Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2018; 24(31): 3556-3566
Published online Aug 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i31.3556
Published online Aug 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i31.3556
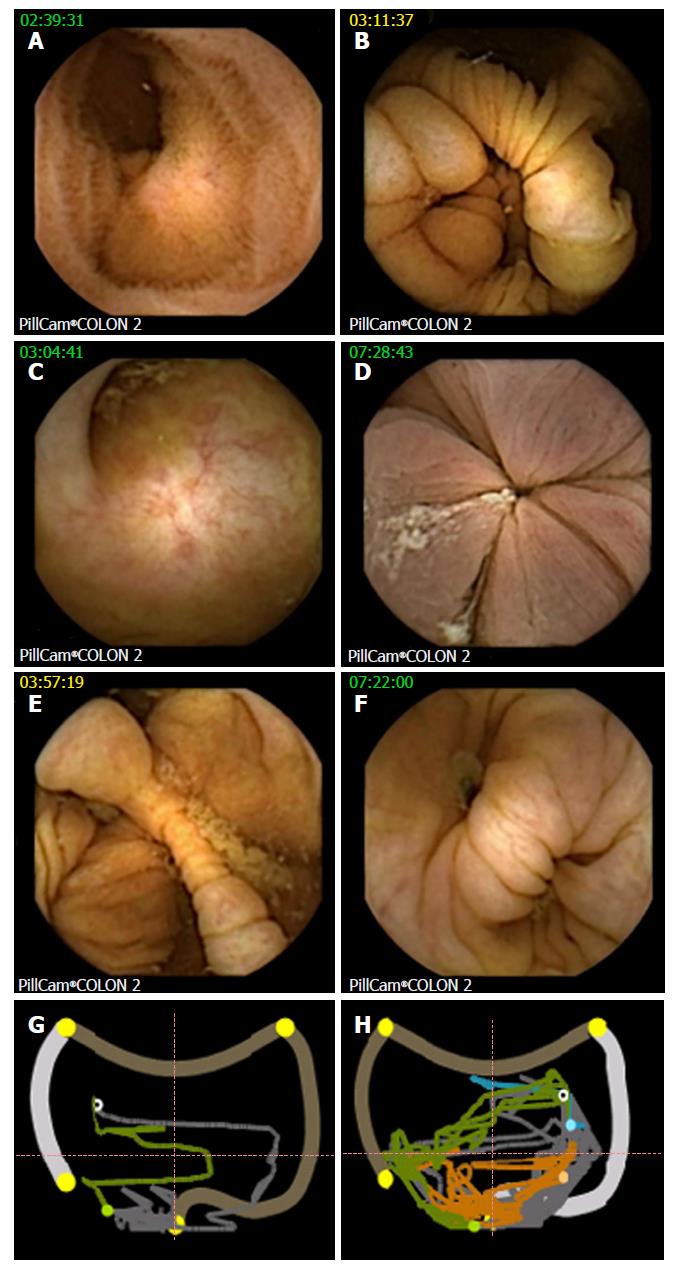
Figure 1 Landmarks at colon capsule endoscopy.
A: Terminal ileum; B: IC valve; C: Appendix; D: Hemorrhoidal plexus, hepatic flexure - CCE image (E) with corresponding localization trace (G), white circle showing actual capsule position, green colon already displayed, grey colon yet to be analyzed, orange small bowel, blue stomach, outer pictogram the position to the colonic segment as manually defined by setting the landmarks; F and H: CCE image and localization trace of splenic flexure in another patient. CCE: Colon capsule endoscopy.
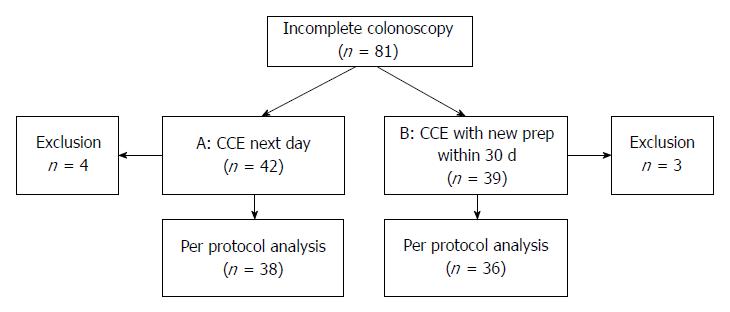
Figure 2 Flow chart protocol A (colon capsule endoscopy the day after colonoscopy) and protocol B (colon capsule endoscopy within 30 d after incomplete colonoscopy).
