Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2018; 24(45): 5120-5130
Published online Dec 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5120
Published online Dec 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5120
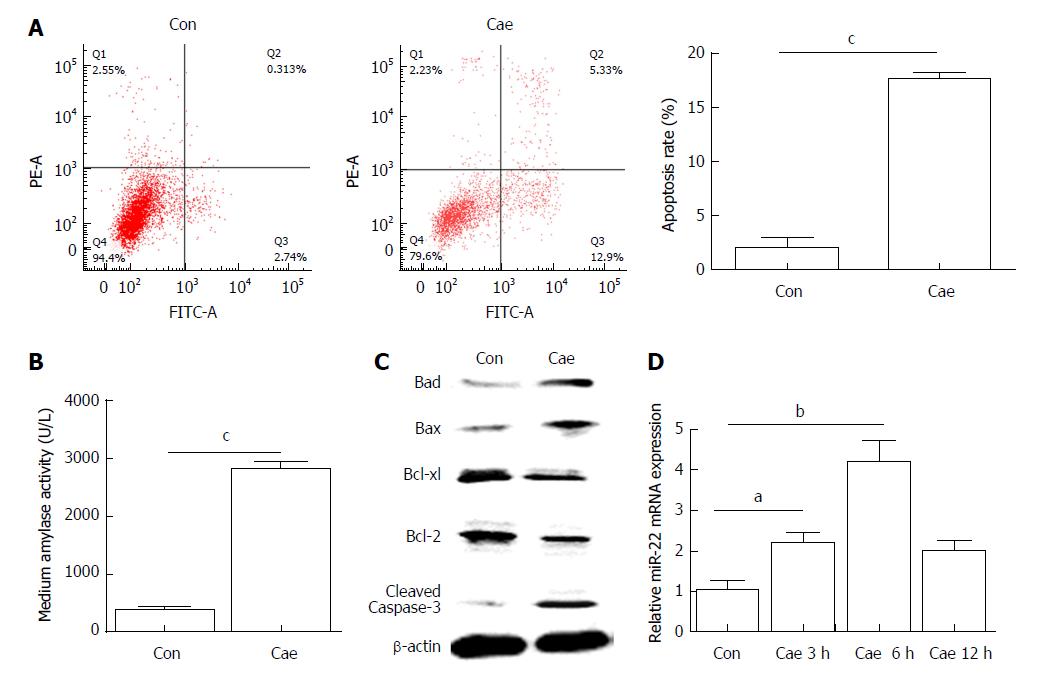
Figure 1 The apoptosis rate and levels of amylase, apoptosis-associated proteins, and microRNA-22 in caerulein-induced AR42J cells.
A: The apoptosis rate of AR42J cells after incubation with caerulein for 24 h; B: Amylase levels in the medium; C: Western blot analysis of the levels of apoptosis-associated proteins in AR42J cells; D: MicroRNA-22 levels in AR42J cells. Data were obtained from three independent experiments performed in triplicate and are shown as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs control group. Cae: Caerulein; miR-22: MicroRNA-22.
