Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2019; 25(17): 2029-2044
Published online May 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i17.2029
Published online May 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i17.2029
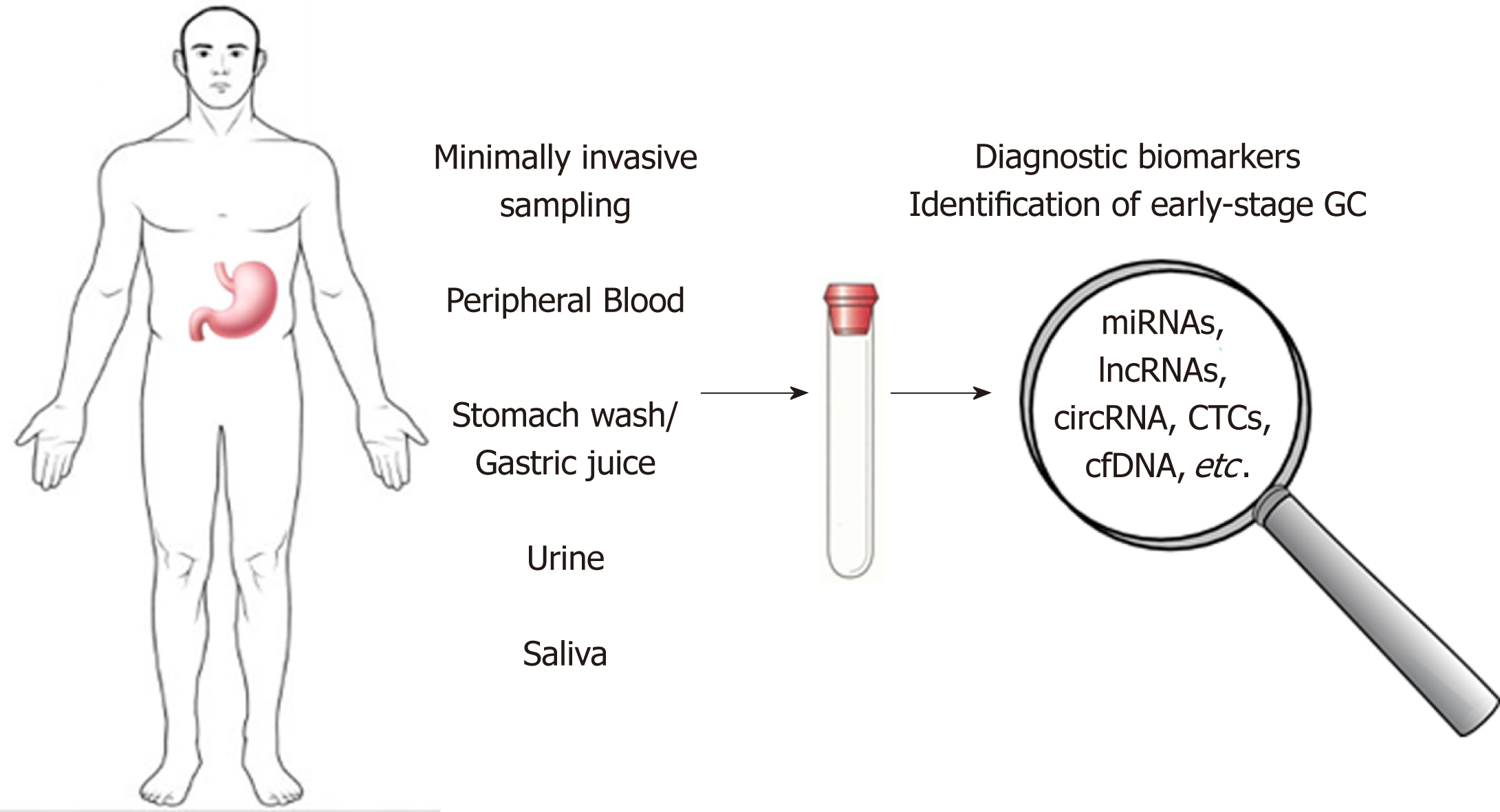
Figure 1 Possible non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers for early-stage gastric cancer.
Genetic and epigenetic alterations, microRNAs, long non-coding RNAs and circular RNA, circulating tumor cells and tumor DNA represent promising candidates for the development of new non-invasive methods in early-diagnosis of gastric cancer. GC: Gastric cancer; miRNAs: MicroRNAs; lncRNAs: Long non-coding RNAs; circRNA: circular RNA; CTCs: Circulating tumor cells; cfDNAs: Cell-free circulating DNA.
