Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2017; 23(43): 7765-7775
Published online Nov 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i43.7765
Published online Nov 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i43.7765
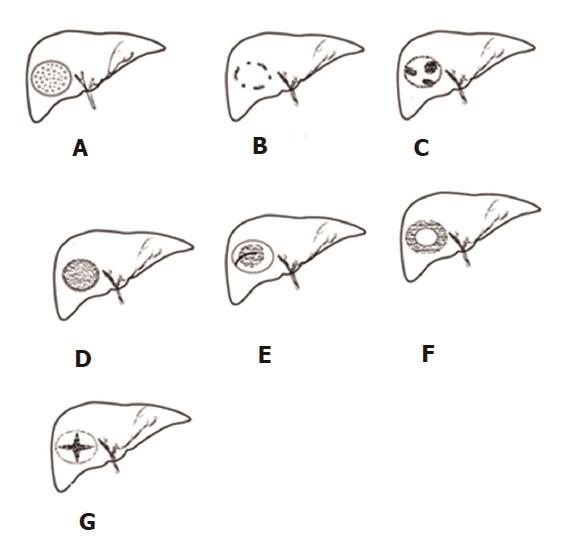
Figure 1 A simplified diagram of the seven superb microvascular imaging types.
A: Type I, diffuse dot-like type; B: Type II, strip rim type; C: Type III, nodular rim type; D: Type IV, diffuse honeycomb type; E: Type V, non-specific type; F: Type VI, thick rim type; G: Type VII, spoke-wheel type.
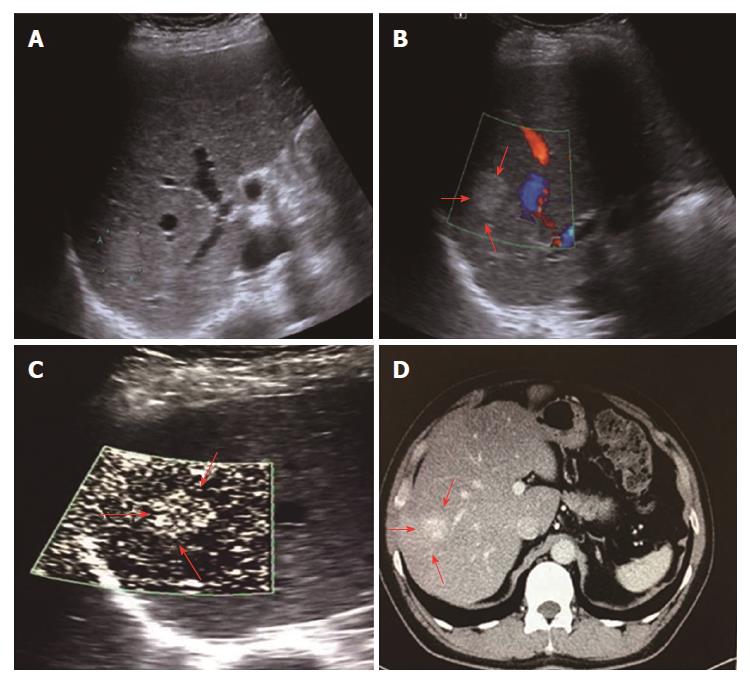
Figure 2 Diffuse dot-like type (type I) in a 52-year-old male diagnosed with hemangioma.
A: A high-echo lesion with a clear margin was evident in the right liver lobe; B: CDFI showed no blood flow signals for this lesion; C: SMI showed a diffuse dot-like microvascular structure; D: Contrast-enhanced CT showed diffuse enhancement of the lesion in the arterial phase. SMI: Superb microvascular imaging.
