Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2018; 24(42): 4759-4772
Published online Nov 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i42.4759
Published online Nov 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i42.4759
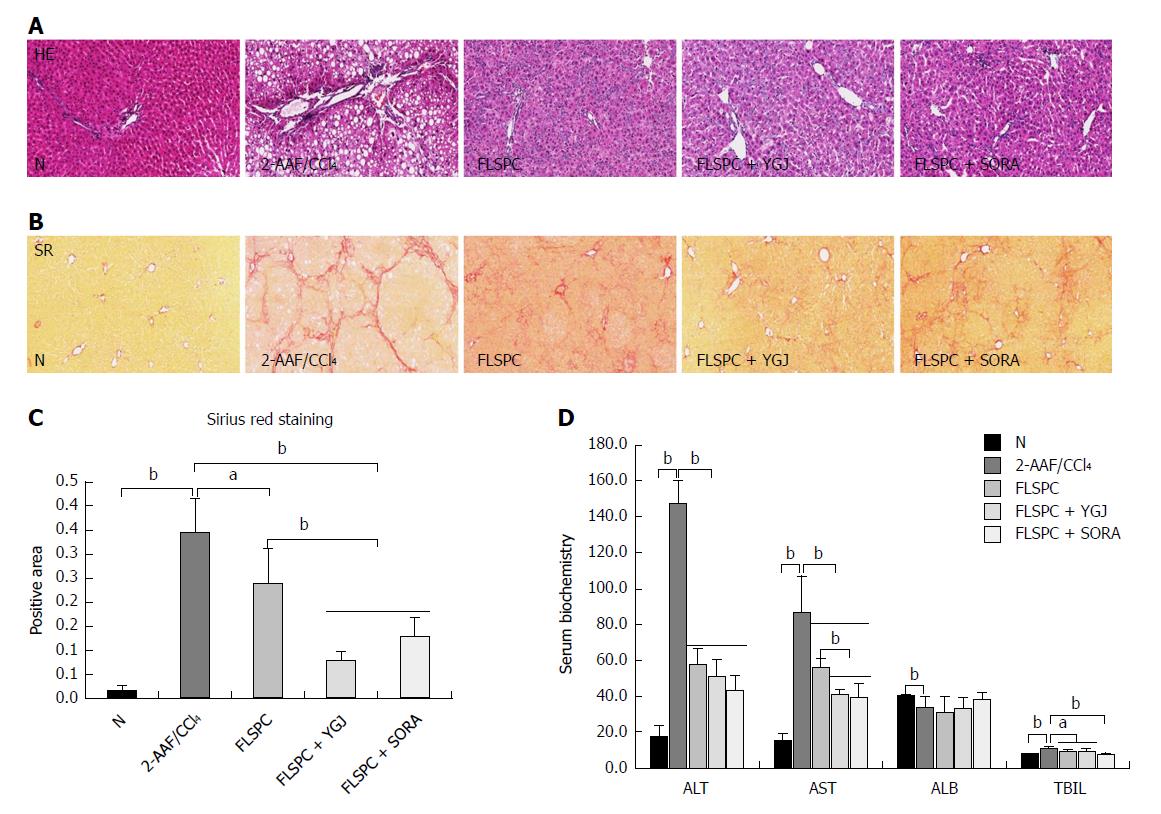
Figure 1 Yiguanjian decoction enhances the reparative effects of fetal liver stem cells on the hepatic inflammatory response and fibrosis.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining (× 100). B: Sirius Red staining (× 100). C: The positive area of Sirius Red staining. D: Serum biochemistry. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. N: Normal control group; 2-AAF/CCl4: 2-acetylaminofluorene/carbon tetrachloride group; FLSPC: Fetal liver stem/progenitor cells group; FLSPC + YGJ: FLSPCs plus Yiguanjian decoction group; FLSPC + SORA: FLSPCs plus sorafenib group; YGJ: Yiguanjian decoction; ALT: Serum alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase.