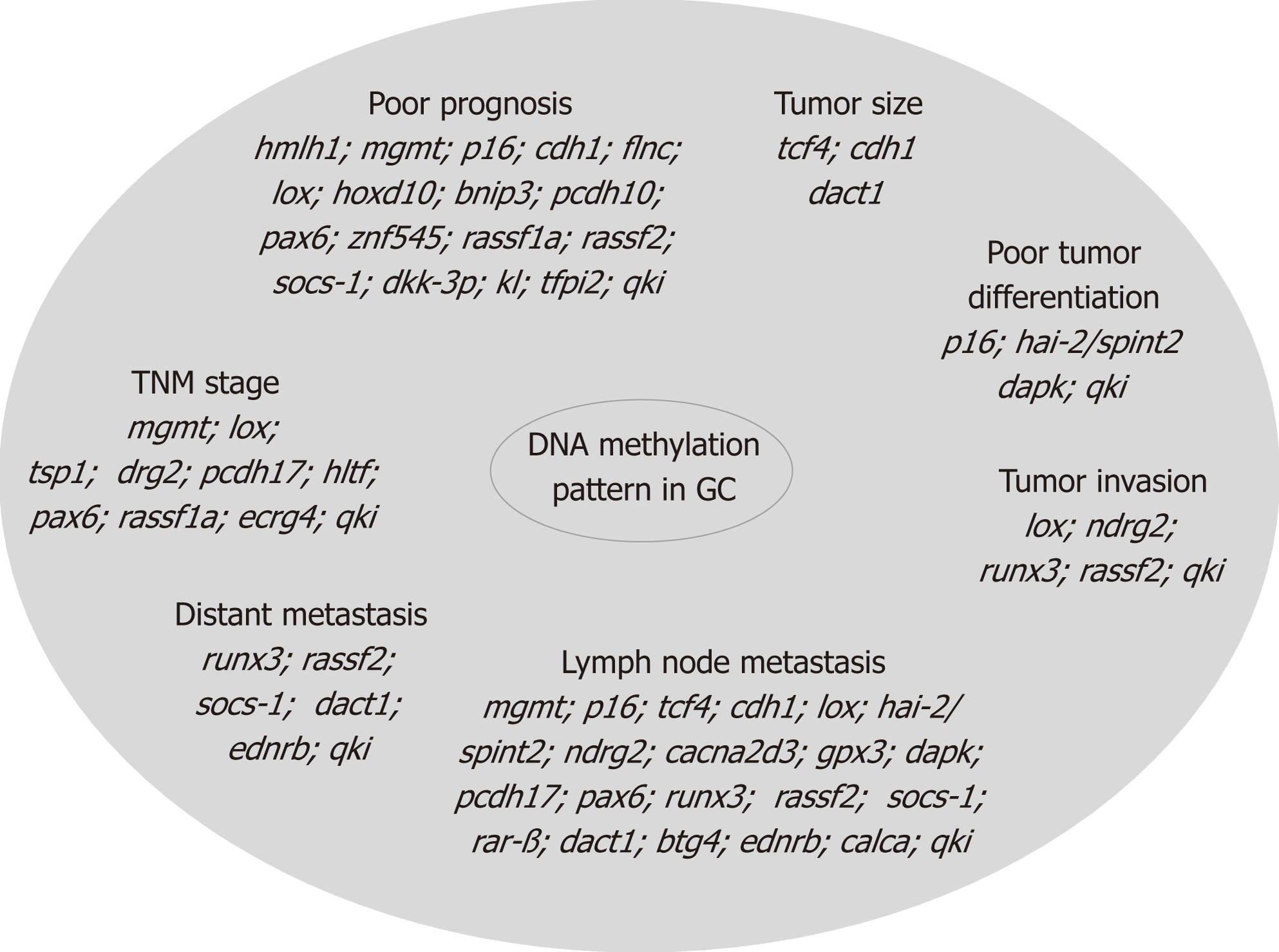
Figure 2 Methylation changes in gastric cancer.
Epigenetic alteration by methylation occurs in specific genes involved in various processes such as cell cycle regulation, DNA repair, cell growth/differentiation, transcriptional regulation, cell adhesion/invasion/migration, apoptosis, angiogenesis, as well as in multidrug resistance genes, and in genes associated with Epstein-Barr virus-type tumors or Helicobacter pylori positive tumors. These gene alterations are correlated with tumor size, localization, differentiation, invasion, lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, TNM stage, and prognosis. GC: Gastric cancer.
- Citation: Necula L, Matei L, Dragu D, Neagu AI, Mambet C, Nedeianu S, Bleotu C, Diaconu CC, Chivu-Economescu M. Recent advances in gastric cancer early diagnosis. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(17): 2029-2044
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i17/2029.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i17.2029