Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2018; 24(45): 5109-5119
Published online Dec 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5109
Published online Dec 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5109
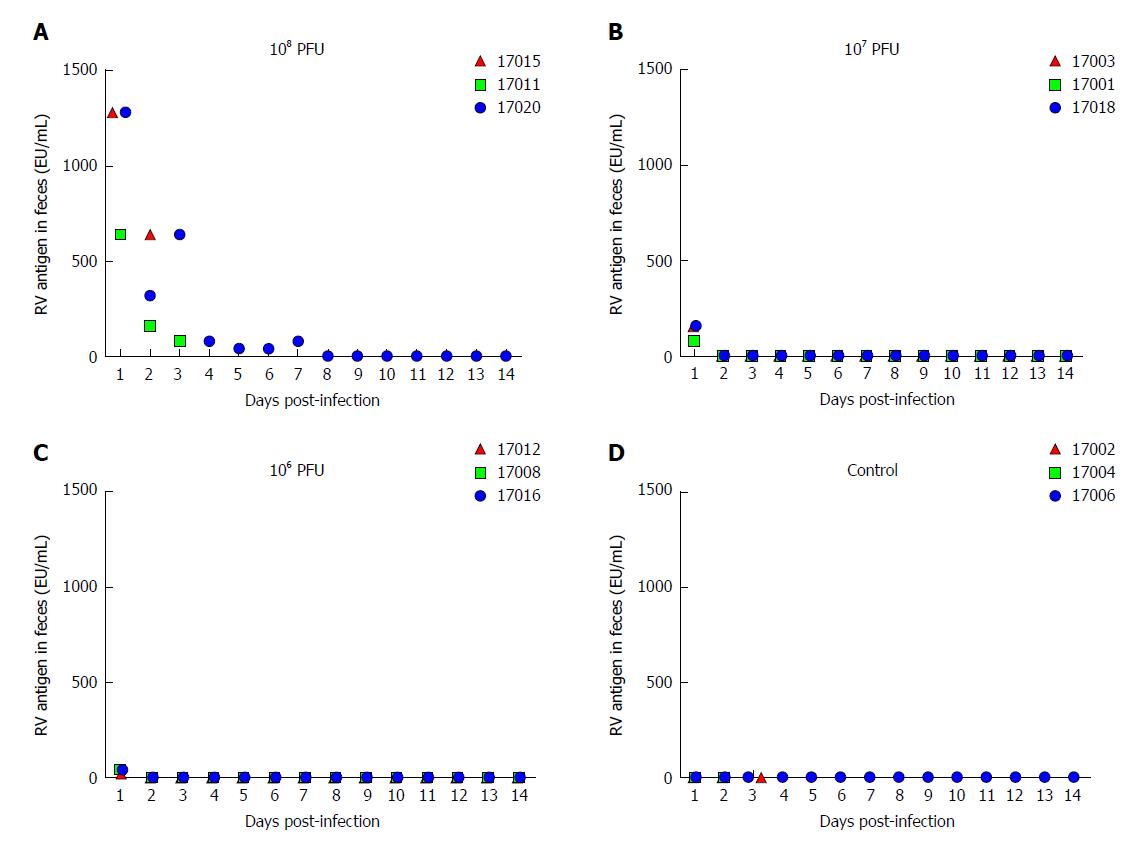
Figure 1 Rotavirus antigen shedding in feces of neonatal rhesus monkeys inoculated with SA11 or medium without serum from 0 dpi to 14 dpi.
A: 10 mL of 108 PFUs of SA11; B: 10 mL of 107 PFUs of SA11; C: 10 mL of 106 PFUs of SA11; D: 10 mL of medium without serum. PFUs: Plaque forming units.