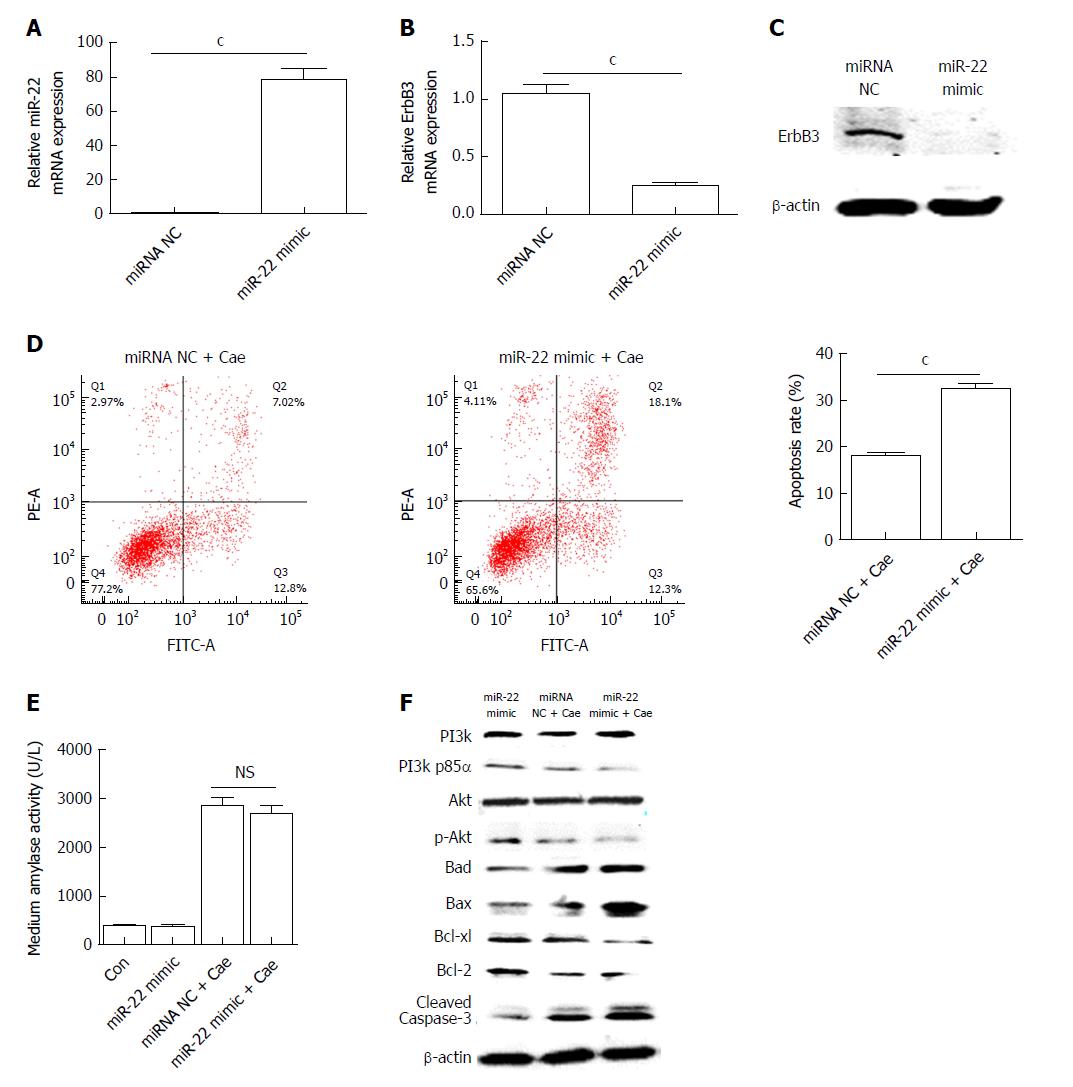
Figure 2 Upregulation of microRNA-22 promotes the apoptosis of AR42J cells by suppressing the PI3k/Akt signaling pathway.
A: MicroRNA-22 expression level; B: Erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 3 (ErbB3) mRNA expression level; C: ErbB3 protein expression level; D: The apoptosis rate of AR42J cells induced with caerulein (Cae) after transfection; E: Amylase levels in the medium; F: Western blot analysis of the levels of PI3k, p-PI3k, Akt, p-Akt, and apoptosis-associated proteins in AR42J cells. Data were obtained from three independent experiments performed in triplicate and are shown as the mean ± SD. NSP > 0.05, cP < 0.001 vs miRNA NC or miRNA NC + Cae groups. ErbB3: Erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 3; Cae: Caerulein; miRNA: MicroRNA; miR-22: MicroRNA-22.