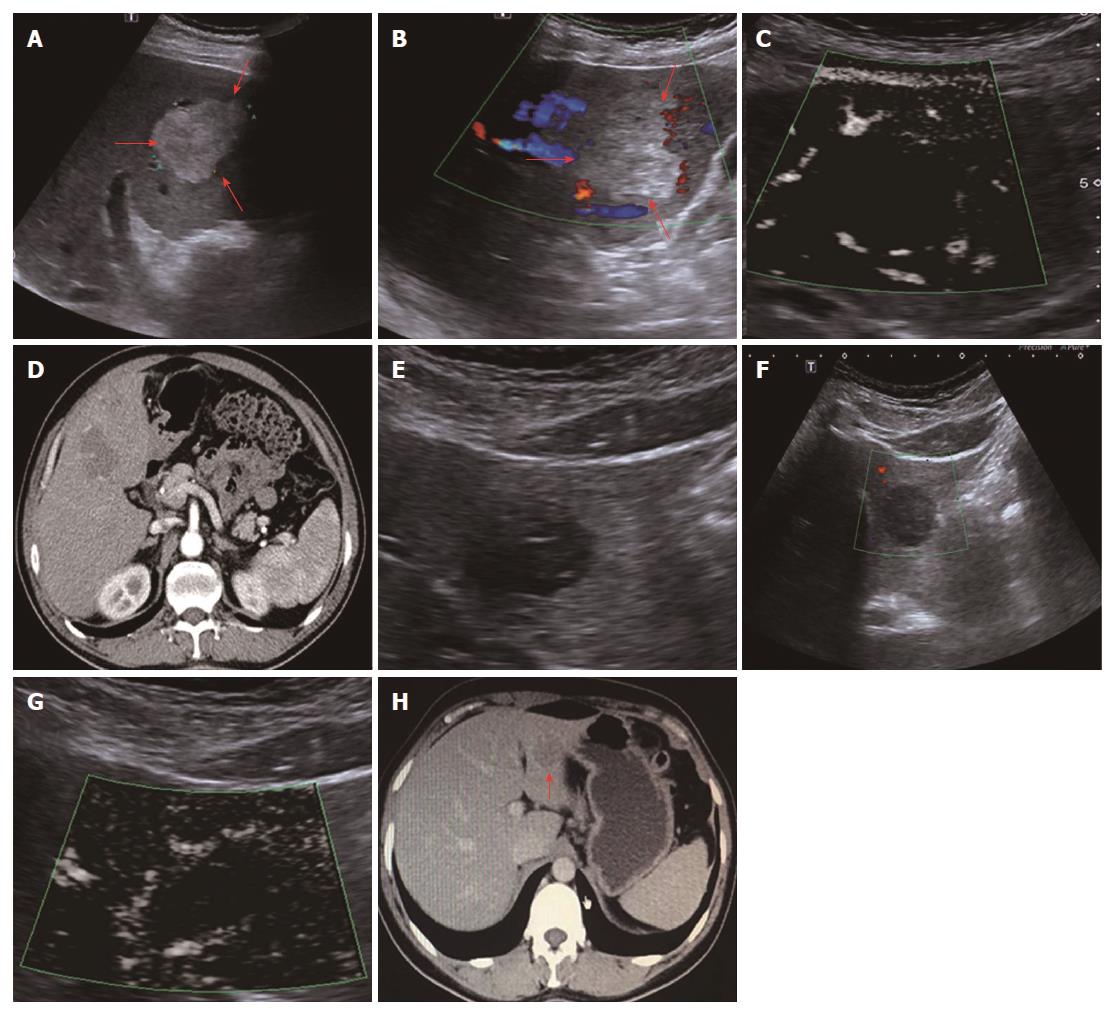
Figure 3 Strip rim type (type II).
A-D: A 61-year-old male diagnosed with hemangioma. A: A high-echo lesion with a clear margin was evident in the left liver lobe; B: CDFI showed an interrupted strip blood flow signal around the edge of this lesion; C: SMI showed a relatively continuous strip rim-distributed microvascular structure; D: Contrast-enhanced CT showed strip rim enhancement of the lesion in the arterial phase. E-H: A 63-year-old male diagnosed with hemangioma. E: A low-echo lesion with a clear margin was evident in the left liver lobe; F: CDFI showed no blood flow signal for this lesion; G: SMI showed a continuous strip rim microvascular structure; H: Contrast-enhanced CT showed strip rim enhancement of the lesion in the arterial phase. SMI: Superb microvascular imaging.
