Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2018; 24(12): 1299-1311
Published online Mar 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i12.1299
Published online Mar 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i12.1299
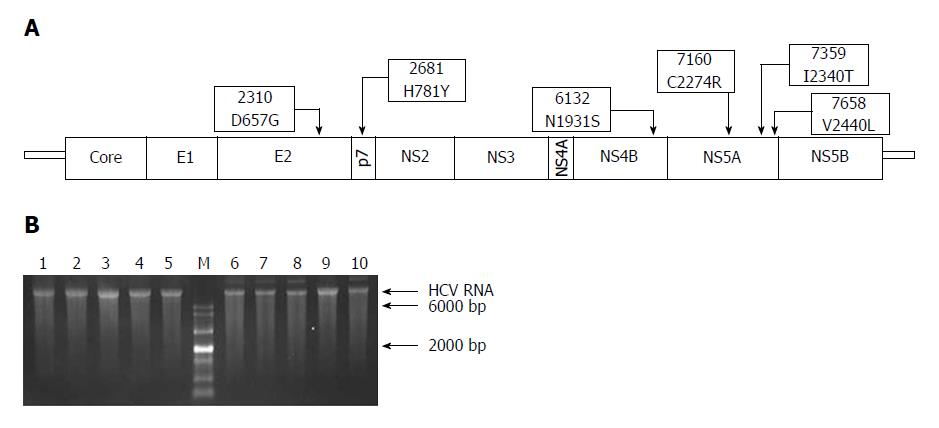
Figure 1 Schematic representation of adaptive mutations used in this study (A) and the electrophoresis results of each mutant virus RNA (B).
A: Both nucleotide substitutions (2310, 2681, 6132, 7160, 7359, and 7658) and amino acid substitutions (D657G, H781Y, N1931S, C2274R, I2340T, and V2440L) are shown; B: HCV RNA (500 ng) was analyzed using formaldehyde agarose gel electrophoresis. Lane 1: JFH1; Lane 2: JFH1-mE2; Lane 3: JFH1-mP7; Lane 4: JFH1-mNS4B; Lane 5: JFH1-mNS5A; Lane 6: JFH1-mE2/NS5A; Lane 7: JFH1-mp7/NS5A; Lane 8: JFH1-mNS4B/NS5A; Lane 9: mJFH1; Lane 10: JFH1-mE2/p7/NS5A; M: RNA marker. HCV: hepatitis C virus.
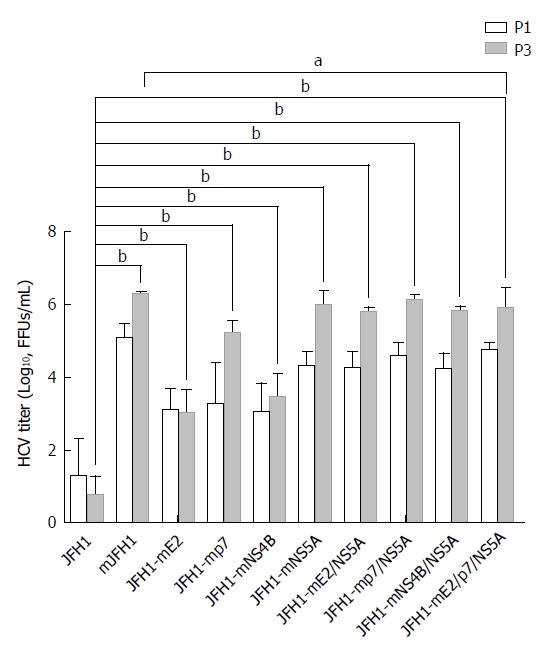
Figure 2 Generation of high titer cell culture-adaptive JFH1 virus.
Hepatitis C virus RNA was electroporated into Huh7.5 cells to produce the recombinants of adapted virus in cell culture. The transfected cells were passaged every three days. The infectivity titers of the culture supernatants at day 3 (P1) and day 9 (P3) were measured. Viral titers are expressed as focus-forming units per milliliter (FFUs/mL). The data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). HCV: Hepatitis C virus. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01.