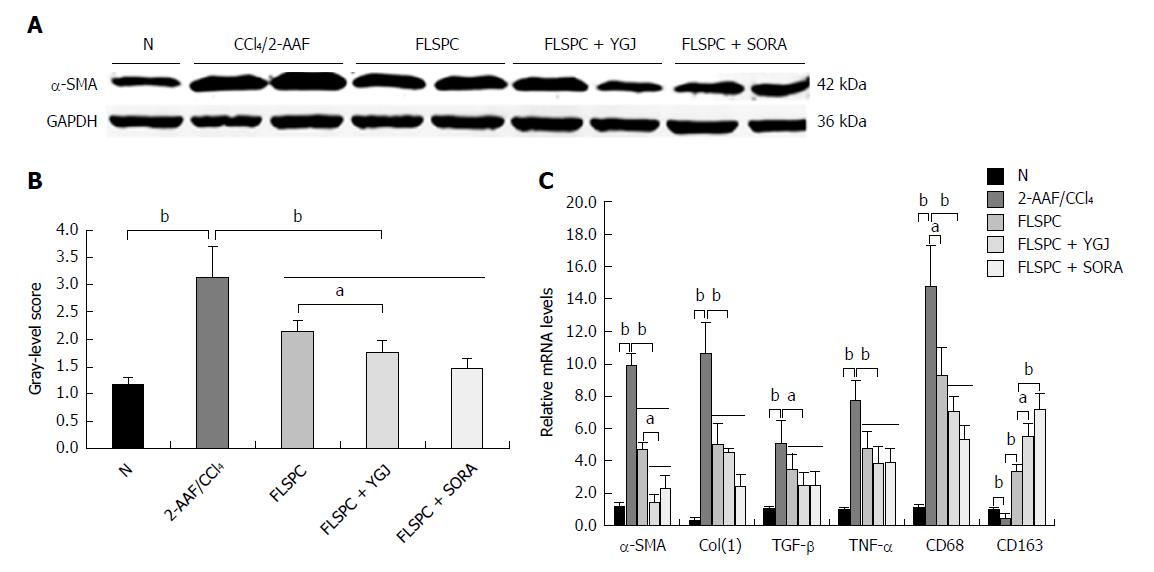
Figure 2 Yiguanjian decoction enhances the inhibitory effect of fetal liver stem cells on hepatic stellate cell activation.
A: Immunoblotting for α-smooth muscle actin. B: The gray-level score indicates the immunoblotting histogram for α-SMA. C: Relative mRNA levels of α-SMA, collagen type I, transforming growth factor beta, tumor necrosis factor alpha, CD68, and CD163. The mRNA levels were normalized to GAPDH expression. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. N: Normal control group; 2-AAF/CCl4: 2-acetylaminofluorene/carbon tetrachloride group; FLSPC: Fetal liver stem/progenitor cell group; FLSPC + YGJ: FLSPCs plus Yiguanjian decoction group; FLSPC + SORA: FLSPCs plus sorafenib group; α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin; Col(1): Collagen type I; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor beta; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha.
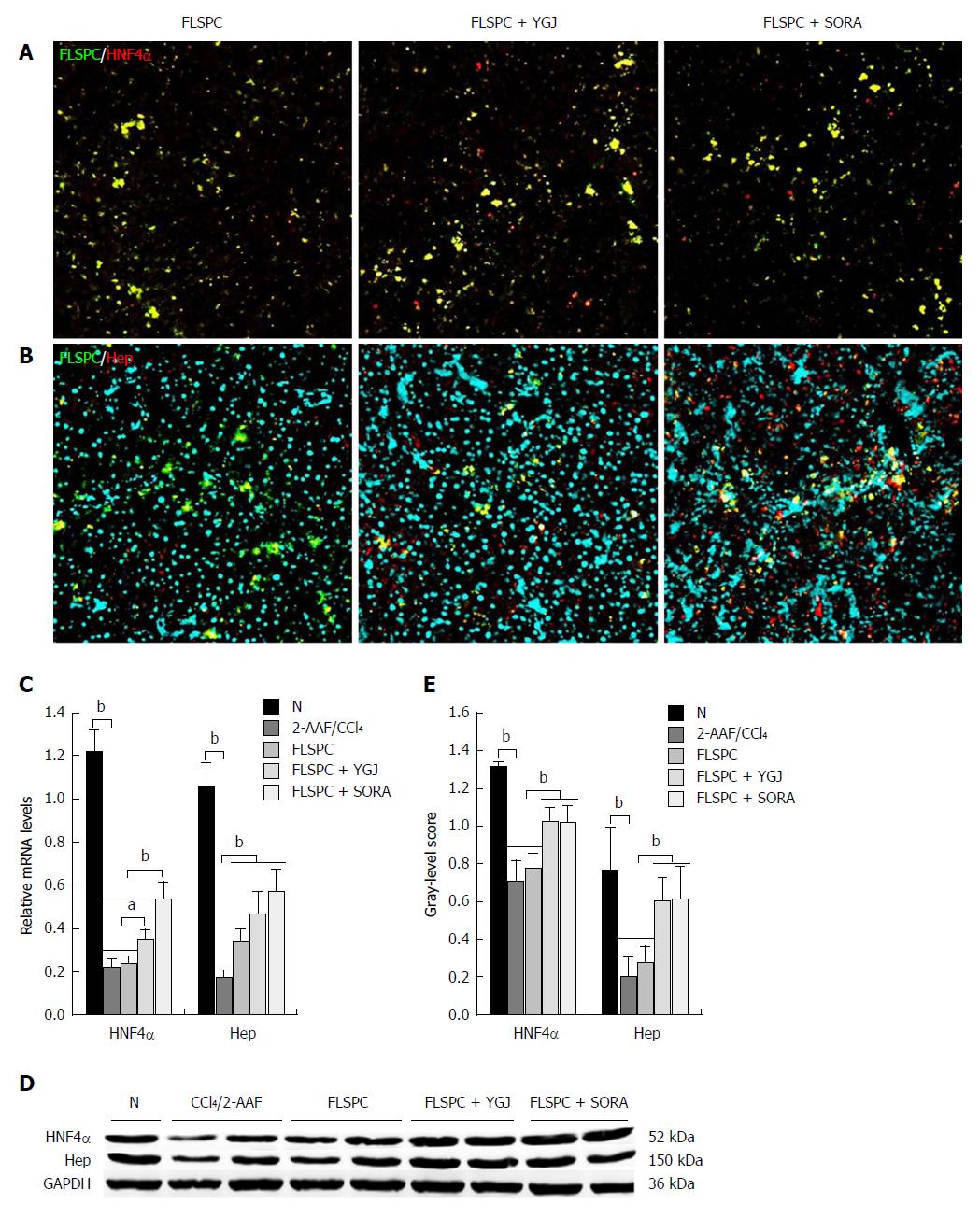
Figure 3 Yiguanjian decoction promotes the differentiation of fetal liver stem/progenitor cells into hepatocytes.
A: Double immunofluorescent staining of fetal liver stem/progenitor cells (green) and HNF4α (red) merged (× 200). B: Double immunofluorescent staining of FLSPCs (green) and Hep Par-1 (Hep) (red) merged (× 200), DAPI (blue) counterstain was used to locate the nuclei. C: Relative mRNA levels of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha and Hep. The mRNA levels were normalized to the GAPDH expression levels. D: Immunoblotting for HNF4α and Hep. E: The gray-level score indicates the immunoblotting histogram for HNF4α and Hep. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. N: Normal control group; 2-AAF/CCl4, 2-acetylaminofluorene/carbon tetrachloride group; FLSPC: Fetal liver stem/progenitor cells group; FLSPC + YGJ: FLSPCs plus Yiguanjian decoction group; FLSPC + SORA: FLSPCs plus sorafenib group; HNF4α: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha; YGJ: Yiguanjian decoction.
