Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2019; 25(32): 4696-4714
Published online Aug 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i32.4696
Published online Aug 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i32.4696
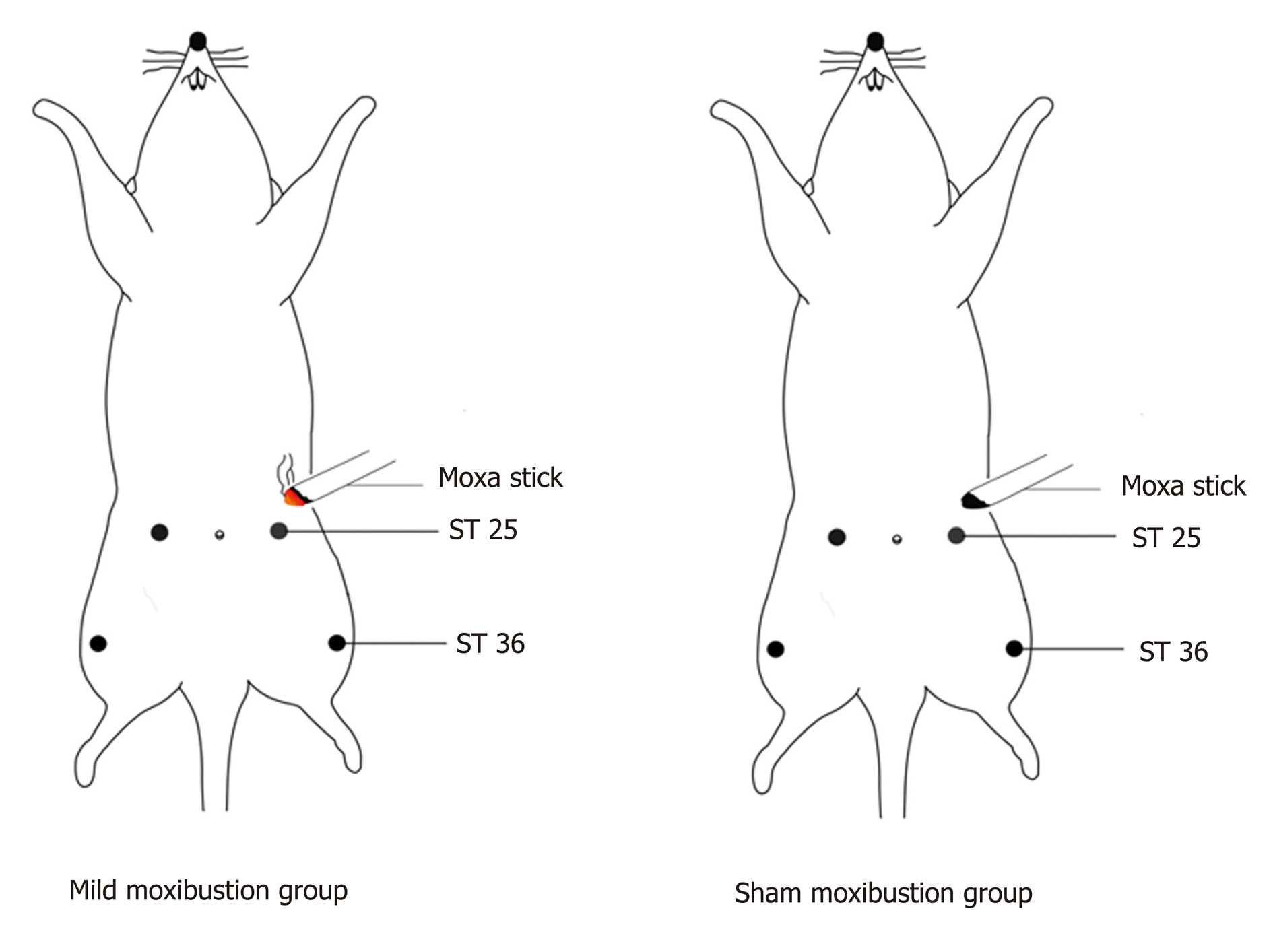
Figure 1 Diagram of moxibustion in rats.
Rats were immobilized on a fixing frame. A: A moxa stick of 5 mm in diameter was ignited and placed 2-3 cm above the bilateral Zusanli (ST26) and Tianshu (ST25) for 10 min per day with 7 d of continuous treatment in the mild moxibustion group; B: The sham moxibustion group was given the same treatment as the mild moxibustion group except that moxibustion was treated with an unlit moxa stick.
