Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2018; 24(36): 4208-4216
Published online Sep 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i36.4208
Published online Sep 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i36.4208
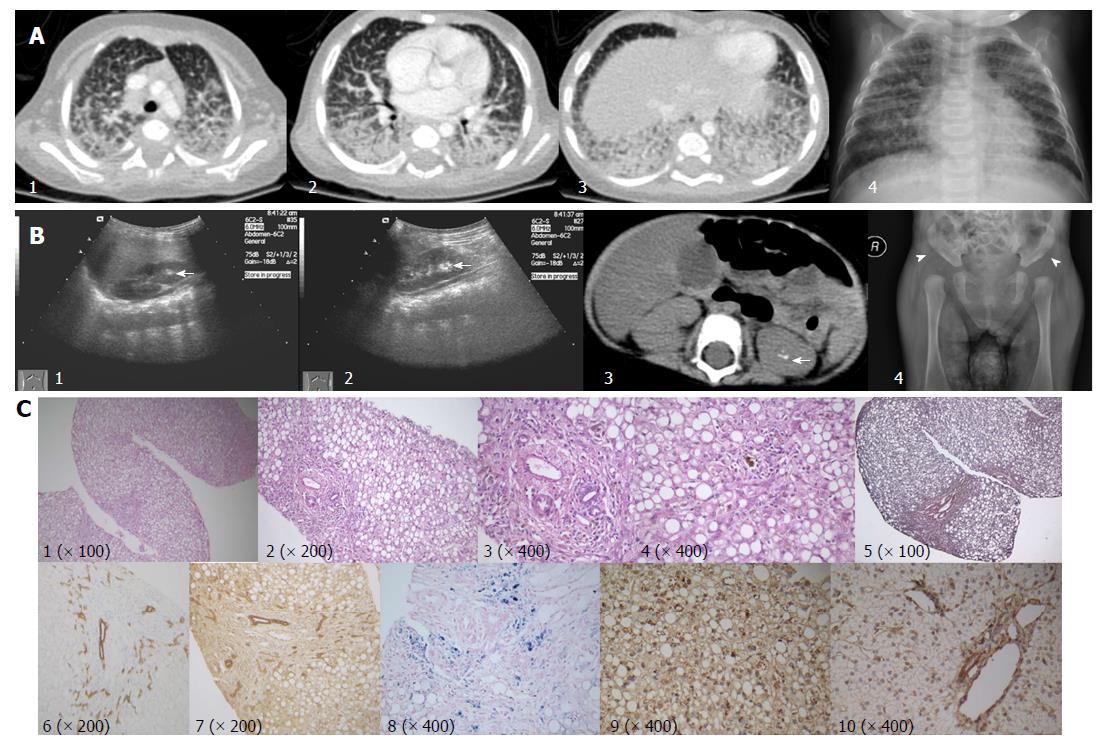
Figure 1 Imaging and histopathological features.
A: Contrast enhanced pulmonary CT scan (1-3), and chest X-ray (4) showing pulmonary effusion with marked interstitial lung involvement; B: Hyper-echoic lesions consistent with stone formation on ultrasonography (arrows; 1, right kidney; 2, left kidney) and non-contrast abdominal computed tomography scan (arrow, 3). Acetabular dysplasia (4, arrowhead showing abnormally shallow hip socket); C: Liver biopsy (all originally magnified principal images): severe steatosis of hepatic cells with ballooning, lobular disarray, and cholestasis (1-4), mild fibrosis (5), mild lymphocyte infiltration (4), bile duct proliferation (6 CK-7, 7 CK-19), and hepatic iron deposition (8). MARS immunohistochemistry staining, coarsely granular pigments within the cytoplasm in the index patient (9), but not in samples of a healthy control (10). MARS: Methionyl-tRNA synthetase gene.