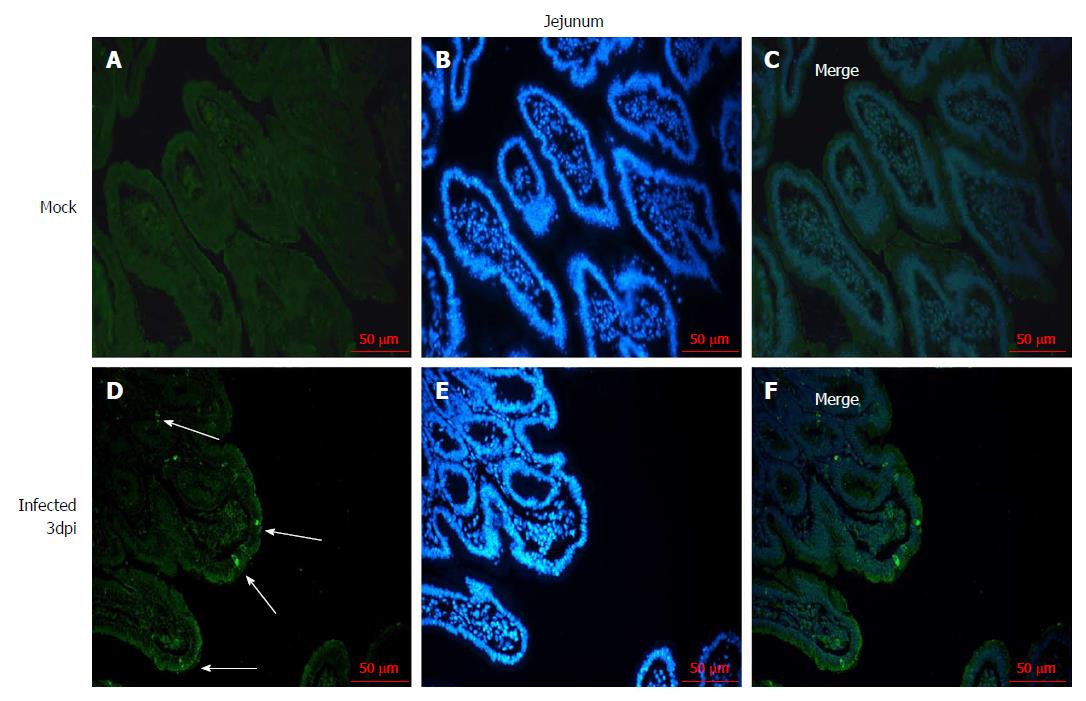
Figure 2 Immunofluorescence of rotavirus antigen in the jejunum of neonatal rhesus monkeys inoculated with SA11 or medium without serum.
A-C: The jejunum of neonatal rhesus monkeys inoculated with medium without serum at 3 dpi; D-F: Jejunum of neonatal rhesus monkeys inoculated with 108 PFUs of SA11/monkey at 3 dpi. The glass slides were incubated with goat anti-rotavirus (RV) polyclonal antibody and then incubated with rabbit anti-goat IgG antibody labeled with FITC (green). Cell nuclei are shown with DAPI staining (blue). White arrows indicate representative RV-positive cells. Magnification, × 20. Bar: 50 μm.