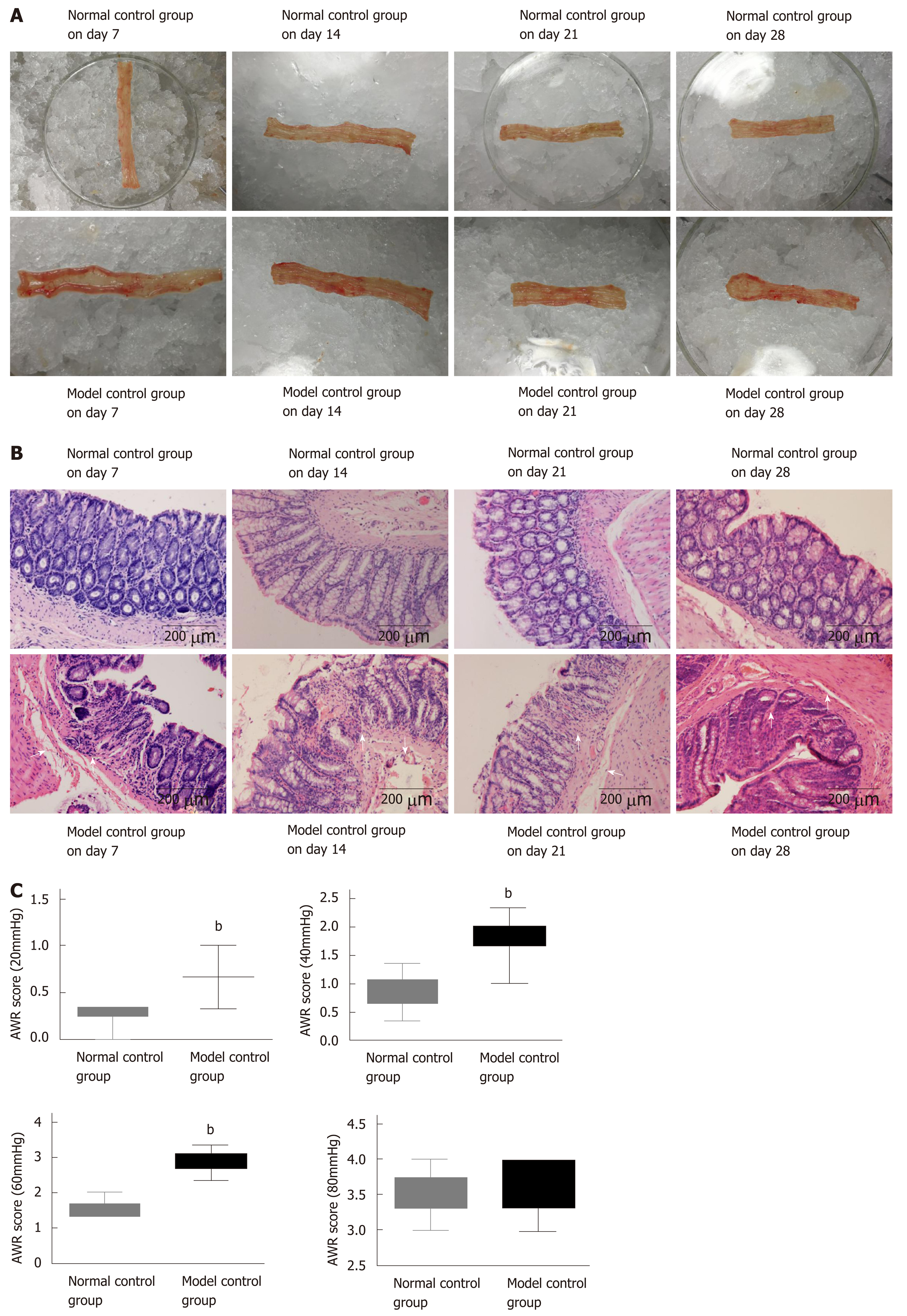
Figure 2 A rat post-infectious/post-inflammatory irritable bowel syndrome model established by 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid induction.
A: Gross structure; B: Pathology of the normal control group and model control group on days 7, 14, 21, and 28; C: Abdominal withdrawal reflex scores of the normal and model control groups under different pressure stimulations on day 28 after model generation. bP < 0.01 vs normal control group. AWR: Abdominal withdrawal reflex.
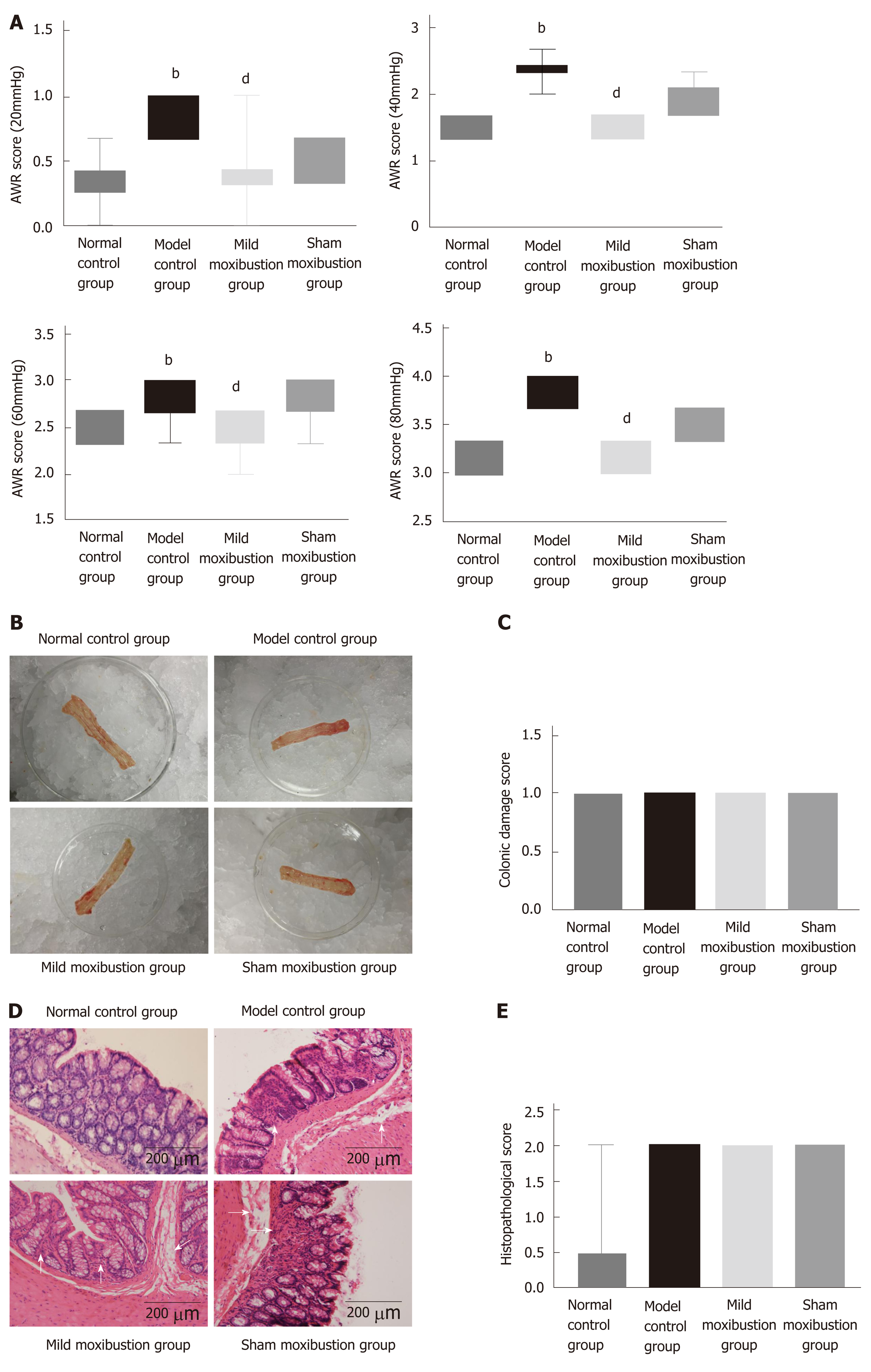
