Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2019; 25(27): 3527-3537
Published online Jul 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i27.3527
Published online Jul 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i27.3527
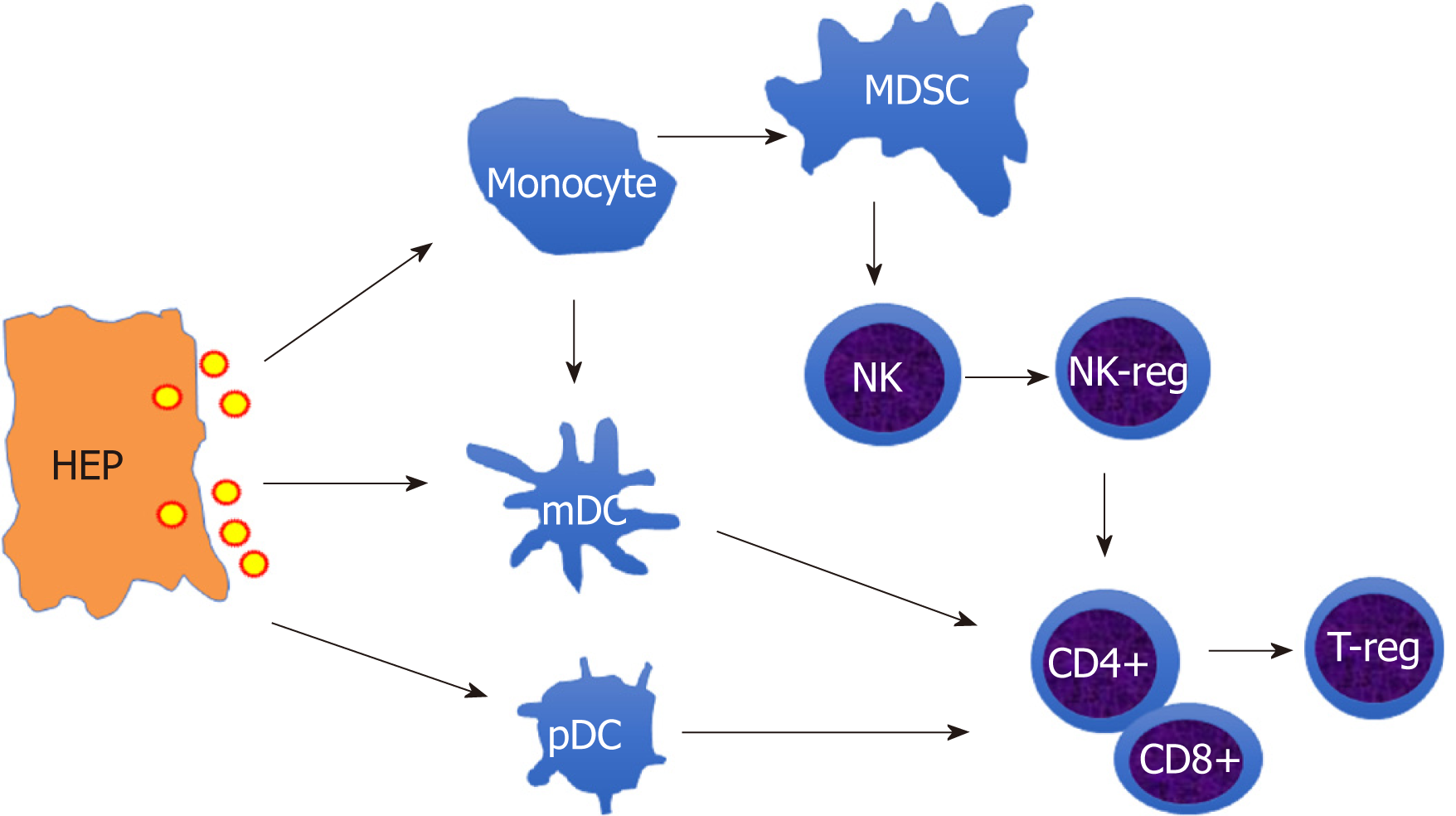
Figure 1 The schematic outline of hepatitis B virus-induced immune suppression network.
The infected hepatocytes release hepatitis B virus virion to induce suppressive monocytes (Myeloid derived suppressive cells) and dendritic cells (tolerogenic dendritic cells), which initiate directly inducible T-reg to inhibit T cell activation or mediate indirectly by educating natural killer cell (NK) cells differentiation into NK-reg. HEP: Hepatocytes; MDSC: Myeloid derived suppressive cells; DC: Dendritic cells NK: Natural killer cell; T-reg: Regulatory T cell.
- Citation: Li TY, Yang Y, Zhou G, Tu ZK. Immune suppression in chronic hepatitis B infection associated liver disease: A review. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(27): 3527-3537
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i27/3527.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i27.3527