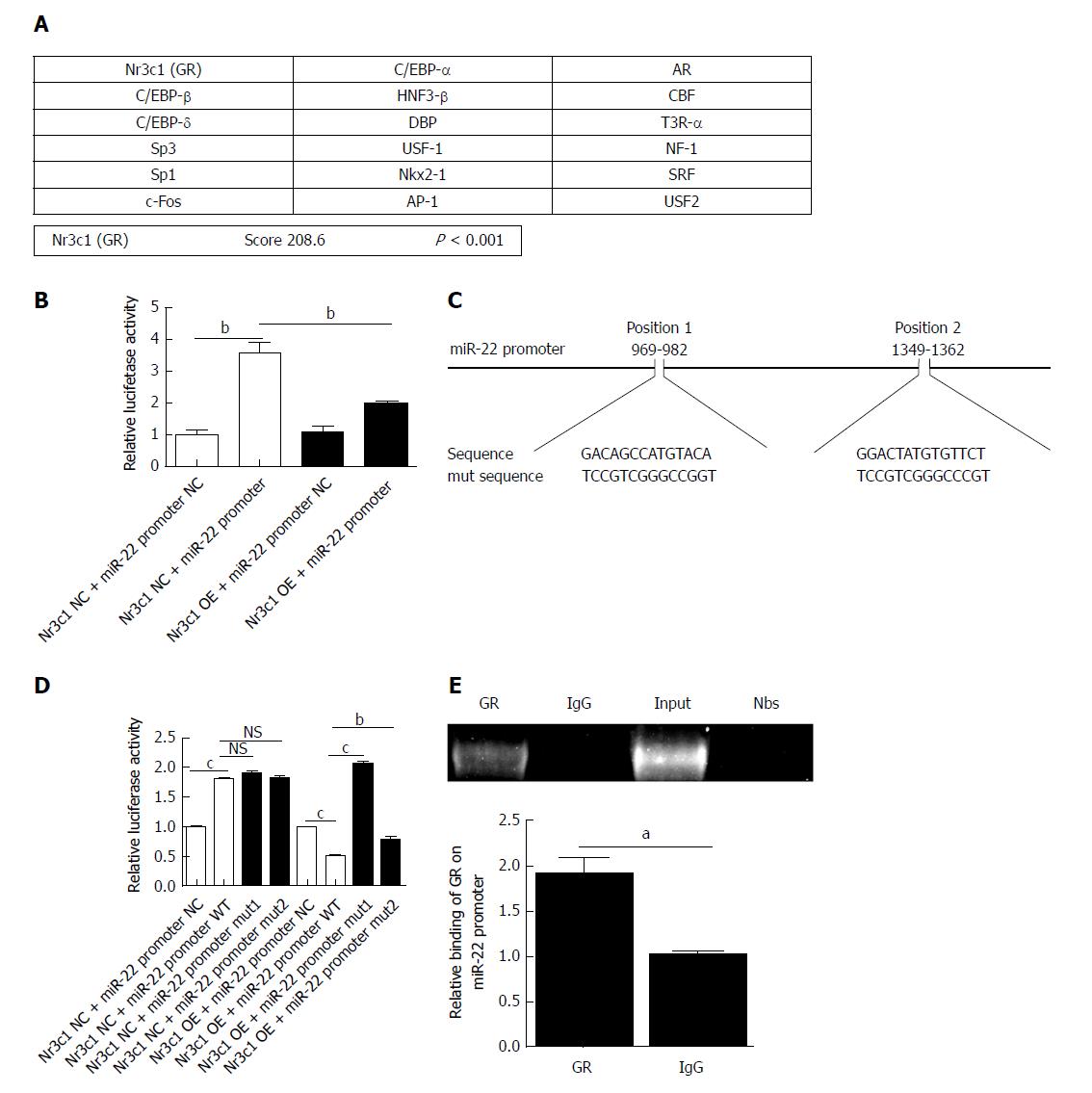
Figure 3 Prediction of the transcription factors of microRNA-22 and the luciferase reporter.
A: The possible transcription factors of microRNA-22 (miR-22) were predicted, of which Nr3c1 had the highest score; B: The luciferase reporter expression after the overexpression of Nr3c1; C: The predicted glucocorticoid receptor binding sites within the miR-22 promoter and the mutant versions generated by site mutagenesis are shown; D: The luciferase reporter expression after mutagenesis. MiR-22 promoter NC, mut 1, or mut 2 plasmid was co-transfected with Nr3c1 NC or Nr3c1 OE plasmid into AR42J cells, respectively. Dual luciferase reporter assays were performed 48 h after transfection; E: Results of the chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay and ChIP-qPCR. Data were obtained from three independent experiments performed in triplicate and are shown as the mean ± SD. NSP > 0.05, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs Nr3c1 NC + miR-22 promoter NC, Nr3c1 NC + miR-22 promoter, Nr3c1 NC + miR-22 promoter WT, Nr3c1 OE + miR-22 promoter NC, Nr3c1 OE + miR-22 promoter WT or IgG groups. ChIP: Chromatin immunoprecipitation; GR: Glucocorticoid receptor; mut: Mutagenesis; OE: Overexpression; miR-22: MicroRNA-22.