Figure 3 Effects of mild moxibustion on abdominal withdrawal reflex scores and low-grade inflammation of the colon in each group.
A: Abdominal withdrawal reflex score; B: Observed gross structure; C: Histological score; D: Observed histopathology; E: Pathological score. bP < 0.01 vs normal control group; dP < 0.01 vs model control group. AWR: Abdominal withdrawal reflex.
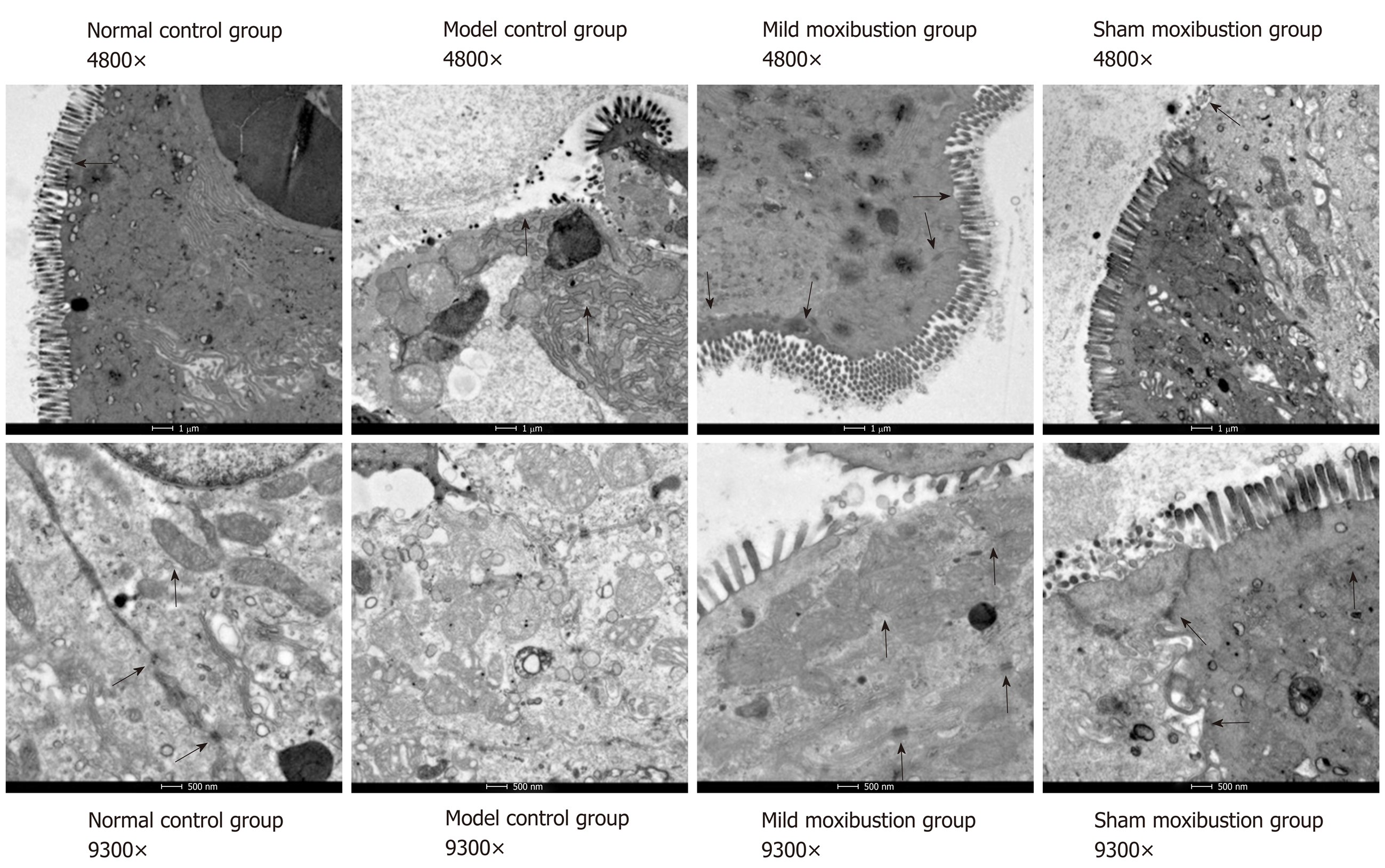
Figure 4 Effects of mild moxibustion on colonic ultrastructure of rats with post-infectious/post-inflammatory irritable bowel syndrome.