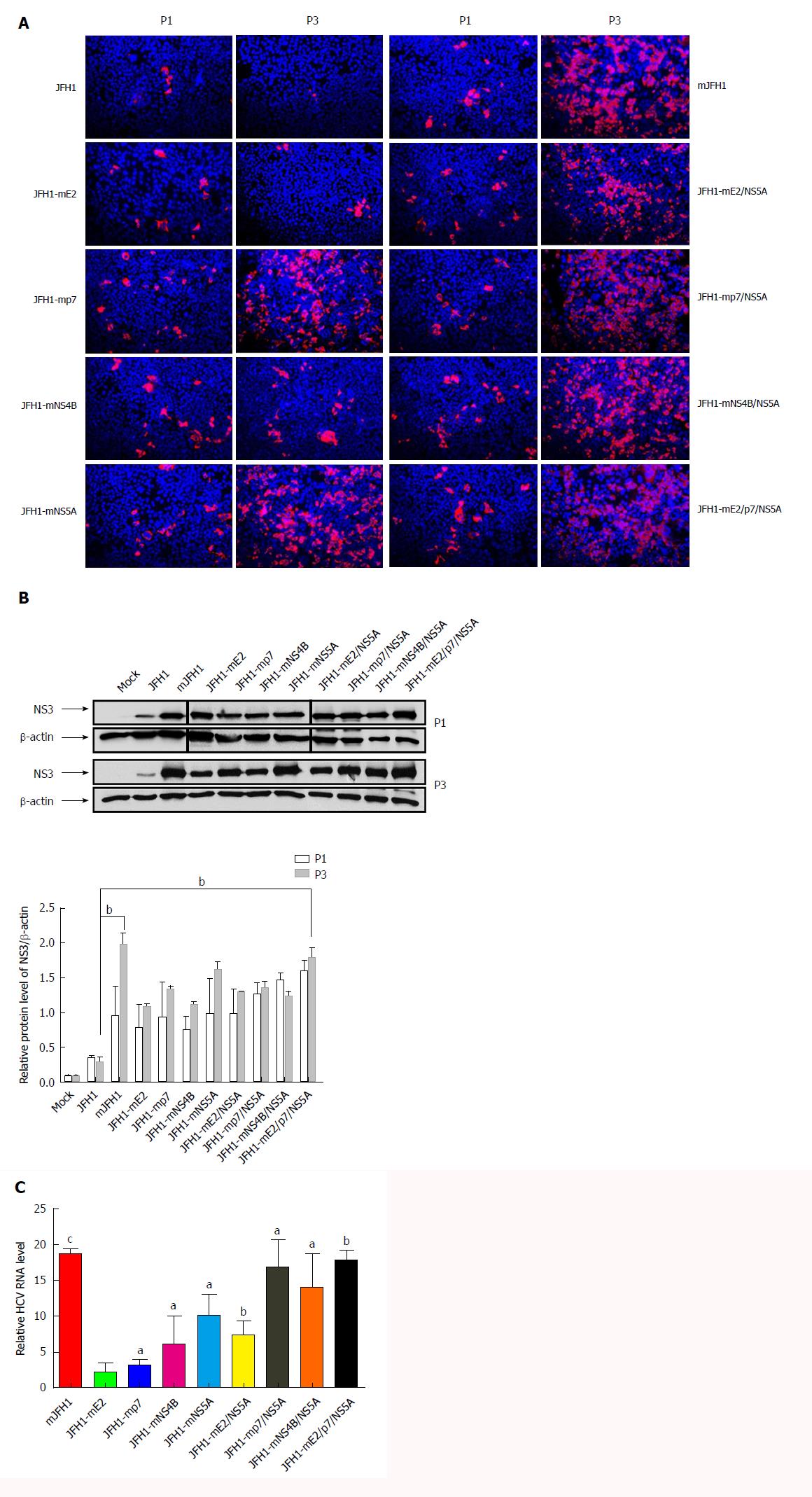
Figure 3 Effects of the adaptive mutations on the hepatitis C virus RNA replication.
A: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA was electroporated into Huh7.5 cells to produce the recombinants of adapted virus. The transfected cells were passaged every 3 d. Cells were fixed 48 h after passage and infected cells were identified by fluorescence immunostaining and microscopy. Nuclear DNA was stained with DAPI (blue); B: HCV RNA was electroporated into Huh7.5 cells to produce the recombinants of adapted virus in cell culture. The transfected cells were passaged every 3 d. Cells were lysed at 72 h after passage. The HCV NS3 protein levels were analysis by Western blot. bP < 0.01; C: HCV RNA levels in cells 3 d after transfection. Intracellular HCV RNA levels were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR. The mean ± SD for three independent experiments are presented (qPCR assays, n = 3). aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001.