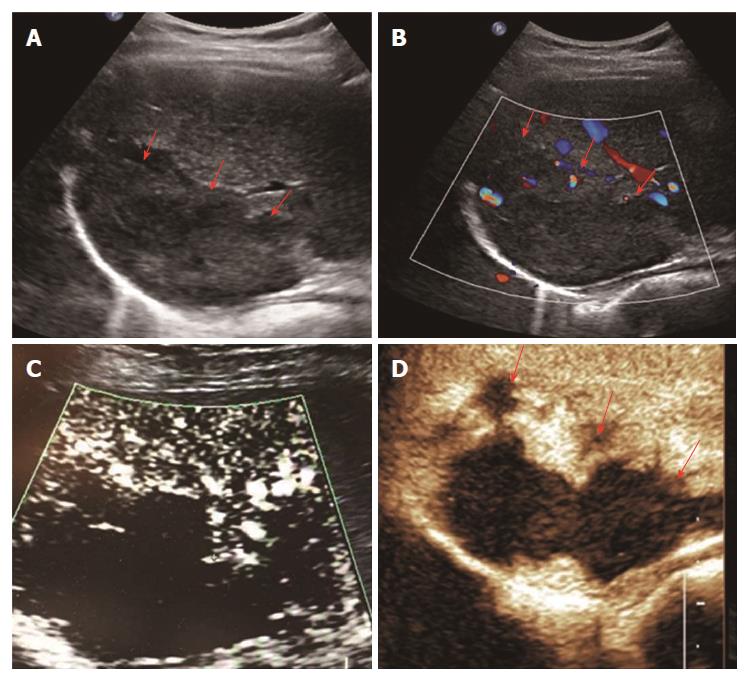
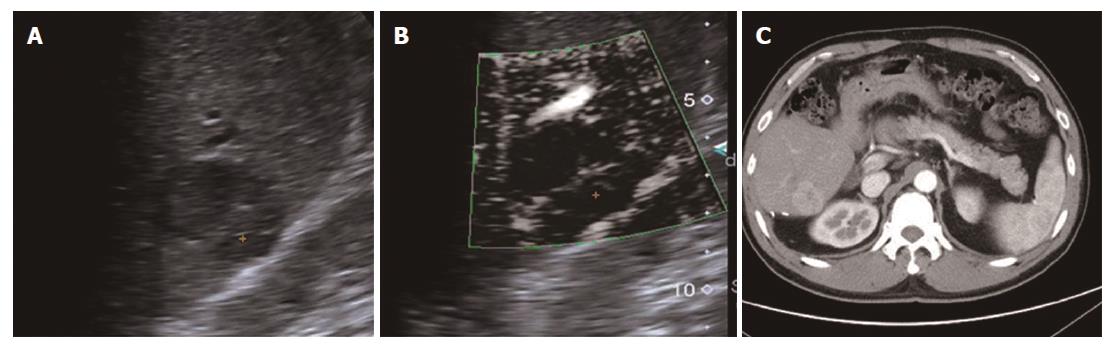
Figure 4 Nodular rim type (type III) in a 51-year-old female diagnosed with hemangioma.
A: A mixed-echo lesion with a relatively clear margin was evident in the right liver lobe; B: CDFI showed a sporadic short strip blood flow signal around the edge of this lesion; C: SMI showed a nodular rim-distributed microvascular structure; D: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound showed nodular rim enhancement of the lesion in the arterial phase. SMI: Superb microvascular imaging.
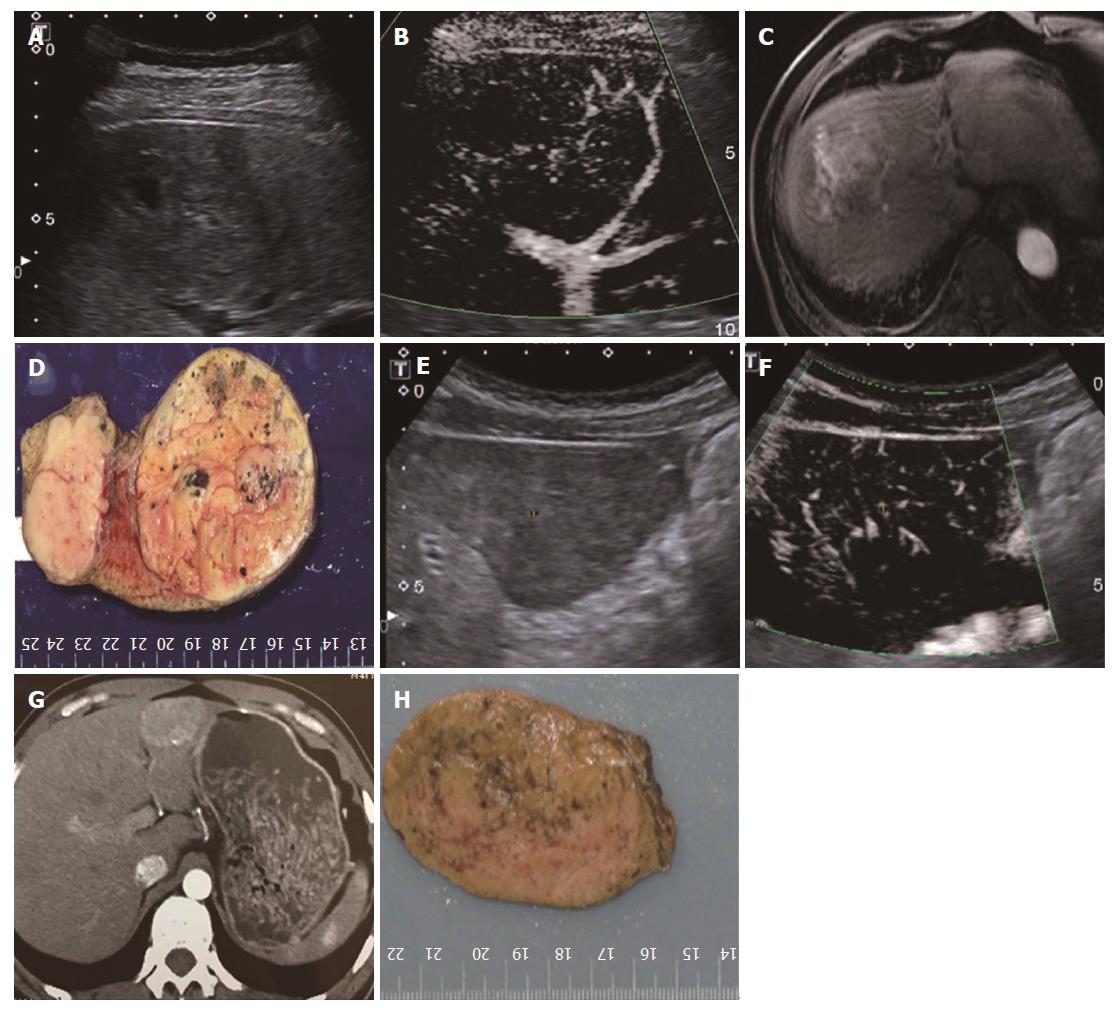
Figure 5 Diffuse honeycomb type (type IV).
A-D: A 68-year-old male diagnosed with hepatic cellular carcinoma. A: A mixed-echo lesion with a relatively unclear margin was evident in the right liver lobe; B: SMI showed a diffuse honeycomb-distributed microvascular structure; C: Contrast-enhanced MRI showed diffuse enhancement of the lesion in the arterial phase; D: The pathology result showed that the inter-tumor blood vessels