved in fatty acid β-oxidation, was detected by western blot analysis. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs PA(+) AITC(-). PA: Palmitate acid; AITC: Allyl isothiocyanate; PGC1α: Proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α; SREBP1: Sterol regulatory elementbinding protein 1; SCD1: Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase 1; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; ACC1: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1; Sirt1: Sirtuin 1; AMPKα: AMP-activated protein kinase α; p-AMPKα: Phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase α.
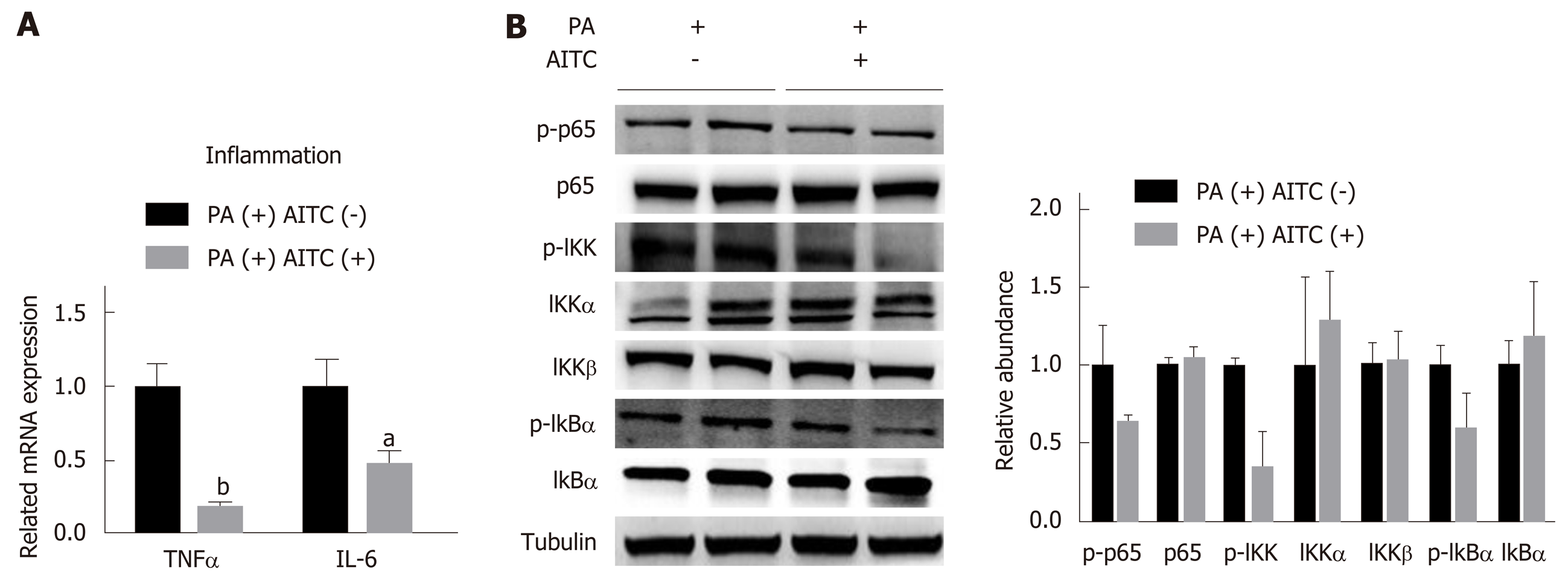
Figure 6 Allyl isothiocyanate downregulates the mRNA levels of proinflammatory markers and inhibits the IκB kinase /nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway in vitro.
A: Palmitate acid (PA) (200 μmol/L)-stimulated AML-12 cells were treated with allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) (20 μmol/L) or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (vehicle) for 6 h (n = 3/group). The mRNA levels of proinflammatory cytokines were measured by quantitative real-time PCR. (B) PA (200 μmol/L)-stimulated AML-12 cells were treated with AITC (20 μmol/L) or DMSO (vehicle) for 24 h. The protein expression of phosphorylated p65, p65, phosphorylated IκB kinase (IKK), IKKα, IKKβ, total and phosphorylated inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B α (IκB α) was detected by western blot analysis. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs PA(+) AITC(-). TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor α; IL-6: Interleukin-6; PA: Palmitate acid; AITC: Allyl isothiocyanate; p-p65: Phosphorylated p65; IKK: IκB kinase; IκBα: Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B α.