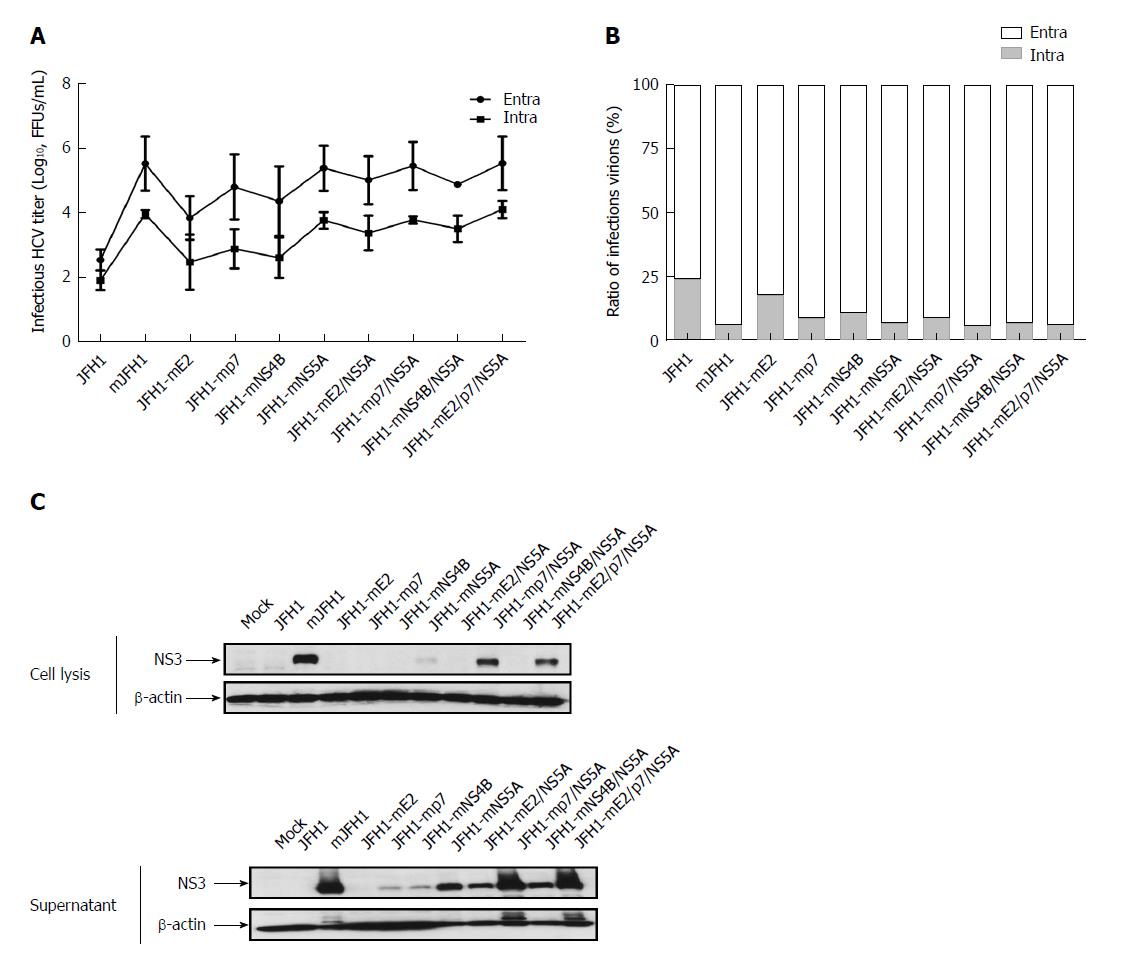
Figure 4 Effect of the adaptive mutations on the virion release.
A: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA was electroporated into Huh7.5 cells to produce the recombinants of adapted virus. At 72 h after transfection, the infectivity titers of the culture supernatants and cell lysates were measured. Viral titers are expressed as FFUs/mL. The data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3); B: HCV RNA was electroporated into Huh7.5 cells to produce the recombinants of adapted virus. At 72 h after transfection, the infectivity titers of the culture media and cell lysates were measured. The extracellular and intracellular viral titers were measured. The relative ratios of infectious virions are shown. The results were from three independent experiments; C: The naive Huh7.5 cells were infected with the culture media and cell lysates. At 72 h after infection, cells were lysed with RIPA buffer, and analyzed by Western blot.