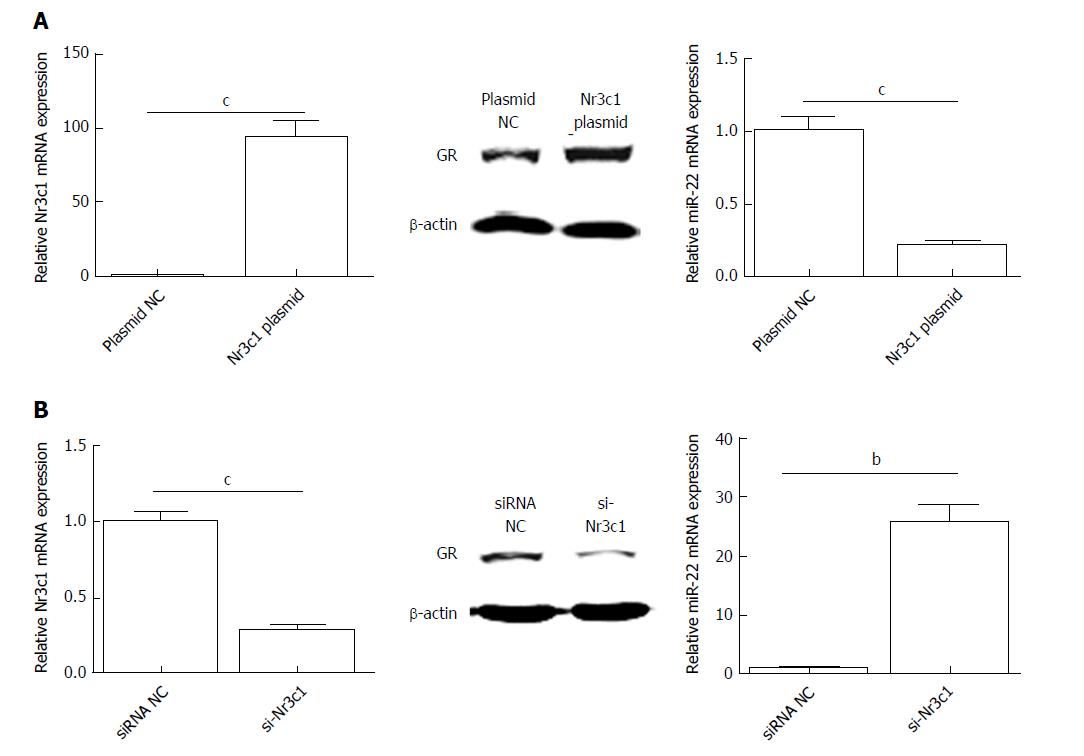
Figure 4 Expression of Nr3c1 mRNA, glucocorticoid receptor protein, and microRNA-22 level after transfection.
A: The levels of Nr3c1 mRNA, GR protein, and miR-22 after transfection with Nr3c1 plasmid; B: The levels of Nr3c1 mRNA, glucocorticoid receptor protein, and miR-22 after transfection with si-Nr3c1. Data were obtained from three independent experiments in triplicate and are shown as the mean ± SD. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs plasmid NC or siRNA NC groups. GR: Glucocorticoid receptor; miR-22: MicroRNA-22.