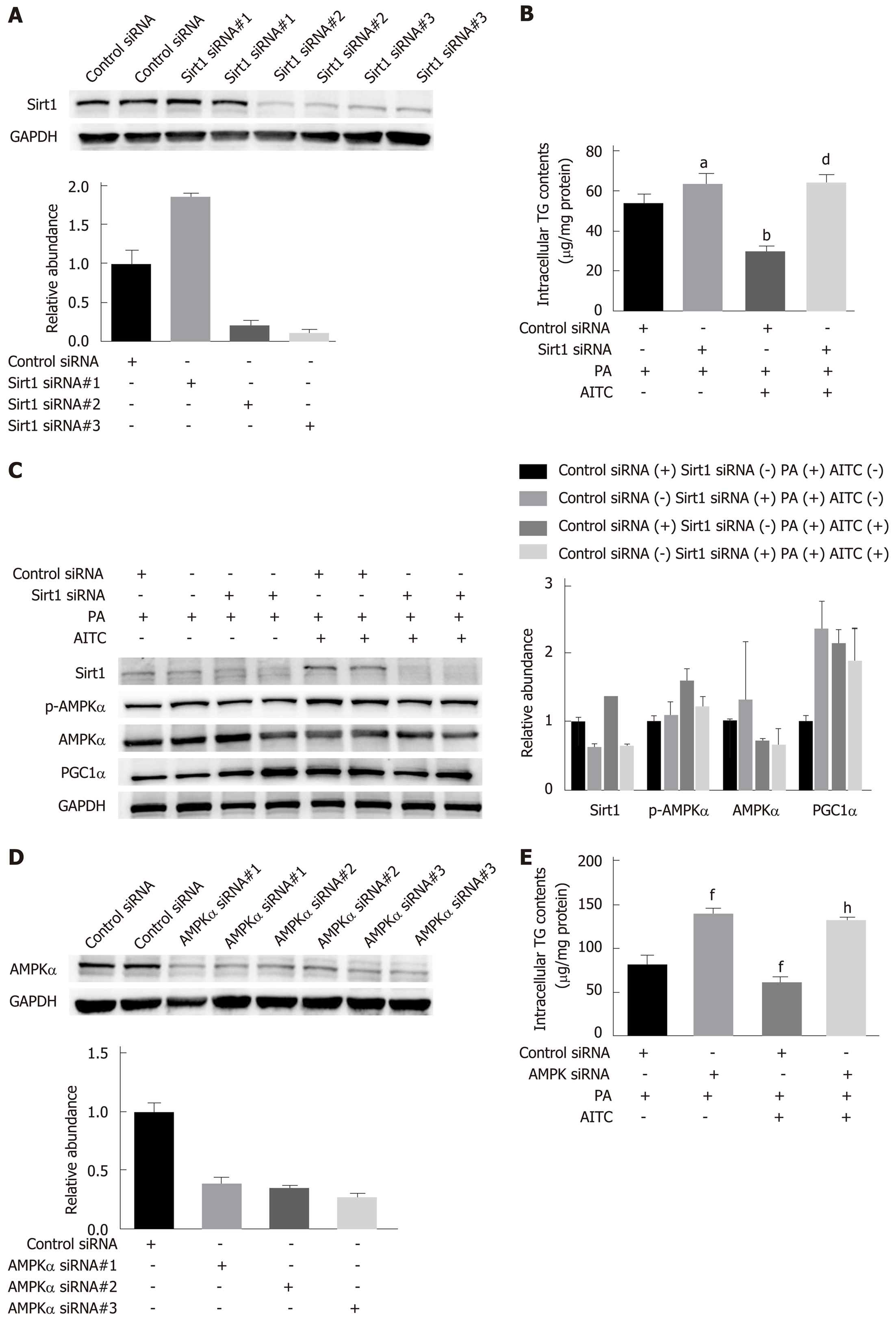
Figure 7 Allyl isothiocyanate ameliorates lipid accumulation by activating the Sirt1/AMPKα signaling pathway.
After transfection with Sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) small interfering RNA (siRNA), AMP-activated protein kinase α (AMPKα) siRNA or the corresponding scrambled control for 48 h, AML-12 cells were incubated in normal medium or medium containing palmitate acid (PA) with or without allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) for 24 h. A: Three different Sirt1 siRNA sequences were used, and Sirt1 protein levels were examined by western blot analysis. In the following experiments, we selected Sirt1 siRNA #3. B: Intracellular triglyceride (TG) content in AML-12 cells (n = 4/group). C: Sirt1, phosphorylated AMPKα and proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator1α (PGC1α) protein expression was detected by western blot analysis. D: Three different AMPKα siRNA sequences were used, and AMPKα protein levels were examined by western blot analysis. In the subsequent experiments, we selected AMPKα siRNA #3. (E) Intracellular TG content in AML-12 cells (n = 4/group). Data are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs Control siRNA + PA, dP < 0.01 vs Control siRNA + PA + AITC, fP < 0.01 vs Control siRNA + PA, hP < 0.01 vs Control siRNA + PA + AITC. PA: Palmitate acid; AITC: Allyl isothiocyanate; PGC1α: Proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α; Sirt1: Sirtuin 1; AMPKα: AMP-activated protein kinase α; p-AMPKα: Phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase α; TG: Triglyceride.