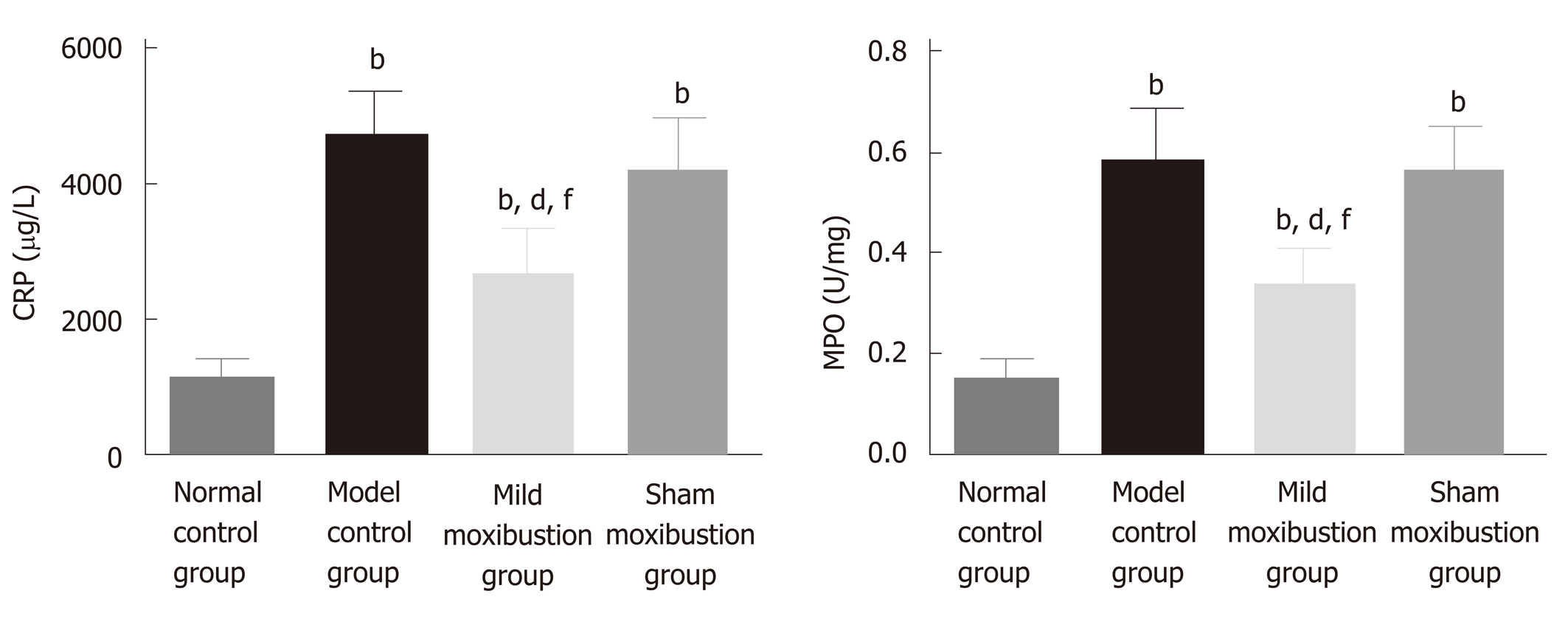
Figure 5 Effects of mild moxibustion on serum C-reactive protein levels and colonic myeloperoxidase activities in post-infectious/post-inflammatory irritable bowel syndrome rats in each group.
A: Serum C-reactive protein levels; B: Myeloperoxidase activities. bP < 0.01 vs normal control group; dP < 0.01 vs model control group; fP < 0.01 vs sham moxibustion group. CRP: C-reactive protein; MPO: Myeloperoxidase.