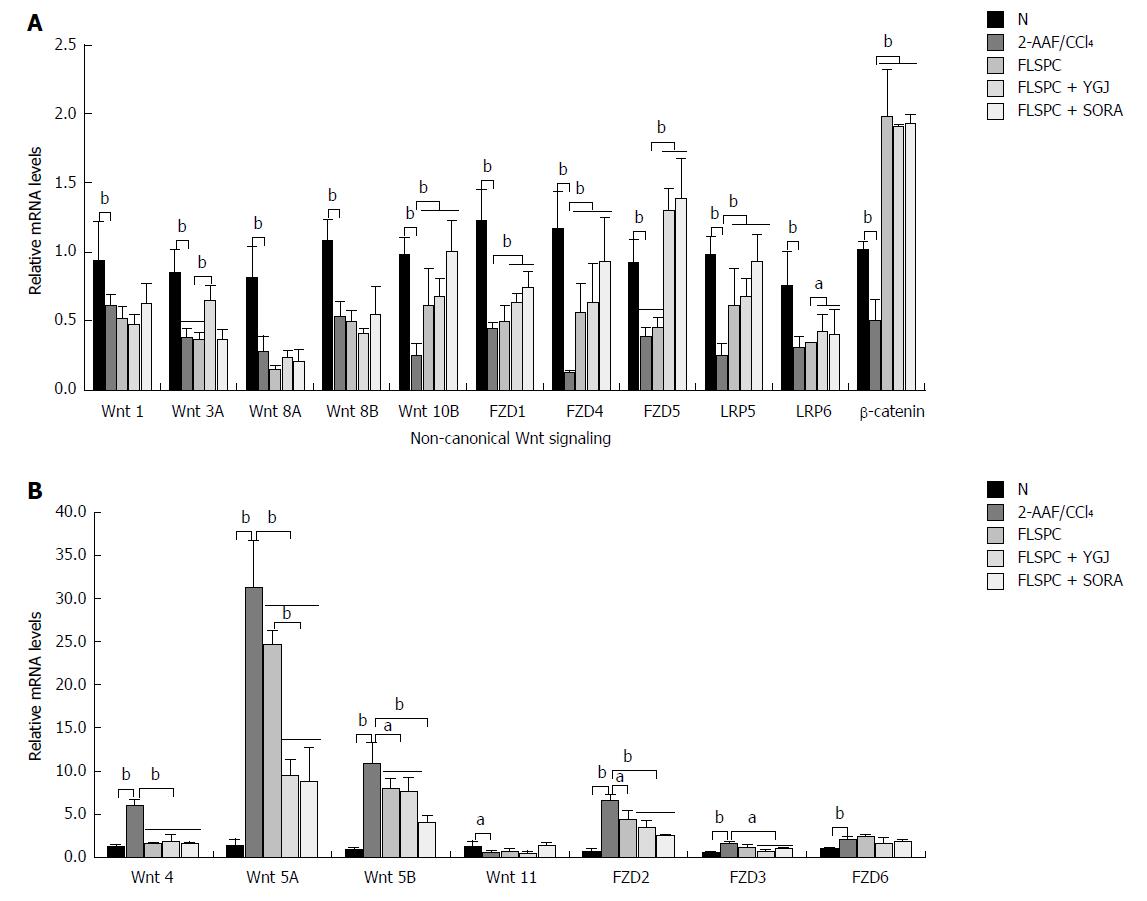
Figure 4 Yiguanjian decoction regulates the Wnt signaling pathway.
A: Relative mRNA levels of canonical Wnt signaling pathway components. B: Relative mRNA levels of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway components. The mRNA levels were normalized to GAPDH expression. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. N: Normal control group; 2-AAF/CCl4: 2-acetylaminofluorene/carbon tetrachloride group; FLSPC: Fetal liver stem/progenitor cells group; FLSPC + YGJ: FLSPCs plus Yiguanjian decoction group; FLSPC + SORA: FLSPCs plus sorafenib group.