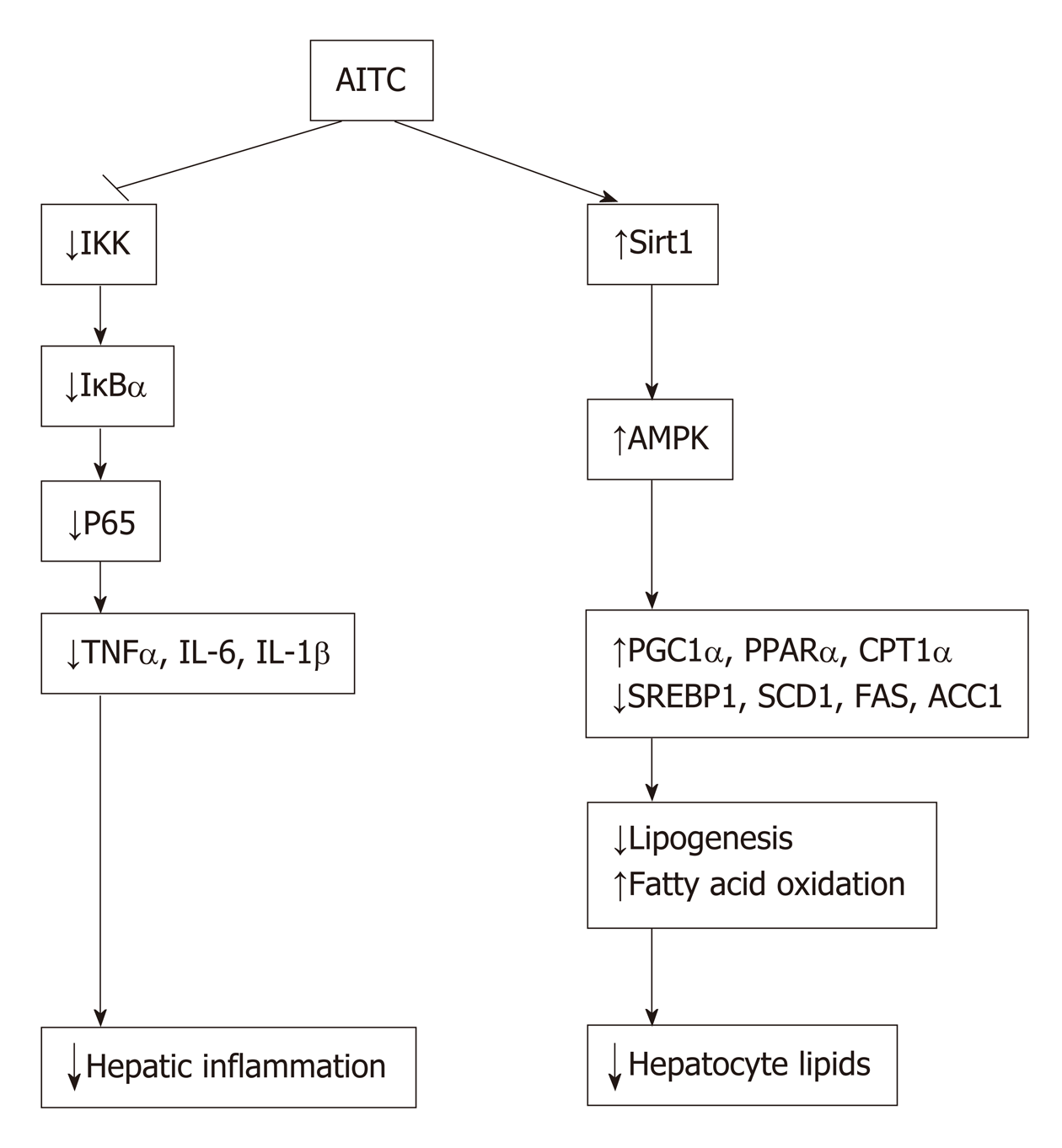
Figure 8 Model of allyl isothiocyanate action.
Schematic diagram: allyl isothiocyanate ameliorates hepatic lipid accumulation and hepatic inflammation by activating the Sirt1/AMPK signaling pathway and inhibiting the NF-κB pathway. AITC: Allyl isothiocyanate; IKK: IκB kinase; IκBα: Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B α; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor α; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; Sirt1: Sirtuin 1; AMPKα: AMP-activated protein kinase α; PGC1α: Proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α; PPARα: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α; CPT1α: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 α; SREBP1: Sterol regulatory elementbinding protein 1; SCD1: Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase 1; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; ACC1: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1.
- Citation: Li CX, Gao JG, Wan XY, Chen Y, Xu CF, Feng ZM, Zeng H, Lin YM, Ma H, Xu P, Yu CH, Li YM. Allyl isothiocyanate ameliorates lipid accumulation and inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via the Sirt1/AMPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(34): 5120-5133
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i34/5120.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i34.5120