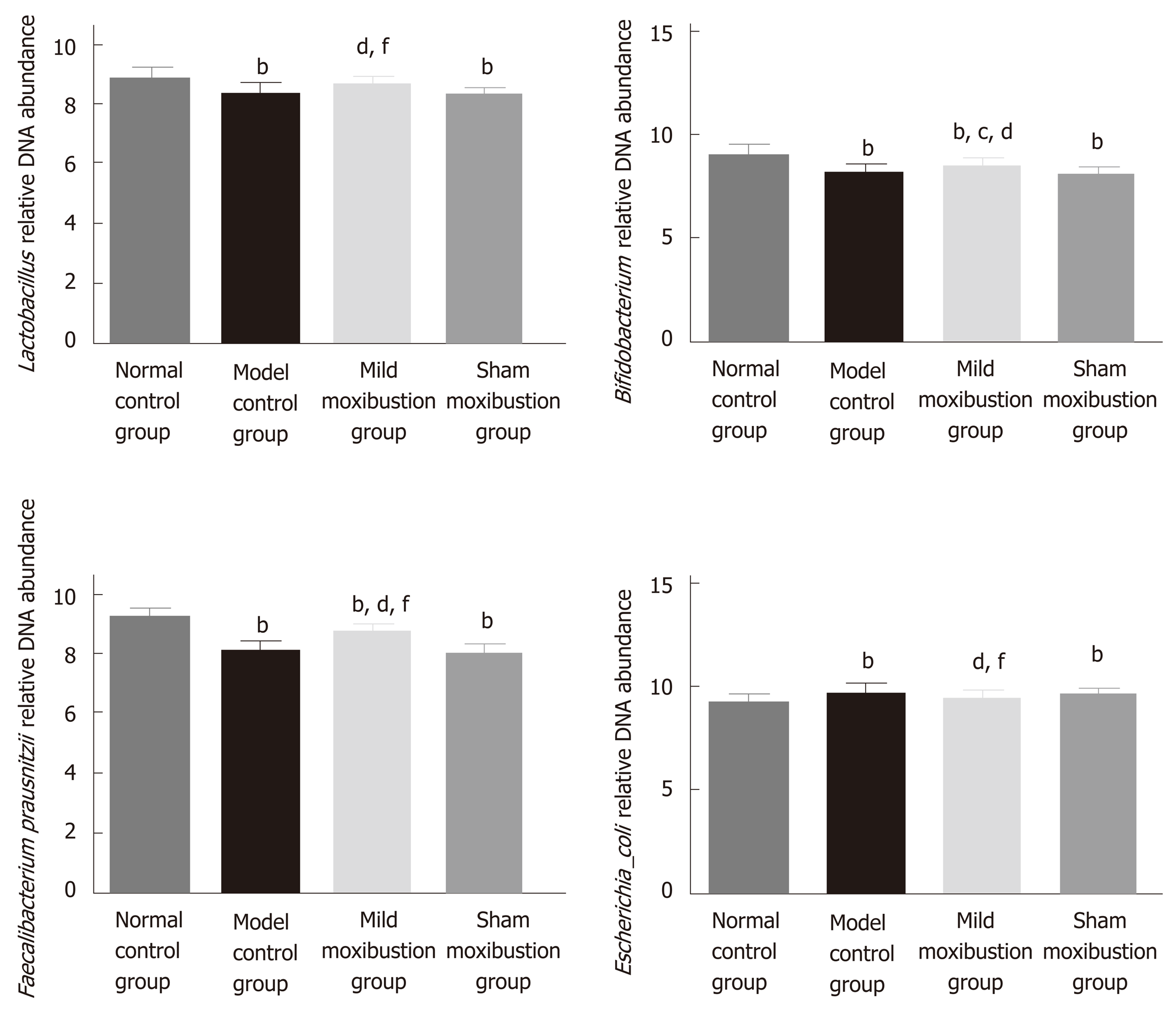
Figure 6 Effects of mild moxibustion on the relative DNA abundances of targeted bacteria in feces of post-infectious/post-inflammatory irritable bowel syndrome rats in each group.
A: Relative DNA abundance of Lactobacillus; B: Relative DNA abundance of Bifidobacterium; C: Relative DNA abundance of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii; D: Relative DNA abundance of Escherichia coli. bP < 0.01 vs normal control group; cP < 0.05 and dP < 0.01 vs model control group; fP < 0.01 vs sham moxibustion group.