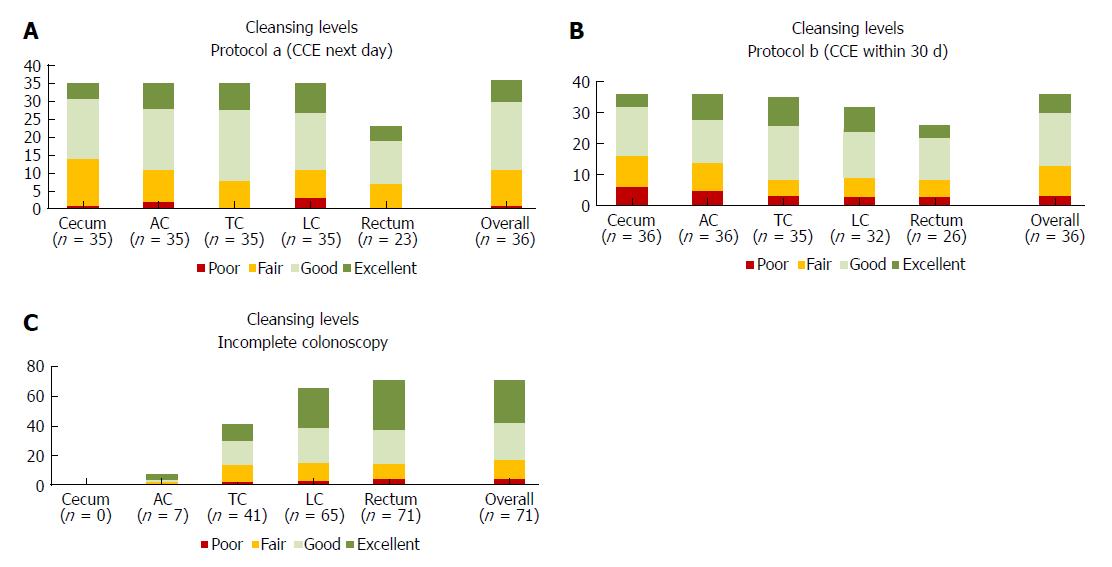
Figure 3 Cleansing levels for the colon segments: cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, left colon, rectum and overall classification for all segments.
Absolute number of patients for each level (poor, fair, good, excellent) are shown A for CCE with protocol a (next day), B for CCE with protocol b (within 30 d), and C for incomplete colonoscopy. AC: Ascending colon; CCE: Colon capsule endoscopy; LC: Left colon; TC: Transverse colon.
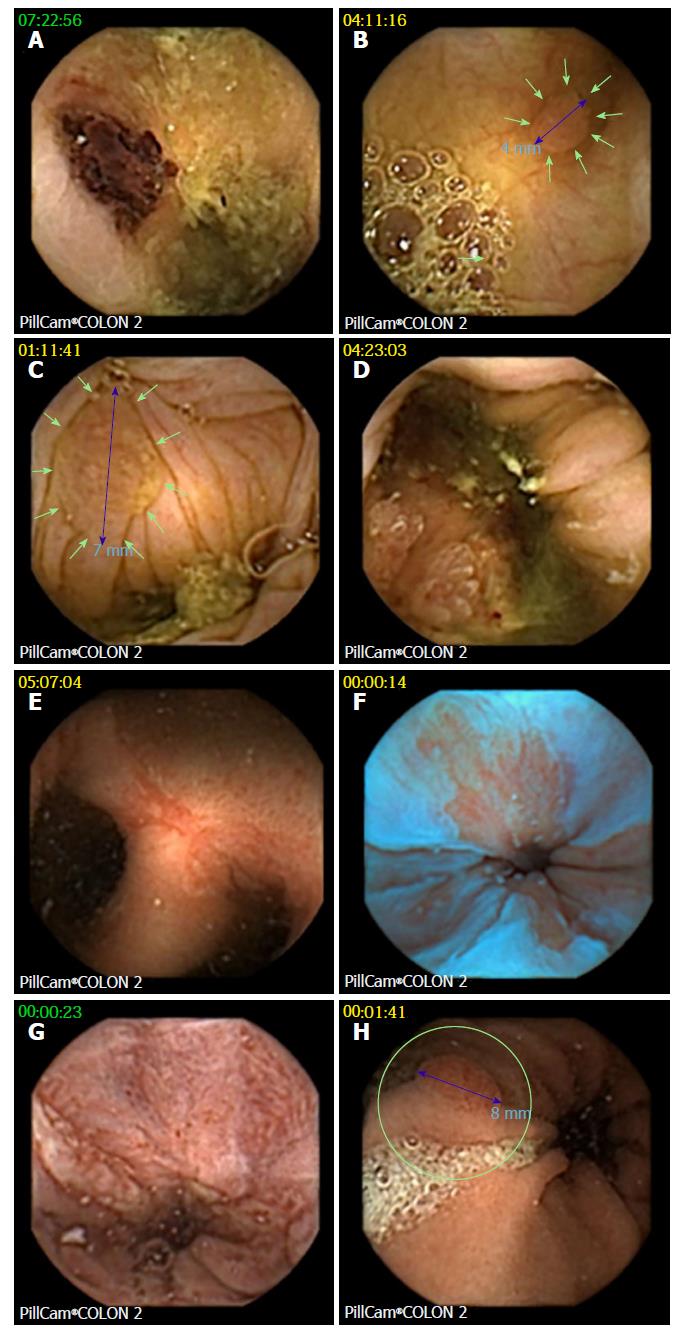
Figure 4 Examples of findings at colon capsule endoscopy.
A: Biopsy tattoo after optical colonoscopy; B: One of three 4 mm polyps in the ascending colon, confirmed at consecutive balloon enteroscopy as tubular adenoma; C: Significant (7 mm) polyp; D: Cecal adenocarcinoma (confirmed by surgery); E: Fistulating and stenosing Crohn´s disease of the ileum (confirmed by enteroclysis, CT scan, and surgery); F: Irregular Z-line suggestive of Barrett´s esophagus (blue mode image); G: Reflux esophagitis; H: Gastric polyp (consecutive gastroscopy found foveolar hyperplasia and autoimmune gastritis with vitamin B12 deficiency).
- Citation: Baltes P, Bota M, Albert J, Philipper M, Hörster HG, Hagenmüller F, Steinbrück I, Jakobs R, Bechtler M, Hartmann D, Neuhaus H, Charton JP, Mayershofer R, Hohn H, Rösch T, Groth S, Nowak T, Wohlmuth P, Keuchel M. PillCamColon2 after incomplete colonoscopy - A prospective multicenter study. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(31): 3556-3566
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i31/3556.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i31.3556