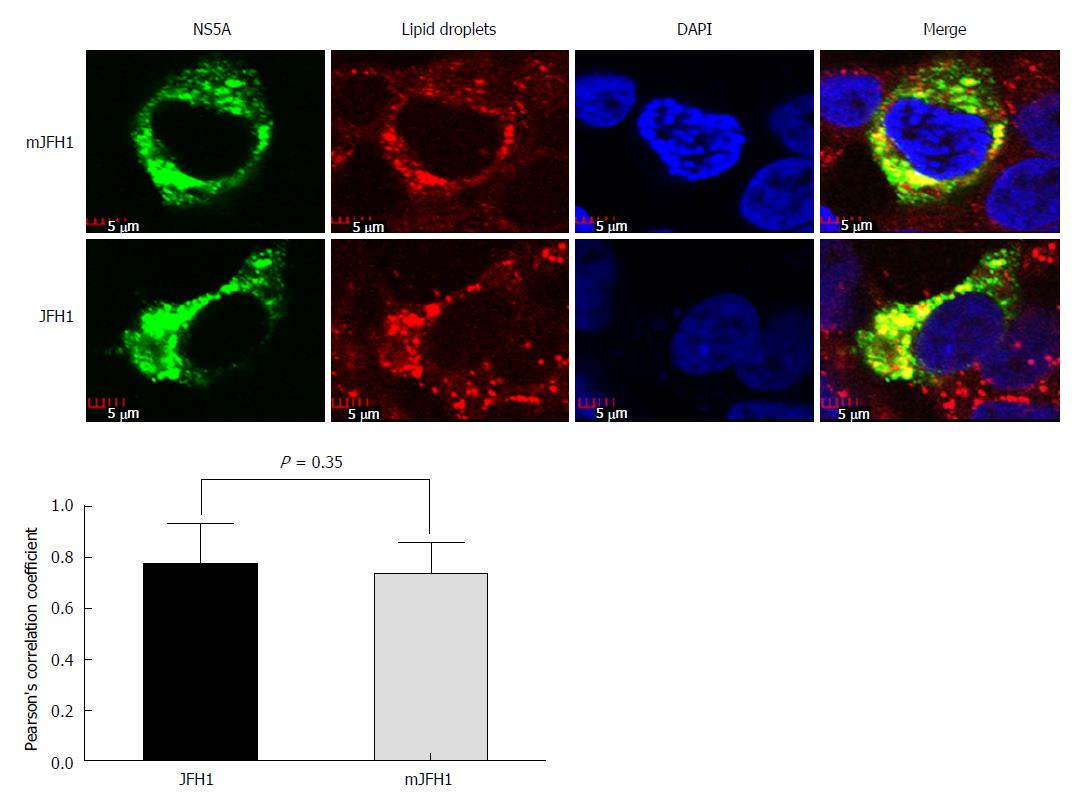
Figure 5 Colocalization analysis of lipid droplets and hepatitis C virus NS5A.
JFH1 and mJFH1 RNA was electroporated into Huh7.5 cells to produce the recombinants of adapted virus. At 48 h after transfection, the cells were fixed. Lipid droplets were stained with LipidTOXRed (Red). The HCV NS5A was stained with anti-NS5A antibody (Green). The nucleus was stained with DAPI (Blue). Each triplicate sample of 25 cells was analyzed using Image J software. The degree of co-localization was quantified and compared using Pearson’s correlation coefficients.
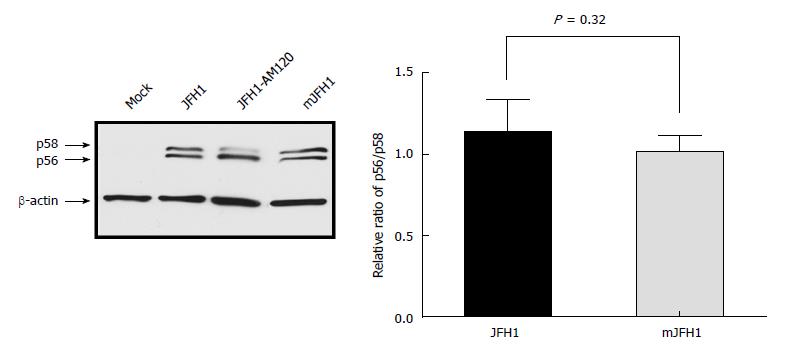
Figure 6 Phosphorylation of NS5A during JFH1 and mJFH1 replication.
Huh7.5 cells were transfected with JFH1 or mJFH1 RNA. After three days of culture, cells were lysed for western blot using anti-NS5A and anti-β-actin antibodies. The quantity of p56 and p58 was determined using Image J software and the ratios of p56/p58 are shown. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). JFH1-AM120 was used as the positive control.
- Citation: Wang Q, Li Y, Liu SA, Xie W, Cheng J. Cell culture-adaptive mutations in hepatitis C virus promote viral production by enhancing viral replication and release. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(12): 1299-1311
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i12/1299.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i12.1299