were distributed in a grid pattern resembling honeycombs. E-H: A 41-year-old male diagnosed with hepatic adenoma. E: A hypo-echo lesion with a clear margin was evident in the left liver lobe; F: SMI showed a diffuse honeycomb-distributed microvascular structure; G: Contrast-enhanced CT showed diffuse enhancement of the lesion in the arterial phase; H: The pathology result showed that the inter-tumor blood vessels were distributed in a grid pattern resembling honeycombs. SMI: Superb microvascular imaging.
Figure 6 Non-specific type (type V) in a 48-year old male diagnosed with hepatic cellular carcinoma.
A: A low-echo lesion with a relatively clear margin was evident in the right liver lobe; B: SMI showed a microvascular distribution of a strip trunk with tiny branches ; C: Contrast-enhanced CT showed diffuse enhancement of the lesion in the arterial phase. SMI: Superb microvascular imaging.
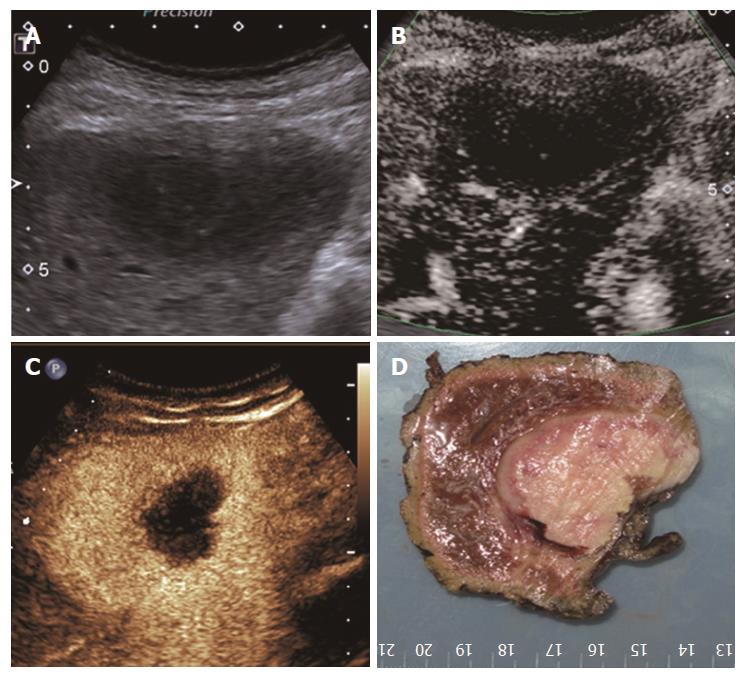
Figure 7 Thick rim type (type VI) in a 71-year-old male diagnosed with primary hepatic lymphoma.
