Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2019; 25(25): 3151-3167
Published online Jul 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i25.3151
Published online Jul 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i25.3151
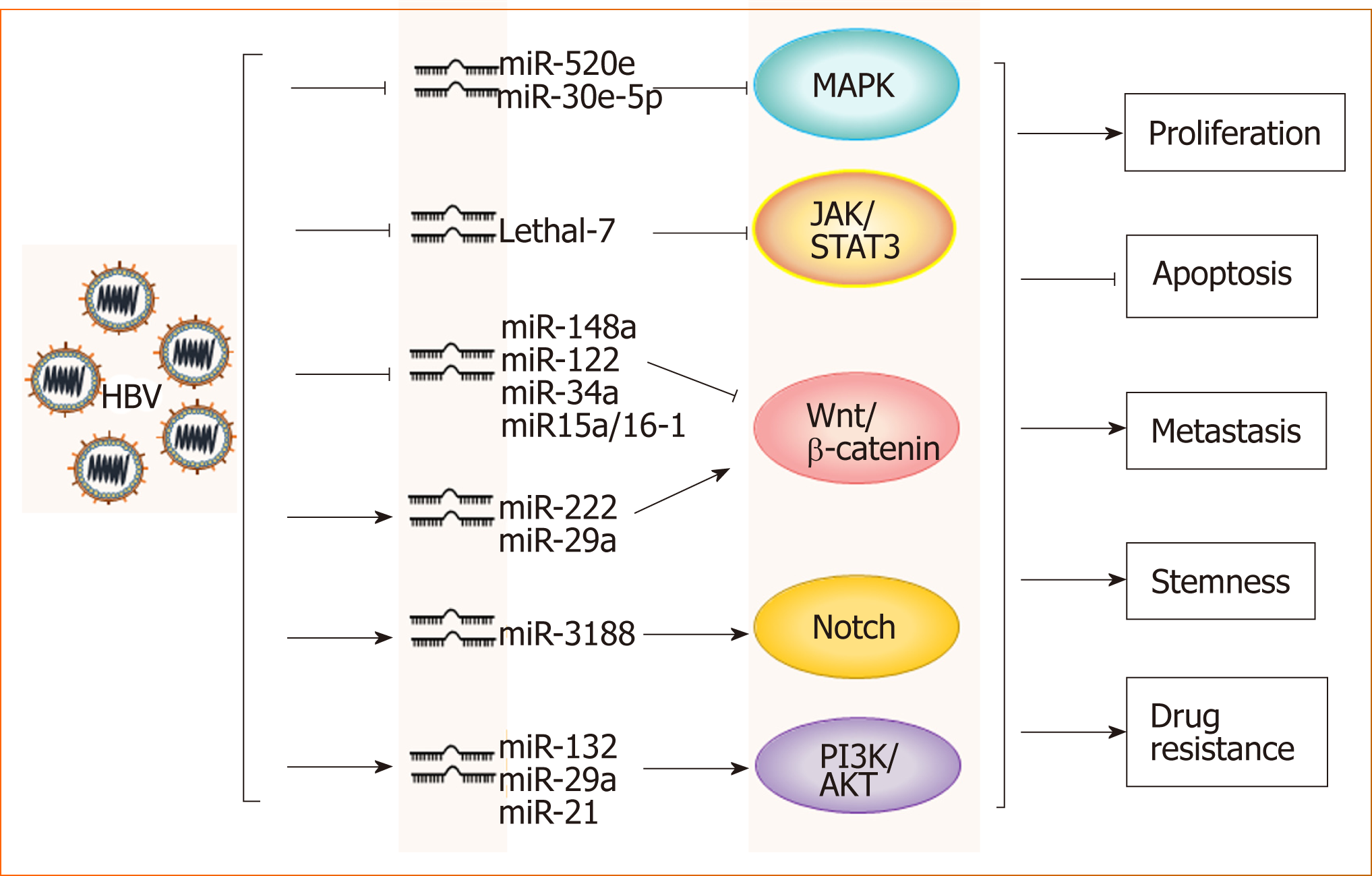
Figure 1 Hepatitis B virus promotes hepatocellular carcinoma by intervening various signal pathways through different microRNAs.