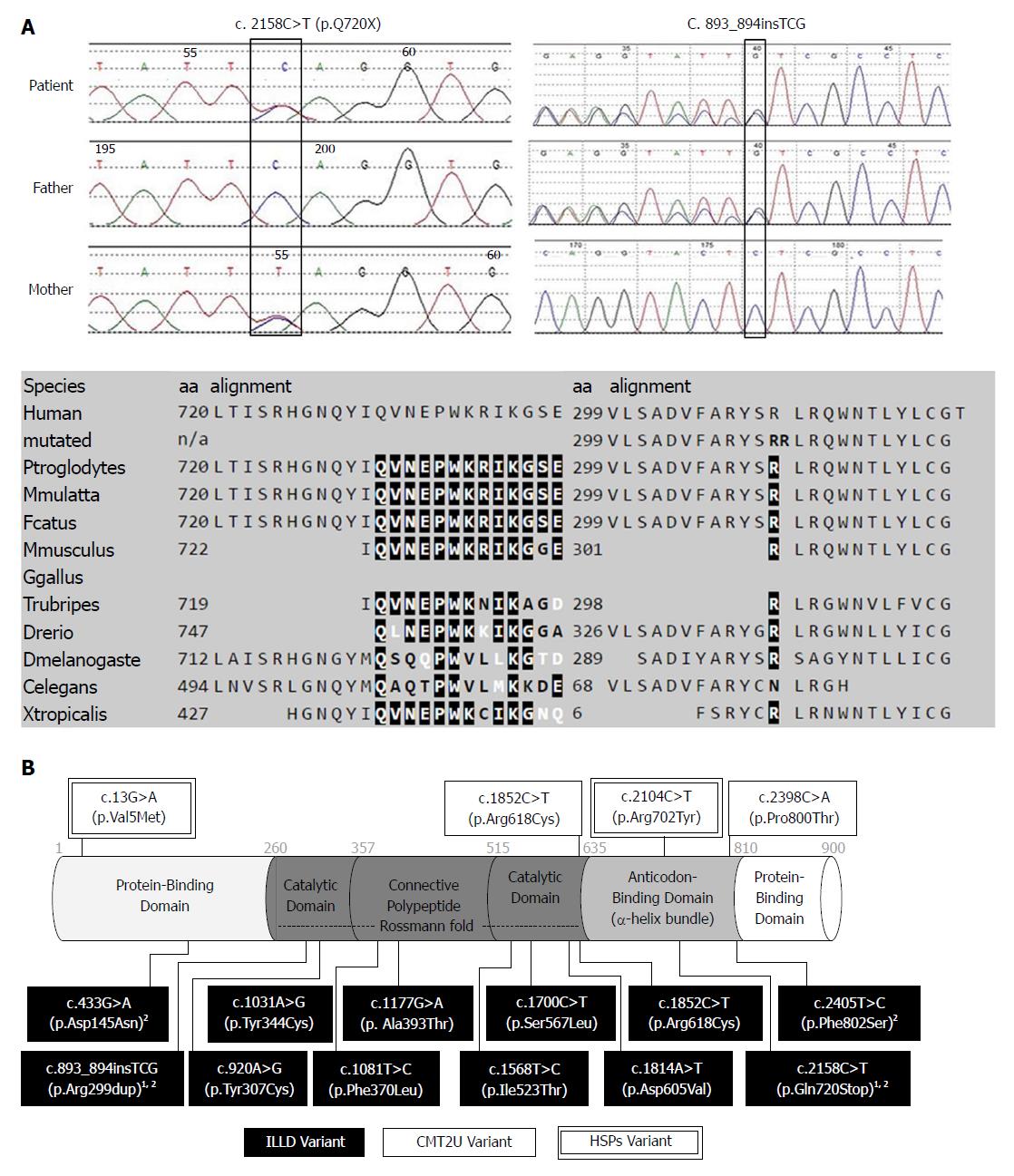
Figure 2 Genetic testing results, protein features, and distribution of reported variants within the methionyl-tRNA synthetase protein.
A: Sanger sequencing confirmation of the index case and parents, both variants affect highly conserved amino acid residues of the MetRS protein; B: Illustration of MetRS protein domains, location of amino acid changes of the reported variants so far. 1Variants from our report; 2Variants from Chinese ILLD cases. MetRS: Methionyl-tRNA synthetase; ILLD: Interstitial lung and liver disease.
- Citation: Abuduxikuer K, Feng JY, Lu Y, Xie XB, Chen L, Wang JS. Novel methionyl-tRNA synthetase gene variants/phenotypes in interstitial lung and liver disease: A case report and review of literature. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(36): 4208-4216
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i36/4208.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i36.4208