A: A low-echo lesion with a relatively clear margin was evident in the left liver lobe; B: SMI showed a thick rim-distributed microvascular structure; C: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound showed thick rim enhancement of the lesion in the arterial phase; D: The gross pathology result showed a thick rim distribution of the vasculature. SMI: Superb microvascular imaging.
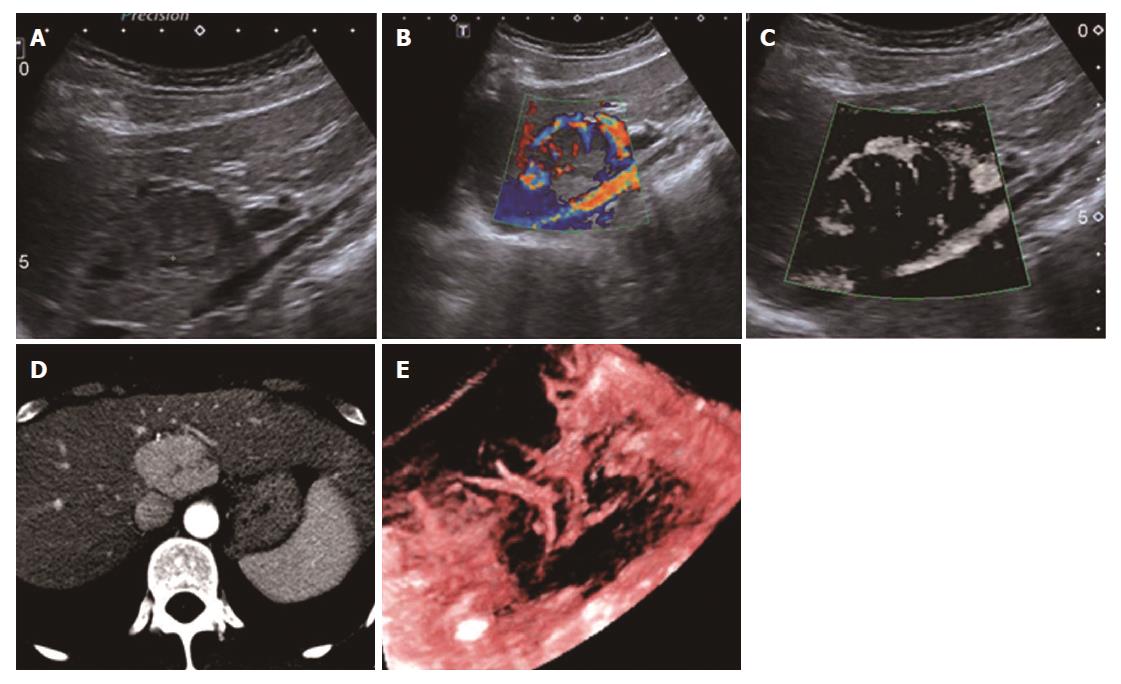
Figure 8 Spoke-wheel type (type VII) in a 39-year-old female diagnosed with focal nodular hyperplasia.
A: A low-echo lesion with a relatively clear margin was evident in the caudate liver lobe; B: CDFI showed a spoke-wheel blood flow signal of this lesion; C: SMI showed a spoke-wheel-distributed microvascular structure; D: Contrast-enhanced CT showed diffuse enhancement with a central scar of the lesion in the arterial phase; E: 3-D vascular remodeling of this lesion was successfully achieved and showed spoke-wheel blood flow. SMI: Superb microvascular imaging.
- Citation: He MN, Lv K, Jiang YX, Jiang TA. Application of superb microvascular imaging in focal liver lesions. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(43): 7765-7775
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i43/7765.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i43.7765