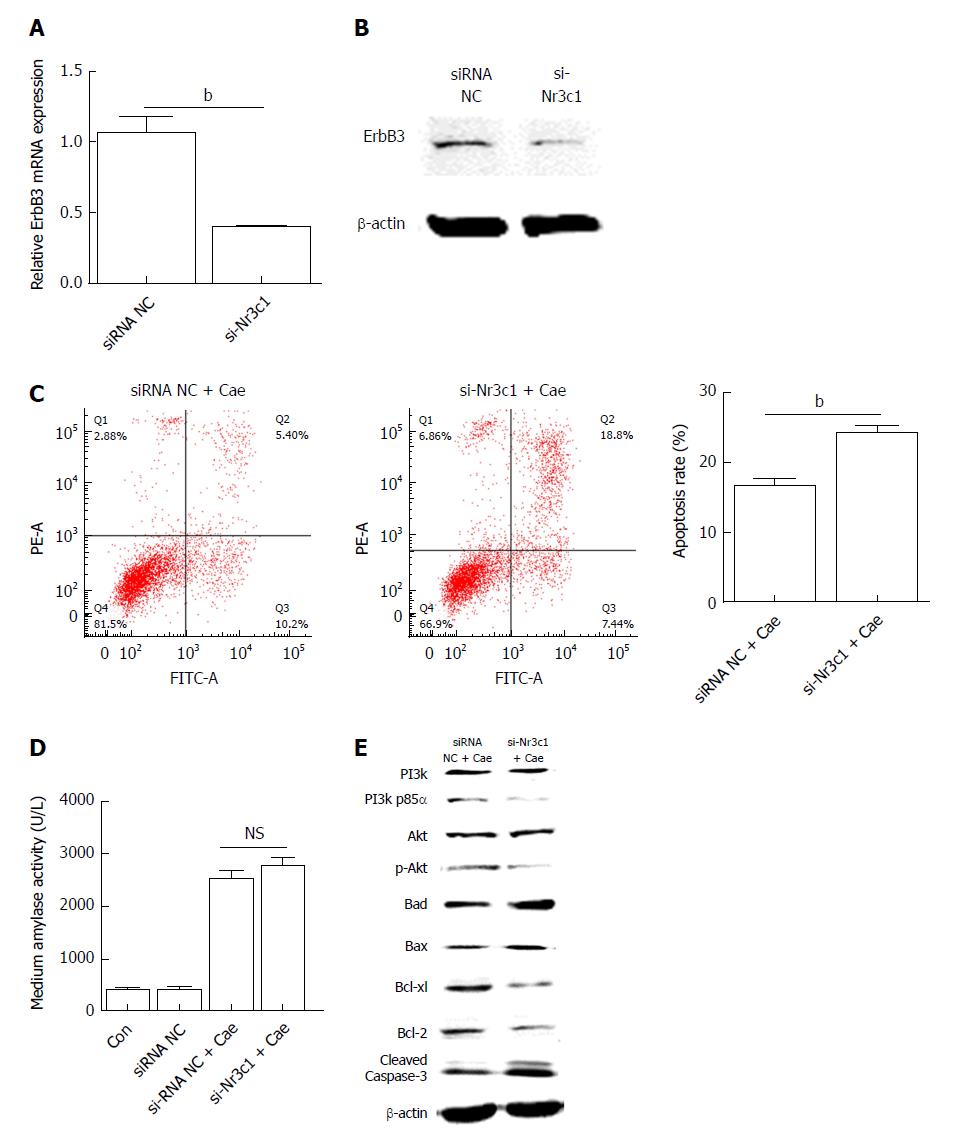
Figure 5 Down-regulation of Nr3c1 by using si-Nr3c1 promotes the apoptosis of AR42J cells by suppressing the PI3k/Akt signaling pathway.
A: Erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 3 (ErbB3) mRNA expression level; B: ErbB3 protein level; C: The apoptosis rate of AR42J cells after the effect of caerulein for 24 h; D: Amylase level in medium; E: Western blot analysis for p-PI3k, p-Akt, and apoptosis associated proteins in AR42J cells. Data were obtained from three independent experiments in triplicate and are shown as the mean ± SD. bP < 0.01 vs siRNA NC groups. ErbB3: Erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 3; Cae: Caerulein; miR-22: MicroRNA-22.
- Citation: Fu Q, Liu CJ, Zhang X, Zhai ZS, Wang YZ, Hu MX, Xu XL, Zhang HW, Qin T. Glucocorticoid receptor regulates expression of microRNA-22 and downstream signaling pathway in apoptosis of pancreatic acinar cells. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(45): 5120-5130
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i45/5120.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5120