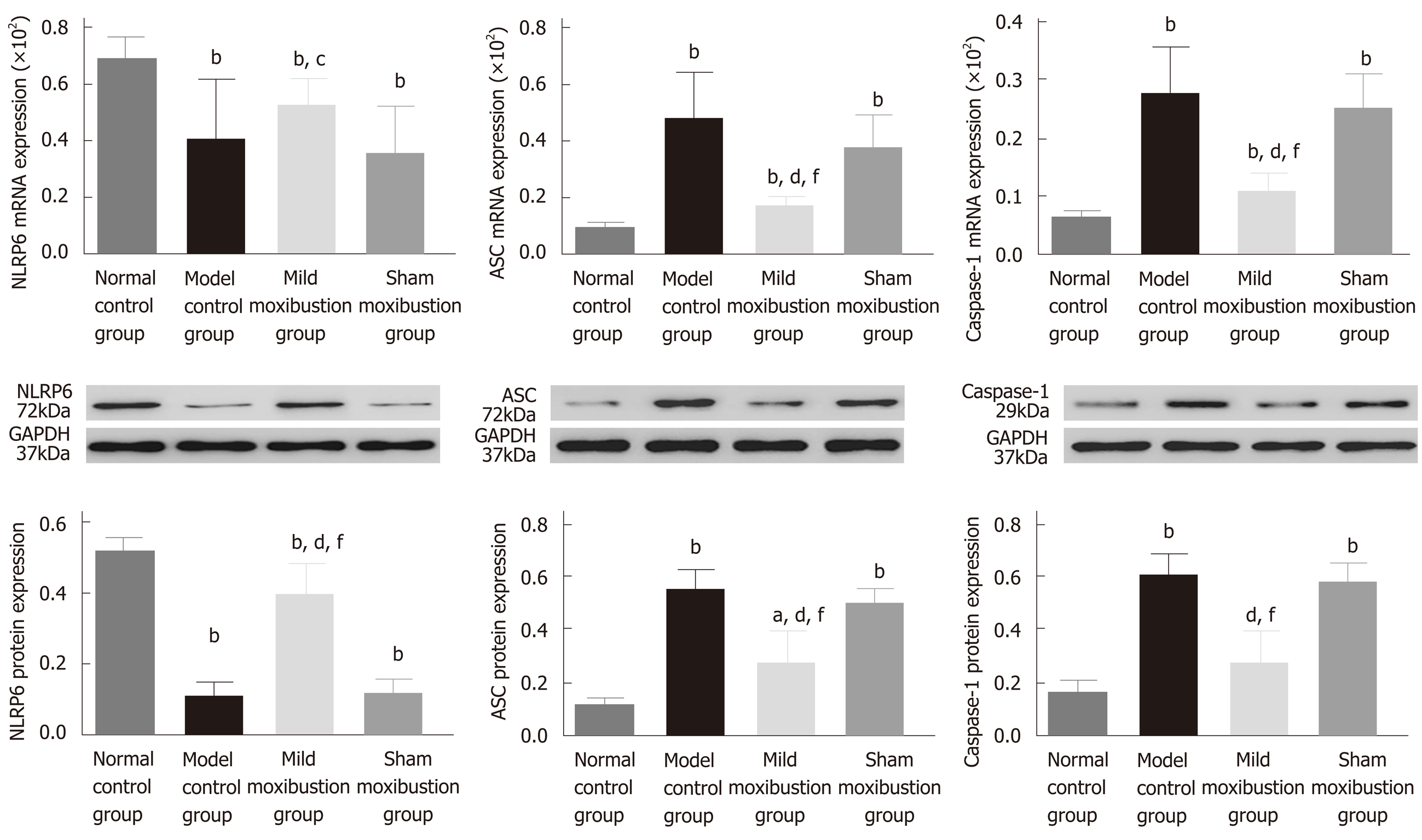
Figure 7 Effects of mild moxibustion on the mRNA and protein expression of NLRP6, ASC, and Caspase-1 in the colon of post-infectious/post-inflammatory irritable bowel syndrome rats in each group.
A: The mRNA expression levels of NLRP6, ASC, and Caspase-1; B: The protein expression of NLRP6, ASC, and Caspase-1. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs normal control group; dP < 0.01 vs model control group; eP < 0.05 and fP < 0.01 vs sham moxibustion group.
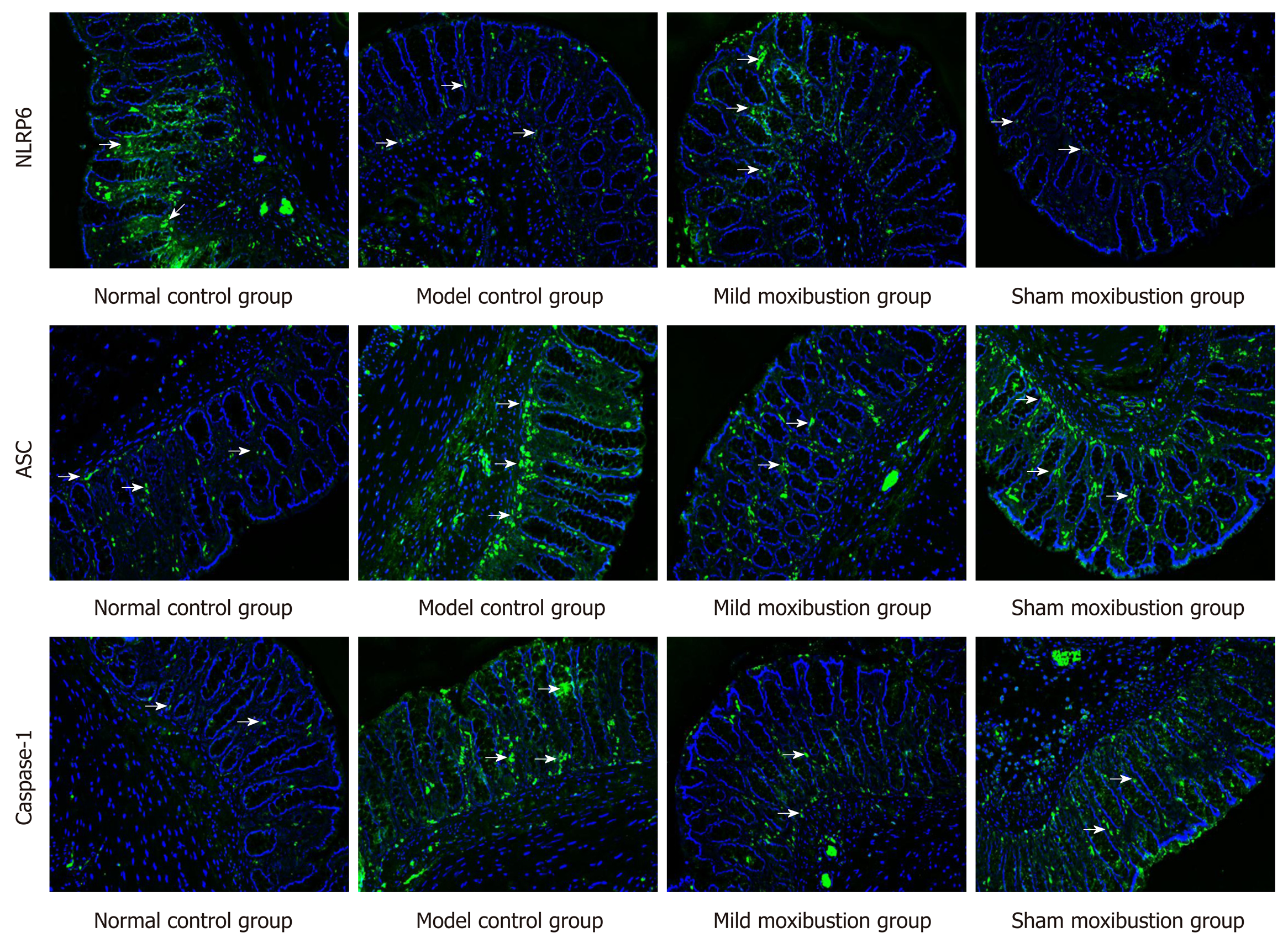
Figure 8 Effects of mild moxibustion on the protein expression of NLRP6, ASC, and Caspase-1 in the colon of post-infectious/post-inflammatory irritable bowel syndrome rats.
