Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2019; 25(12): 1502-1512
Published online Mar 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i12.1502
Published online Mar 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i12.1502
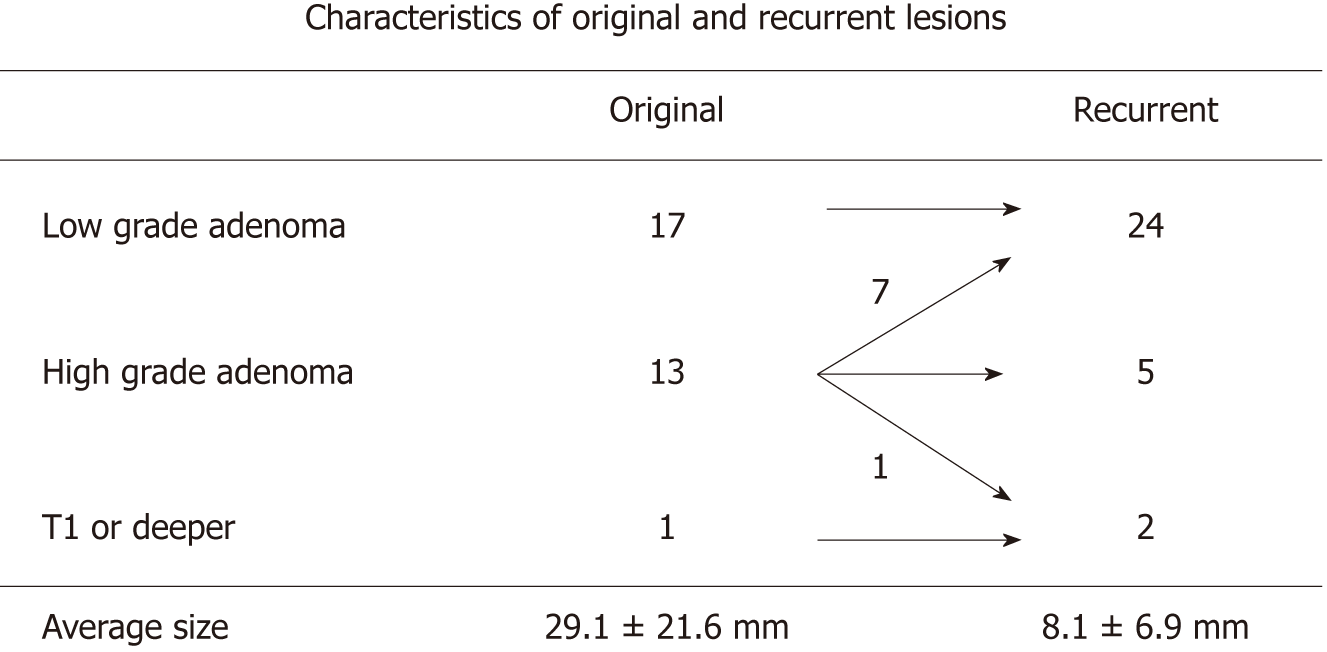
Figure 1 Pathological characteristics of primary and recurrent colorectal tumors.
Most of the recurrent lesions were low grade adenoma.
Figure 2 Endoscopic submucosal dissection was attempted for a lateral spreading tumor-granular measuring 60 mm and was located in the ascending colon.
A: However, the surgery was converted to a piecemeal resection and argon plasma coagulation was performed at the end of the procedure. The tumor histology was tubulovillous adenoma and the horizontal margin was unclear; B: After 3 mo, colonoscopy revealed a recurrent lesion and thus additional endoscopic mucosal resection was performed. Surprisingly, the histological analysis revealed mixed adeno-endocrine carcinoma T1b with indistinct margins. Thereafter, additional surgery was performed. The final depth was T3 (sub-serosal). APC: Argon plasma coagulation; EMR: Endoscopic mucosal resection; ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection; MANEC: Mixed adeno-endocrine carcinoma; LST-G: Laterally spreading tumor granular type.
Figure 3 An 82-year-old woman underwent Endoscopic submucosal dissection for a sessile polyp that measured 20 mm in diameter and was located in the ascending colon.
A: The tumor histology was T1b cancer with an indistinct margin; however, the patient refused surgical operation because of her old age; B: After 3 mo, colonoscopy revealed a recurrent lesion and surgery was performed. ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection.
