Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2018; 24(33): 3799-3805
Published online Sep 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i33.3799
Published online Sep 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i33.3799
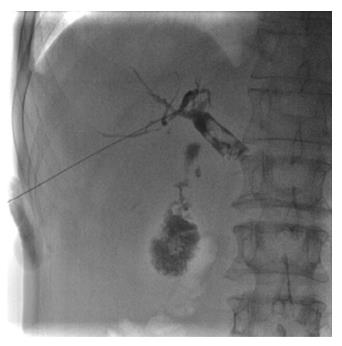
Figure 1 Puncture of the bile duct, and cholangiography showing the number, size, and location of simultaneous gallbladder and common bile duct stones.
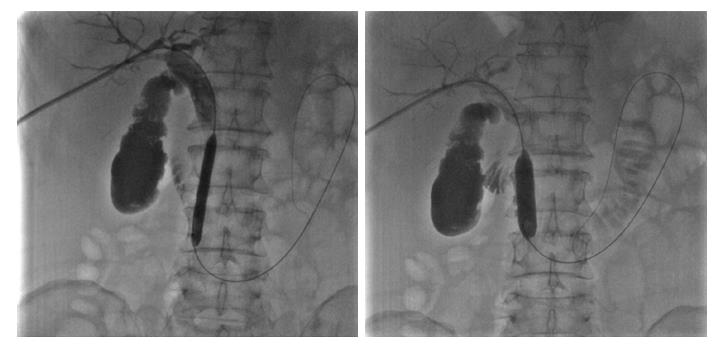
Figure 2 Sequential dilation of the sphincter of Oddi with an 8 mm × 60 mm and a 14 mm × 40 mm balloon.
Figure 3 Empty balloon was then withdrawn above the stones, inflated, and used to push the stones into the duodenum through the sphincter of Oddi.
A: The empty balloon was withdrawn above the common bile duct stones (white arrow) and then re-inflated. B: The common bile duct stones (white arrow) were pushed into the duodenum through the dilated sphincter of Oddi.
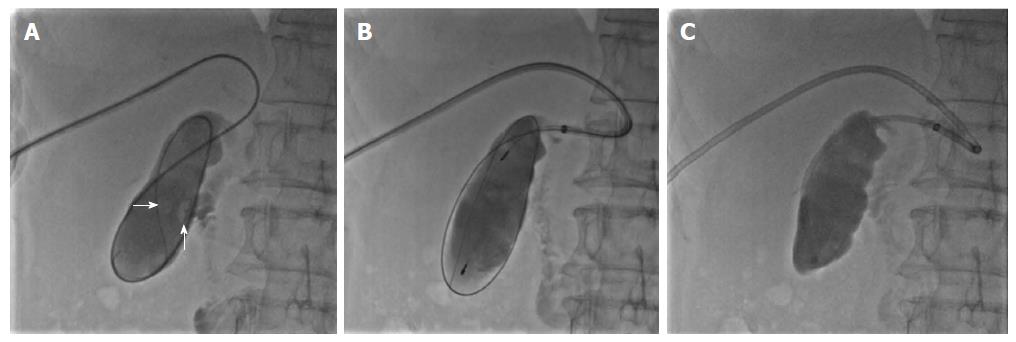
Figure 4 Percutaneous clearance of gallbladder stones.
A: Sequential introduction of a guidewire and 4-Fr single-angle catheter into the gallbladder through the cystic duct, and cholangiography showing the number, size, and location of the gallbladder stones (white arrow); B: Capture of stones in a metallic basket; C: Aspiration of sandy stones out of the body through a guide catheter.
- Citation: Liu B, Wu DS, Cao PK, Wang YZ, Wang WJ, Wang W, Chang HY, Li D, Li X, Hertzanu Y, Li YL. Percutaneous transhepatic extraction and balloon dilation for simultaneous gallbladder stones and common bile duct stones: A novel technique. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(33): 3799-3805
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i33/3799.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i33.3799