NLRP6, ASC, and Caspase-1 are localized in the cytoplasm of mucosal cells in the mucosal layer of rats in each group.
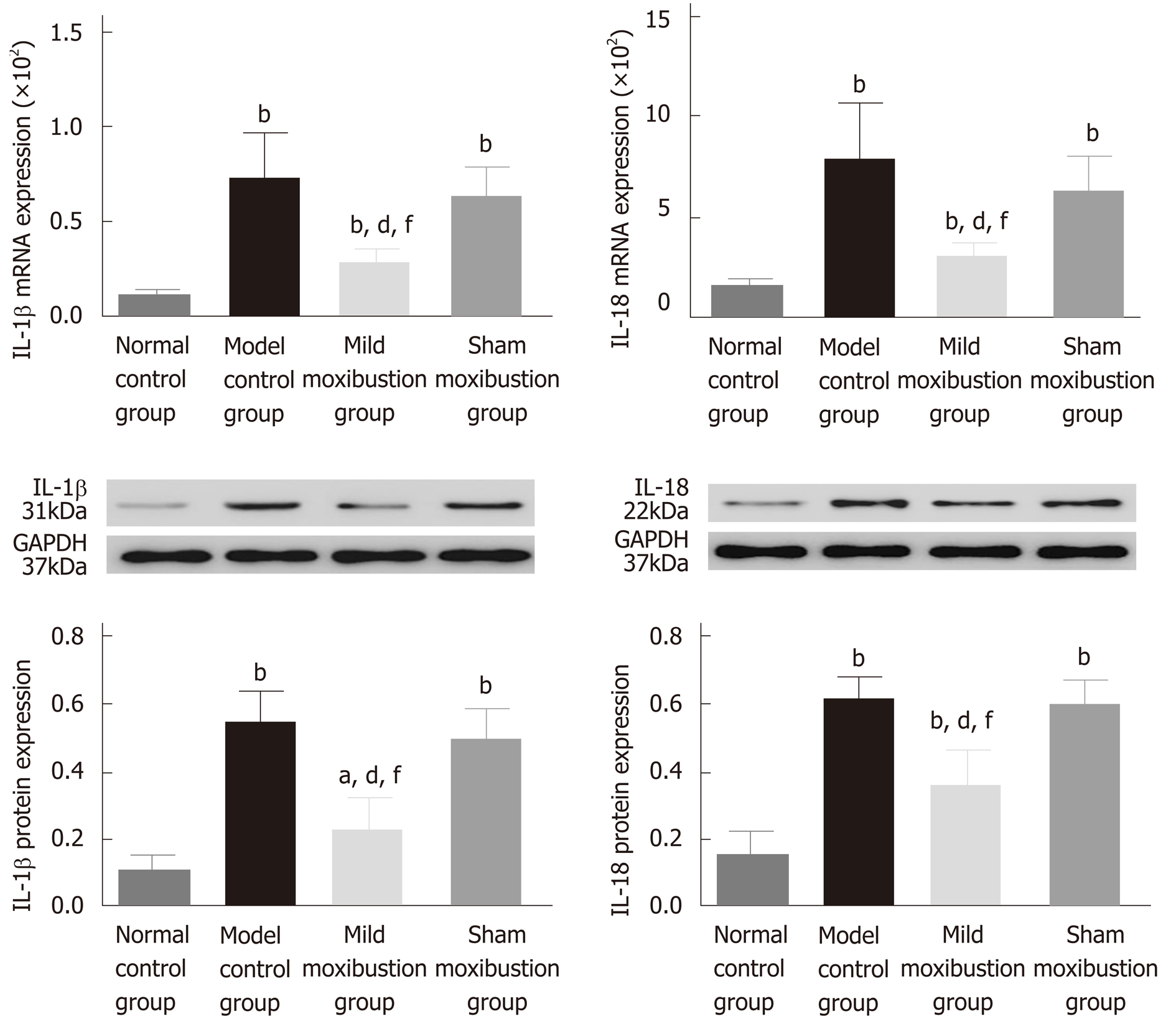
Figure 9 Effects of mild moxibustion on the mRNA and protein expression of IL-1β and IL-18 in the colon of post-infectious/post-inflammatory irritable bowel syndrome rats in each group.