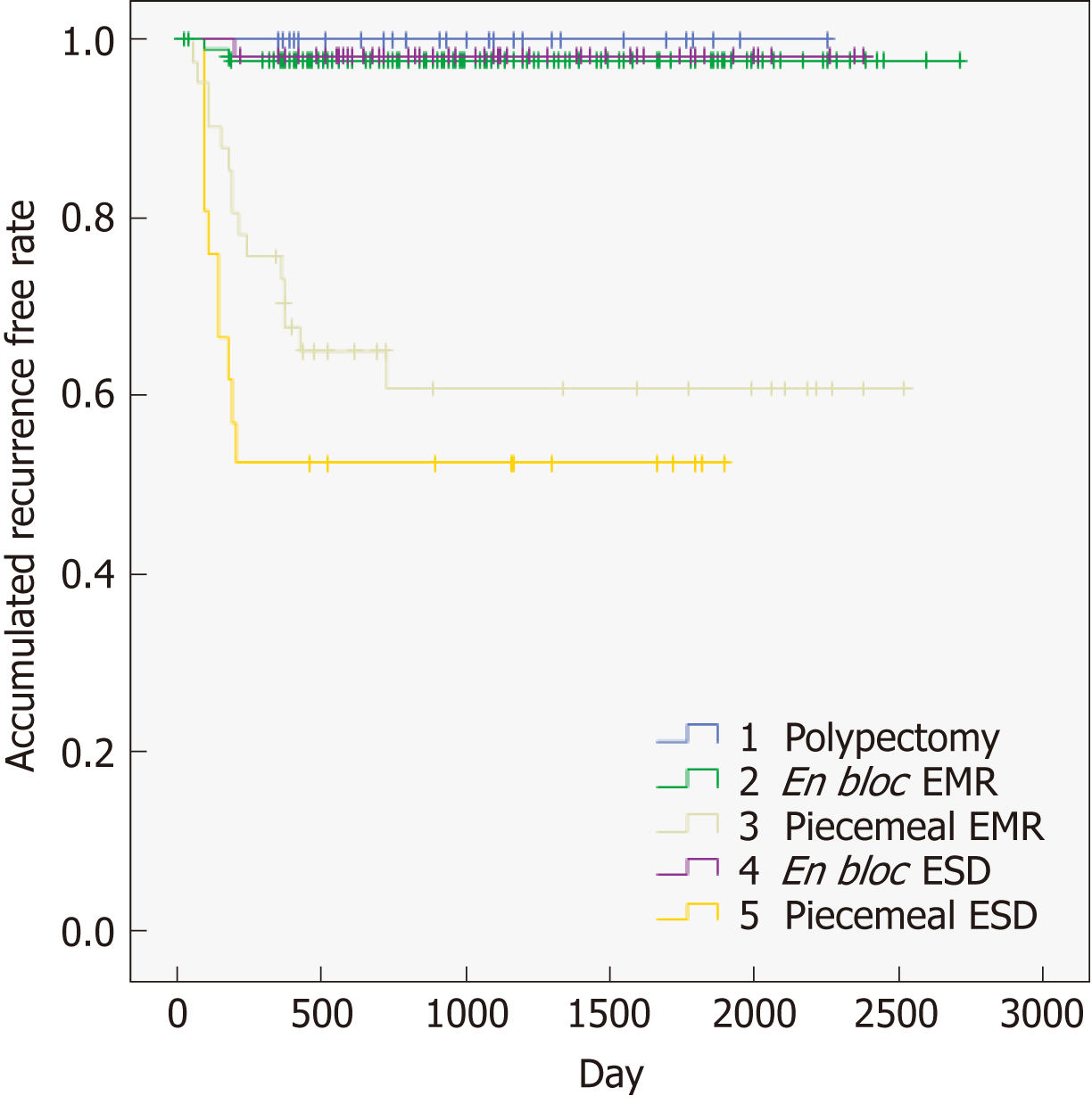
Figure 4 Accumulated recurrence free rate sub-analysis to identify the types of techniques.
EMR: Endoscopic mucosal resection; ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection.
- Citation: Komeda Y, Watanabe T, Sakurai T, Kono M, Okamoto K, Nagai T, Takenaka M, Hagiwara S, Matsui S, Nishida N, Tsuji N, Kashida H, Kudo M. Risk factors for local recurrence and appropriate surveillance interval after endoscopic resection. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(12): 1502-1512
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i12/1502.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i12.1502