Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2017; 23(5): 891-898
Published online Feb 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i5.891
Published online Feb 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i5.891
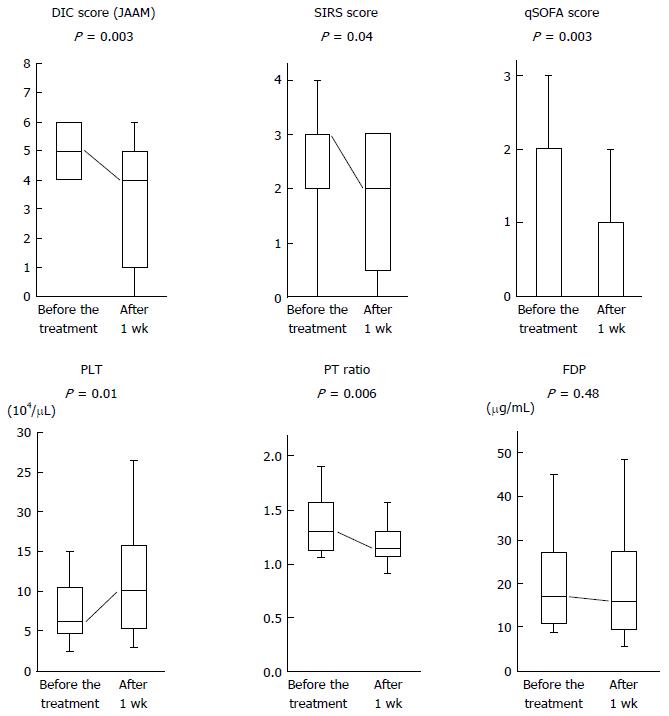
Figure 1 Alterations in disseminated intravascular coagulopathy-associated parameters between before and after 1 wk of treatment with thrombomodulin-α.
Disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC) scores [Japanese Association for Acute Medicine (JAAM)], systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) scores, quick-sequential organ failure assessment (qSOFA) scores, platelet (PLT) counts, prothrombin time (PT) ratios, and fibrin degradation products (FDP) values were compared for before and after 1 wk of thrombomodulin-α (TM-α) treatment. All parameters, except for FDP values, were significantly improved by TM-α administration after 1 wk. The Mann-Whitney U-test was used for the analysis.
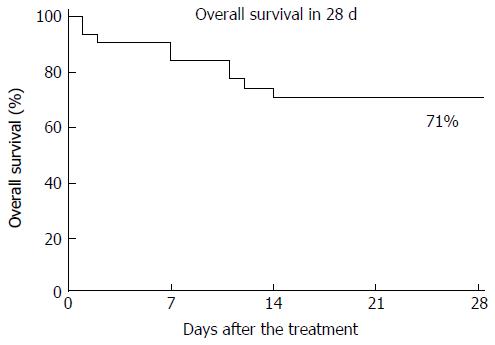
Figure 2 Survival analysis of the disseminated intravascular coagulopathy patients treated with thrombomodulin-α.
Overall survival at 28 d was examined using the Kaplan-Meier method (n = 31) in order to evaluate the efficacy of thrombomodulin-α (TM-α) administration. The patients used in this analysis were treated with TM-α more than 1 d, and the overall survival rate was 71%.
- Citation: Konishi H, Okamoto K, Shoda K, Arita T, Kosuga T, Morimura R, Komatsu S, Murayama Y, Shiozaki A, Kuriu Y, Ikoma H, Nakanishi M, Ichikawa D, Fujiwara H, Otsuji E. Early thrombomodulin-α administration outcome for acute disseminated intravascular coagulopathy in gastrointestinal surgery. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(5): 891-898
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i5/891.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i5.891