Lines ending with arrows or bars indicate promotion or inhibitory effects, respectively. HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
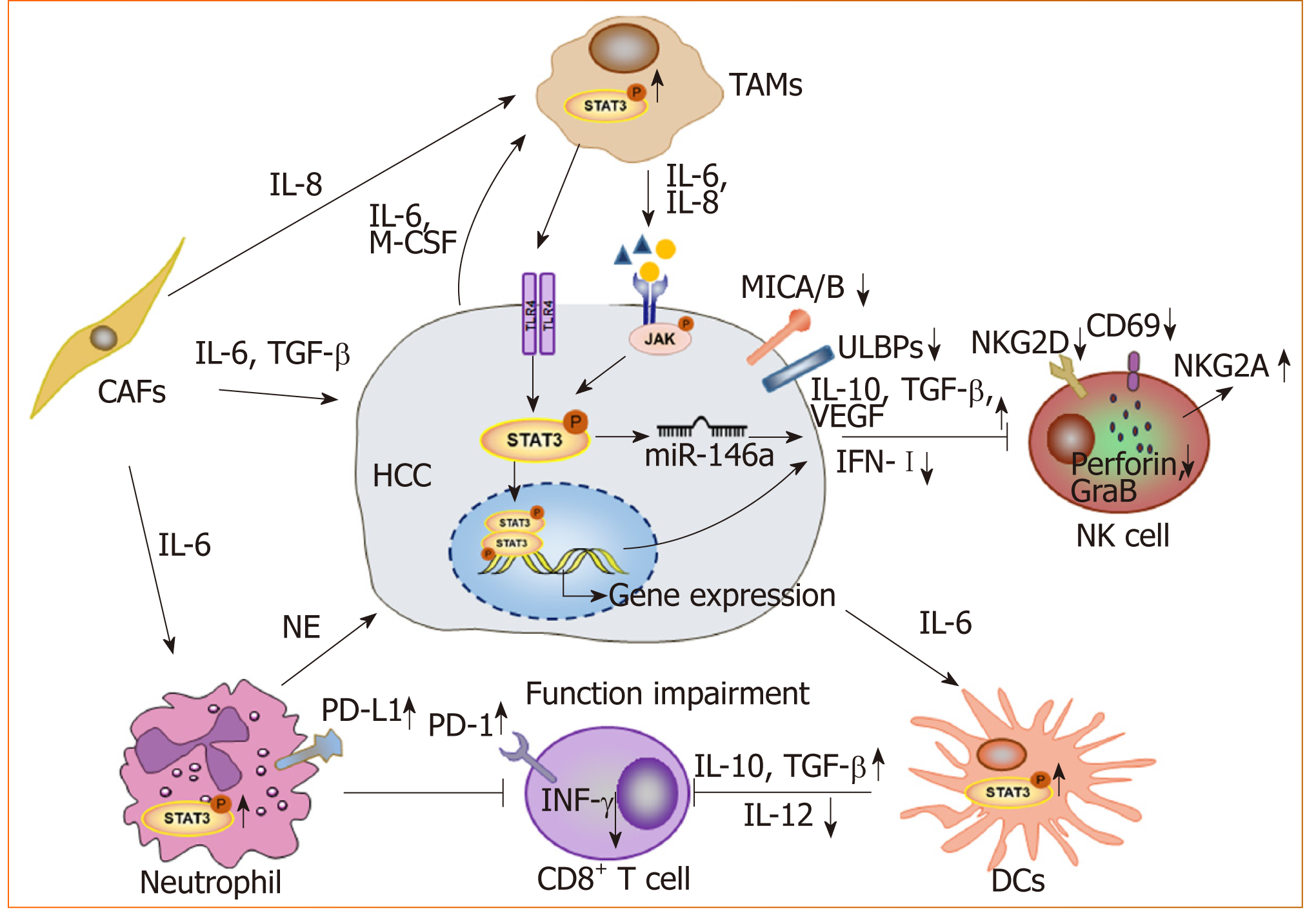
Figure 2 STAT3 signaling contributes to form an immunosuppressive microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Long lines ending with arrows or bars indicate activating or inhibitory effects, respectively. Short arrows pointing up or down indicate up-regulated or down-regulated, respectively. TAMs: Tumor-associated macrophages; CAFs: Cancer-associated fibroblasts; NK cell: Natural killer cell; DCs: Dendritic cells; NE: Neutrophil elastase; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
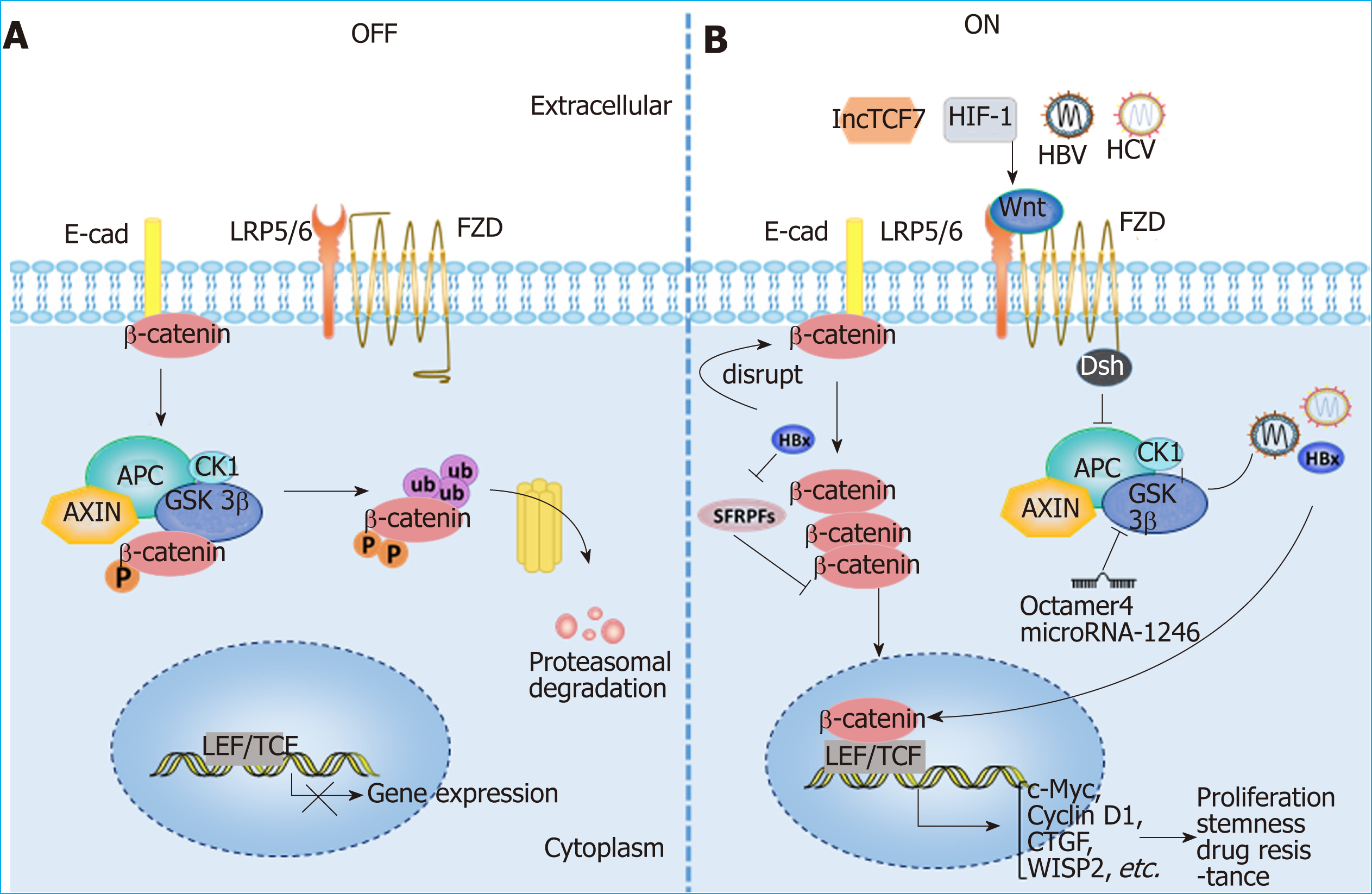
Figure 3 Aberrant activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Wnt signaling is inactive in the absence of Wnt ligands (OFF); B: Wnt signaling can be activated by various molecules in HCC (ON). HBV and HCV can active Wnt/β-catenin signaling by activating TCF or inhibiting GSK3β; HBx can silence SFRPs to activate Wnt signaling; LncTCF7 triggers Wnt7a and TCF7 expression to activate Wnt signaling. Lines ending with arrows or bars indicate activating or inhibitory effects, respectively. HIF1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; LEF: Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor; LRP: Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein; TCF: T cell factor; FZD: Frizzled; E-cad: E-cadherin; SFRPs: Secreted frizzled-related proteins; CTGF: Connective tissue growth factor; WISP2: Wnt1 inducible signaling pathway protein 2.