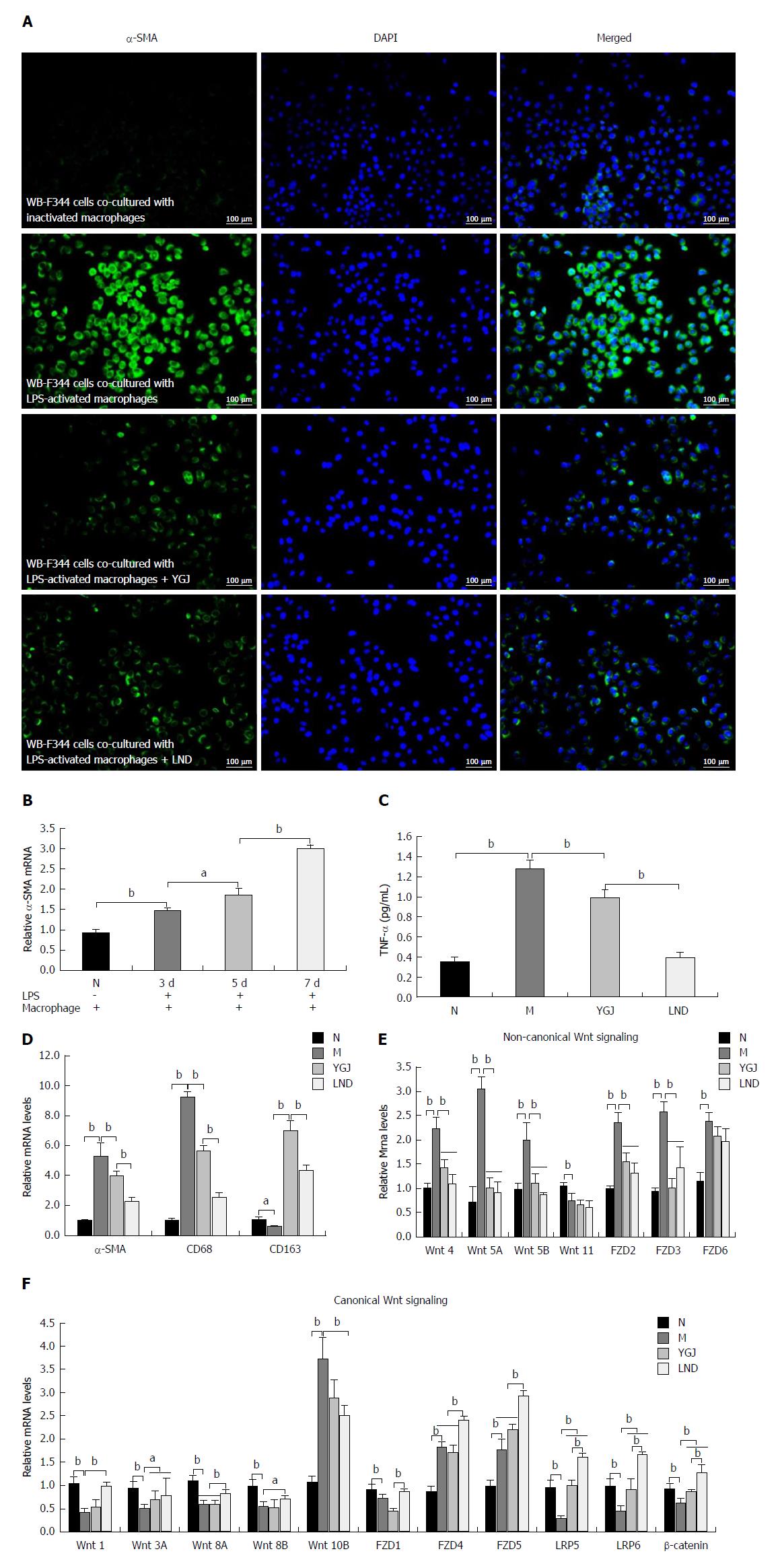
Figure 5 Activation of macrophages and differentiation of WB-F344 to myofibroblasts in vitro.
A: Double immunofluorescent staining of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) (red) and DAPI (blue) merged (× 200). B: The mRNA expression of α-SMA in WB-F344 cells after co-culture with lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated RAW264.7 cells for 3, 5, or 7 d. C: Tumor necrosis factor production in LPS-activated RAW264.7 was detected by enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay. D: Relative mRNA expression levels of α-SMA (WB-F344), CD68 (RAW264.7), and CD163 (RAW264.7). E: Relative mRNA levels of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway components. F: Relative mRNA levels of canonical Wnt signaling pathway components. The mRNA levels were normalized to the GAPDH expression levels. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. N: Normal control group; M: WB-F344 cells co-cultured with LPS-activated RAW264.7 cells group; YGJ: Yiguanjian decoction group; LND: Lenalidomide group.
- Citation: Xu Y, Fan WW, Xu W, Jiang SL, Chen GF, Liu C, Chen JM, Zhang H, Liu P, Mu YP. Yiguanjian decoction enhances fetal liver stem/progenitor cell-mediated repair of liver cirrhosis through regulation of macrophage activation state. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(42): 4759-4772
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i42/4759.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i42.4759