Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2017; 23(6): 957-963
Published online Feb 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i6.957
Published online Feb 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i6.957
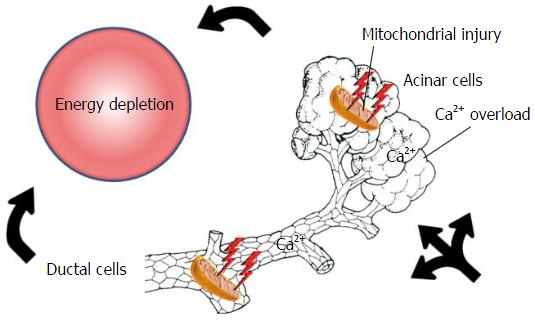
Figure 1 Early events in acute pancreatitis.
Bile acids, ethanol, fatty acids or their non-oxidative metabolites, fatty acid ethyl esthers, induce calcium overload, causing mitochondrial damage and a resultant decrease in intracellular ATP concentration both in acinar and ductal cells. This will lead to general energy depletion in the pancreas.
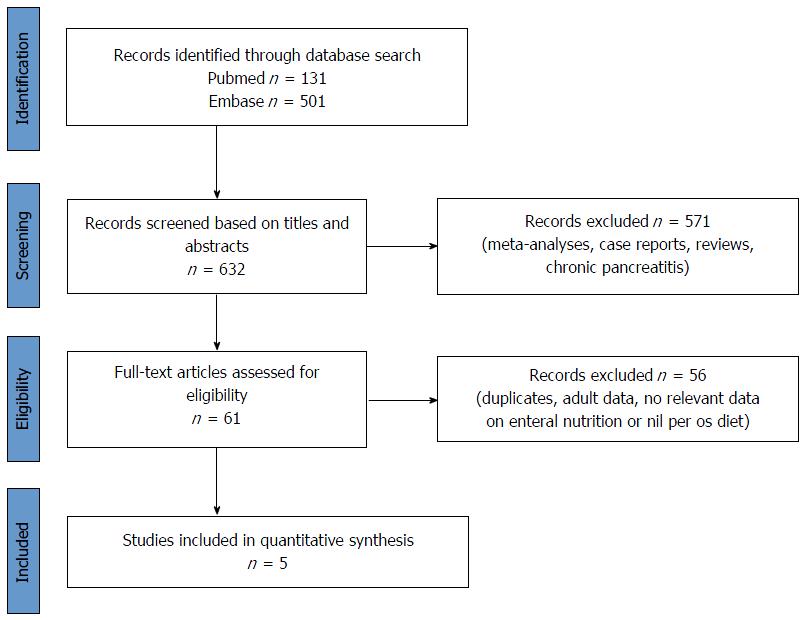
Figure 2 Flow chart on the methods used in the literature search.
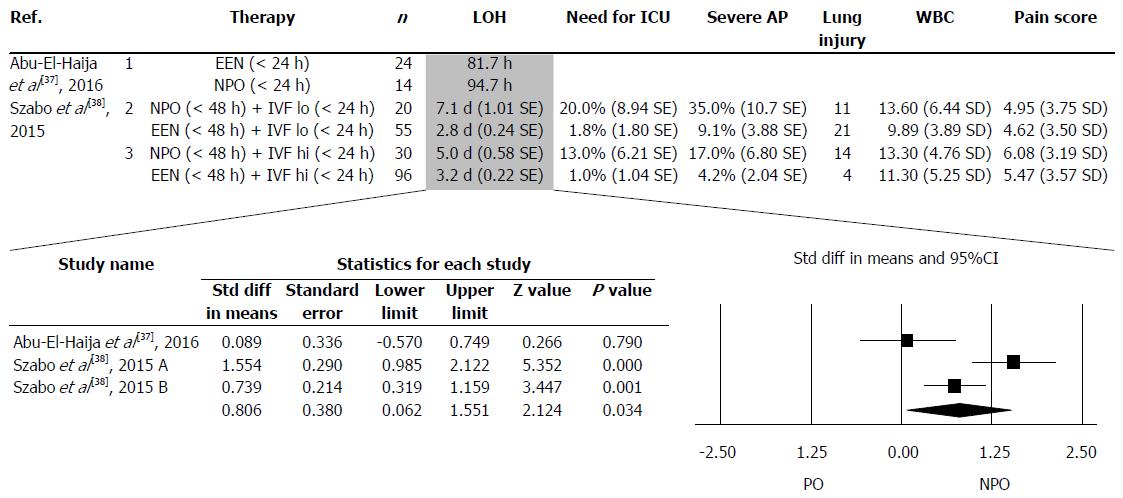
Figure 3 Two articles contained three separate data pairs where early enteral nutrition was compared to nil per os.
LOH: Length of hospitalization; EEN: Early enteral nutrition; NPO: Nil per os. ICU: Intensive care unit; AP: Acute pancreatitis; WBC: White blood cell count.
- Citation: Mosztbacher D, Farkas N, Solymár M, Pár G, Bajor J, Szűcs &, Czimmer J, Márta K, Mikó A, Rumbus Z, Varjú P, Hegyi P, Párniczky A. Restoration of energy level in the early phase of acute pediatric pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(6): 957-963
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i6/957.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i6.957