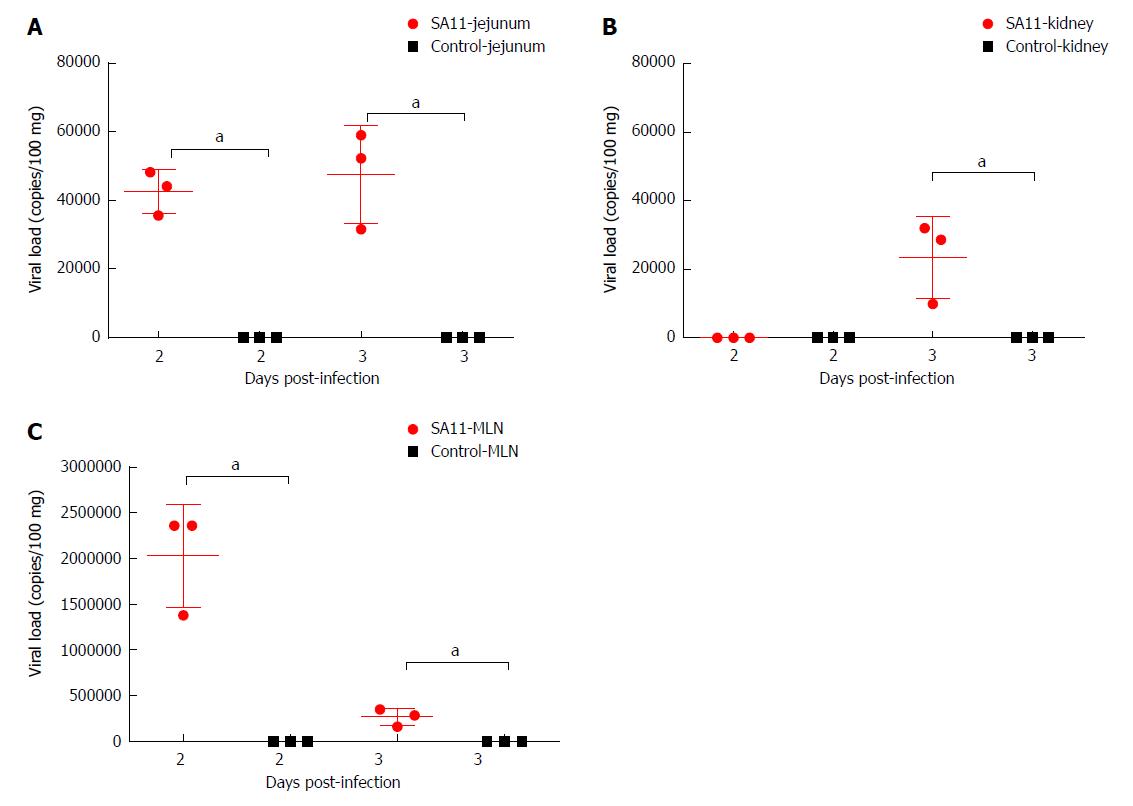
Figure 3 Comparison of viral load in different organs of neonatal rhesus monkeys inoculated with SA11 or medium without serum.
A: Viral load in the jejunum of neonatal rhesus monkeys inoculated with SA11 or medium without serum at 2 dpi and 3 dpi; B: Viral load in kidney of neonatal rhesus monkeys inoculated with SA11 or medium without serum at 2 dpi and 3 dpi; C: Viral load in the mesenteric lymph nodes of neonatal rhesus monkeys inoculated with SA11 or medium without serum at 2 dpi and 3 dpi. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD, n = 3, aP < 0.01.
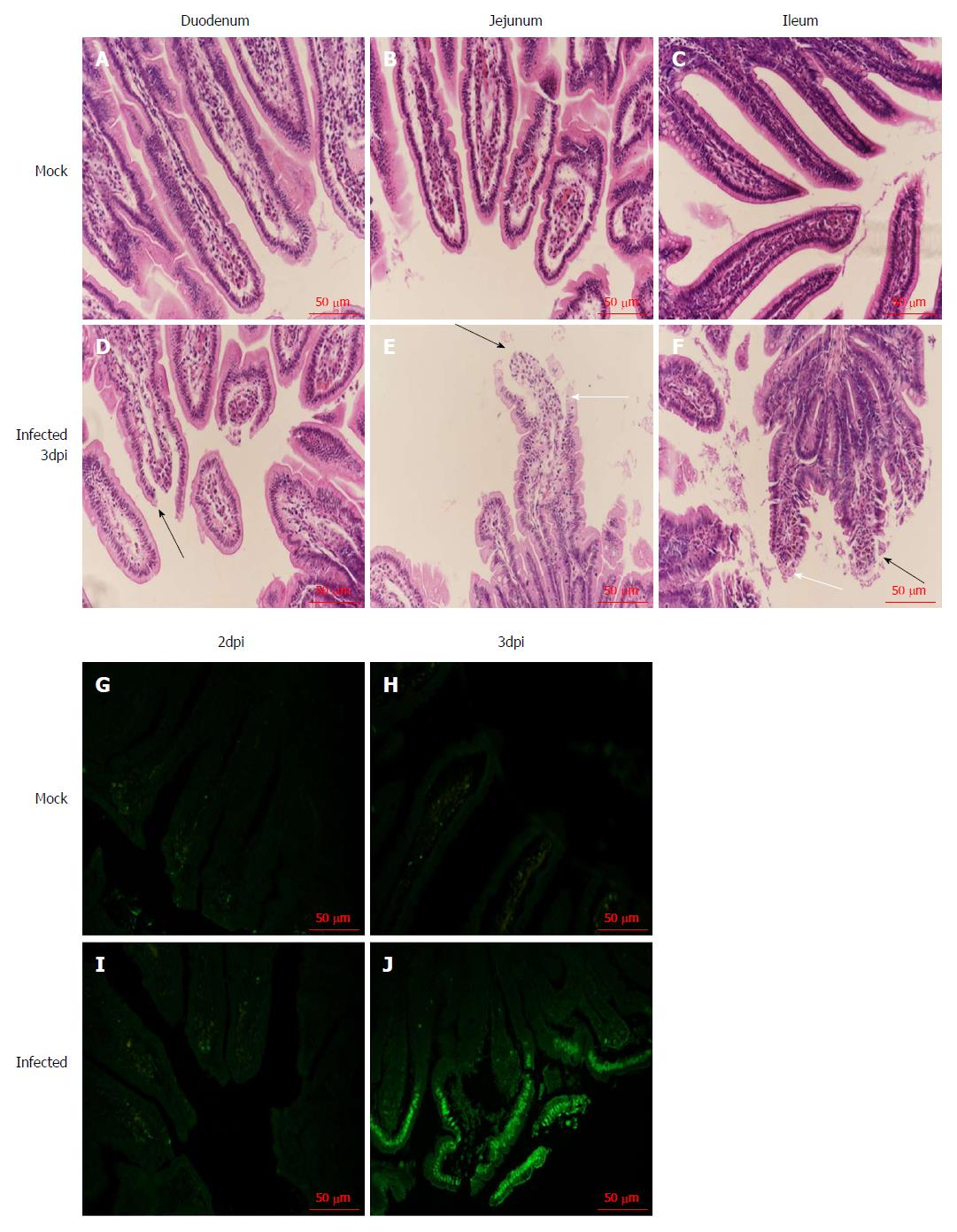
Figure 4 Histopathological changes and apoptosis in the small intestine of neonatal rhesus monkeys infected with SA11 or medium without serum.
A: The duodenum of neonatal rhesus monkeys infected with medium without serum at 3 dpi; B: The jejunum of neonatal rhesus monkeys infected with medium without serum at 3 dpi; C: The ileum of neonatal rhesus monkeys infected with medium without serum at 3 dpi; D: The duodenum of neonatal rhesus monkeys infected with 108 PFUs of SA11 at 3 dpi; E: The jejunum of neonatal rhesus monkeys infected with 108 PFUs of SA11 at 3 dpi; F: The ileum of neonatal rhesus monkeys infected with 108 PFUs of SA11 at 3 dpi; histopathological changes in the small intestinal tissues including vacuolization (white arrow), edema, atrophy, and breakage of the small intestinal villus cells (black arrow); G-J: Apoptosis of jejunal epithelial cells during SA11 infection detected by TUNEL assay; G: Inoculated with medium without serum at 2 dpi; H: Inoculated with medium without serum at 3 dpi; I: Inoculated with 108 PFUs of SA11 at 2 dpi; J: Inoculated with 108 PFUs of SA11 at 3 dpi; the numbers of apoptotic jejunal villus epithelial cells increased significantly at 3 dpi. Magnification: × 20. Bar: 50 μm.
- Citation: Yin N, Yang FM, Qiao HT, Zhou Y, Duan SQ, Lin XC, Wu JY, Xie YP, He ZL, Sun MS, Li HJ. Neonatal rhesus monkeys as an animal model for rotavirus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(45): 5109-5119
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i45/5109.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5109