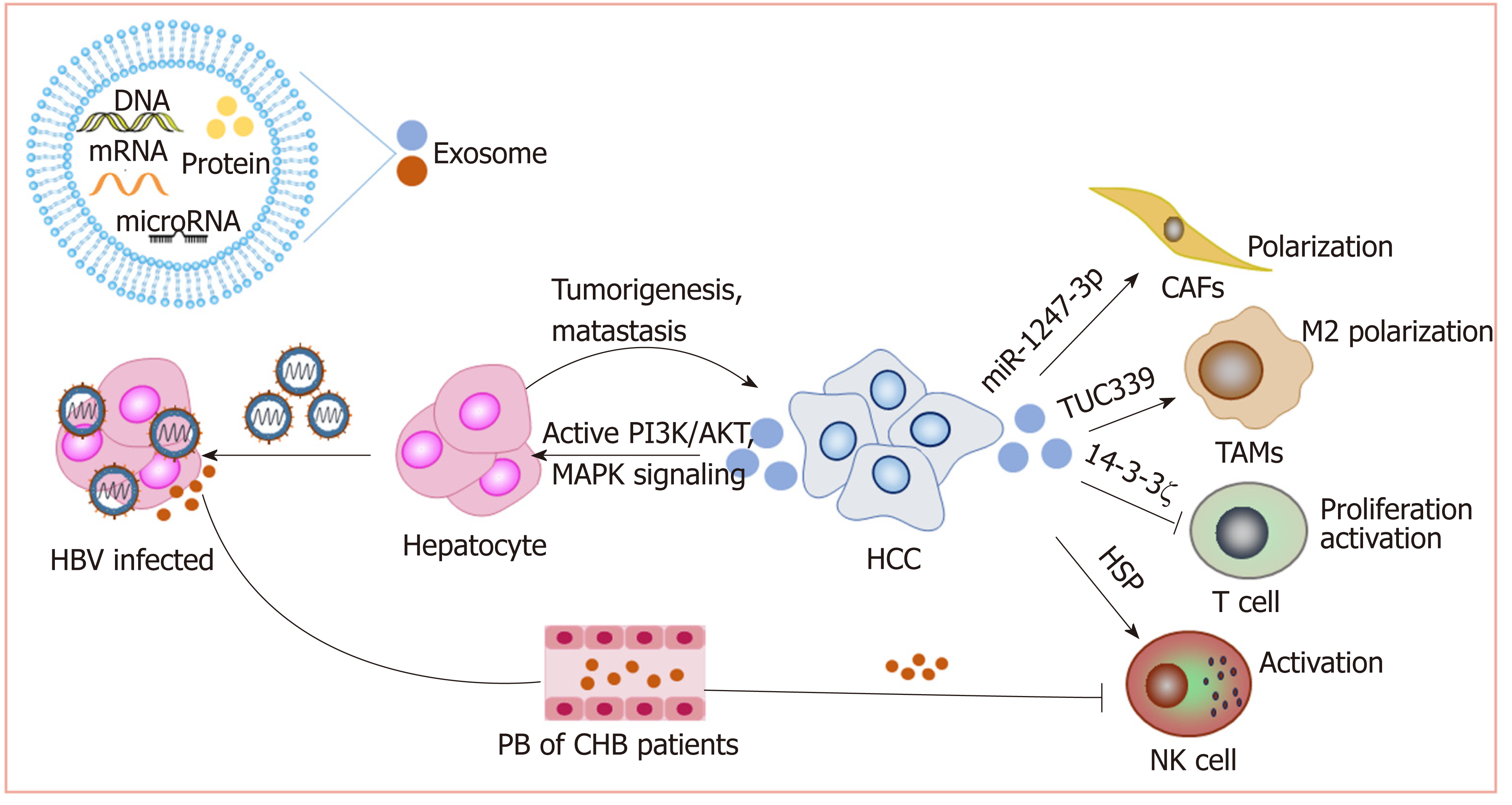
Figure 4 Exosomes play important roles in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Exosomes deliver a variety of biological molecules that have been proven to play important roles in hepatocellular carcinoma progression and immunosuppression. Lines ending with arrows or bars indicate activating or inhibitory effects, respectively. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Jiang Y, Han QJ, Zhang J. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Mechanisms of progression and immunotherapy. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(25): 3151-3167
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i25/3151.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i25.3151