A: The mRNA expression levels of IL-1β and IL-18; B: Protein expression levels of IL-1β and IL-18. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs normal control group; dP < 0.01 vs model control group; fP < 0.01 vs sham moxibustion group.
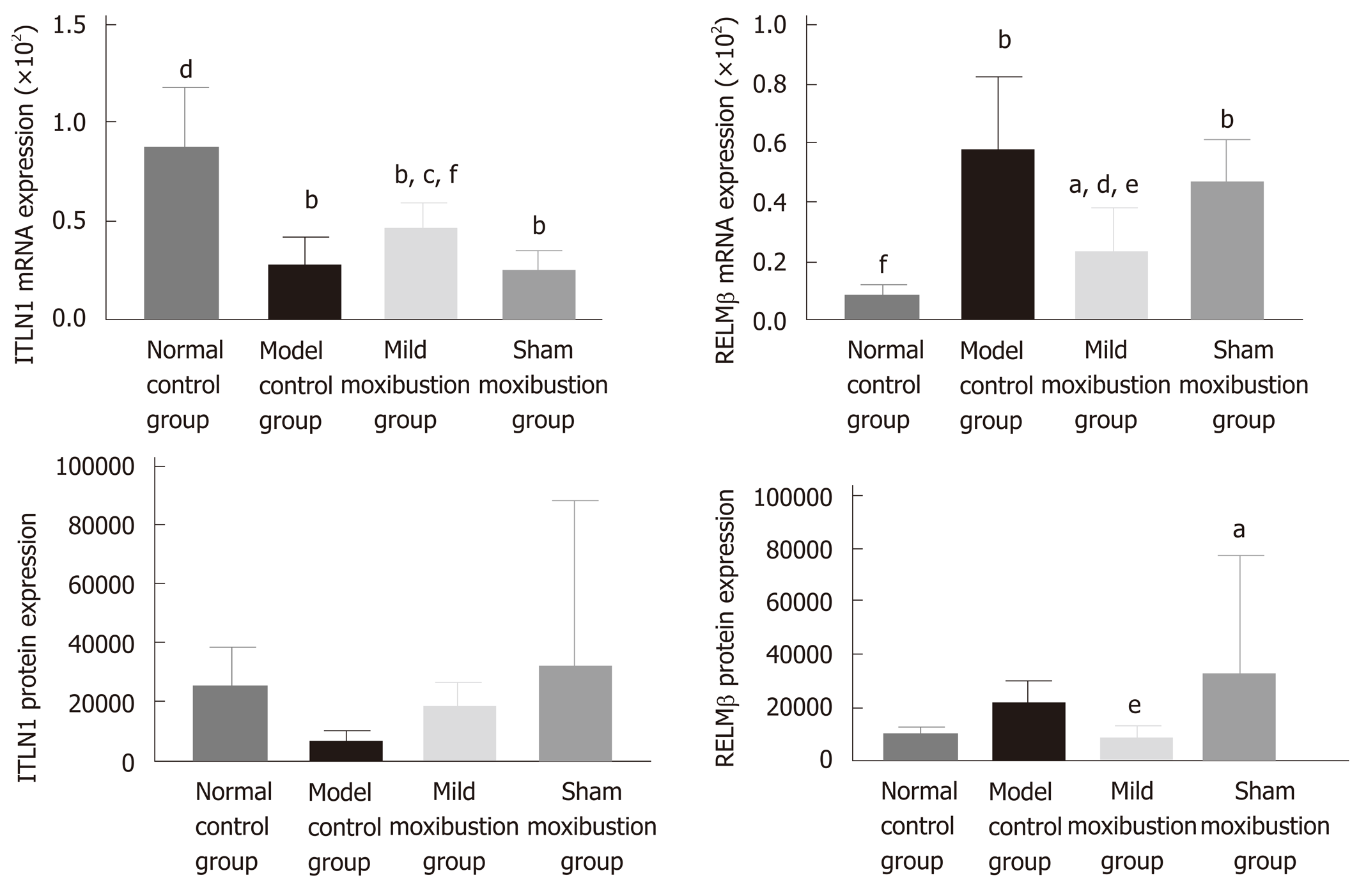
Figure 10 Effects of mild moxibustion on the mRNA and protein expression of ITLN1 and RELMβ in the colon of post-infectious/post-inflammatory irritable bowel syndrome rats in each group.
A: The mRNA expression levels of ITLN1 and RELMβ; B: Protein expression levels of ITLN1 and RELMβ. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs normal control group; dP < 0.01 vs model control group; eP < 0.05 and fP < 0.01 vs sham moxibustion group.
- Citation: Bao CH, Wang CY, Li GN, Yan YL, Wang D, Jin XM, Wu LY, Liu HR, Wang XM, Shi Z, Wu HG. Effect of mild moxibustion on intestinal microbiota and NLRP6 inflammasome signaling in rats with post-inflammatory irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(32): 4696-4714
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i32/4696.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i32.4696