Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2017; 23(33): 6111-6118
Published online Sep 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i33.6111
Published online Sep 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i33.6111
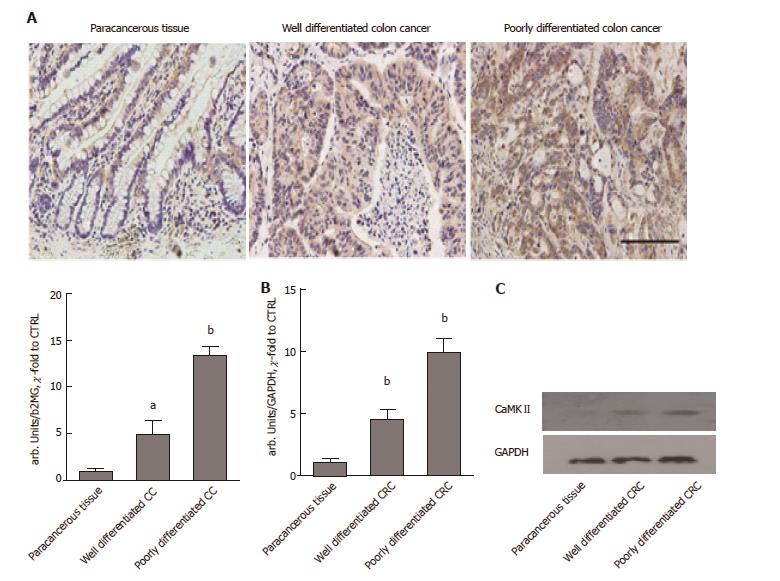
Figure 1 CaMKII over-expressed in colon cancer.
A: Immunochemistry staining of CaMKII in paracancerous tissue, well-differentiated colon cancer and poorly differentiated colon cancer samples. Scale bar, 100 μm; B: qRT-PCR of CaMKII mRNA in paraffin-embedded paracancerous tissue, well-differentiated colon cancer and poorly differentiated colon cancer samples; C: Western blot of CaMKII protein in paraffin-embedded paracancerous tissue, well-differentiated colon cancer and poorly differentiated colon cancer samples. All data are presented as the mean ± standard error of at least three independent experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs paracancerous tissue.
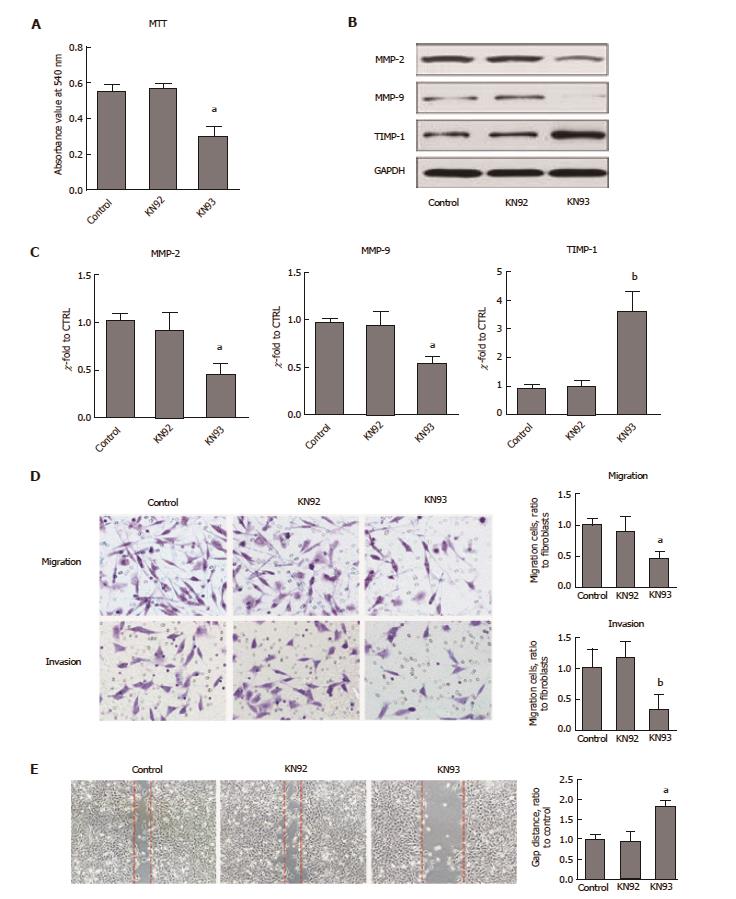
Figure 2 CaMKII is required for colon cancer proliferation and migration.
Human colon cancer cells HCT116 were treated with or without KN93 or KN92 at 10 μmol/L for 24 h. A: MTT analysis for cell proliferation; B: Western blot of MMP2, MMP9 and TIMP-1; C: qRT-PCR assay of MMP2, MMP9 and TIMP-1; D: Immigration and invasion analysis by T transwell assay; E: Wound-healing test. All data are presented as the mean ± standard error SE of at least three independent experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control group.
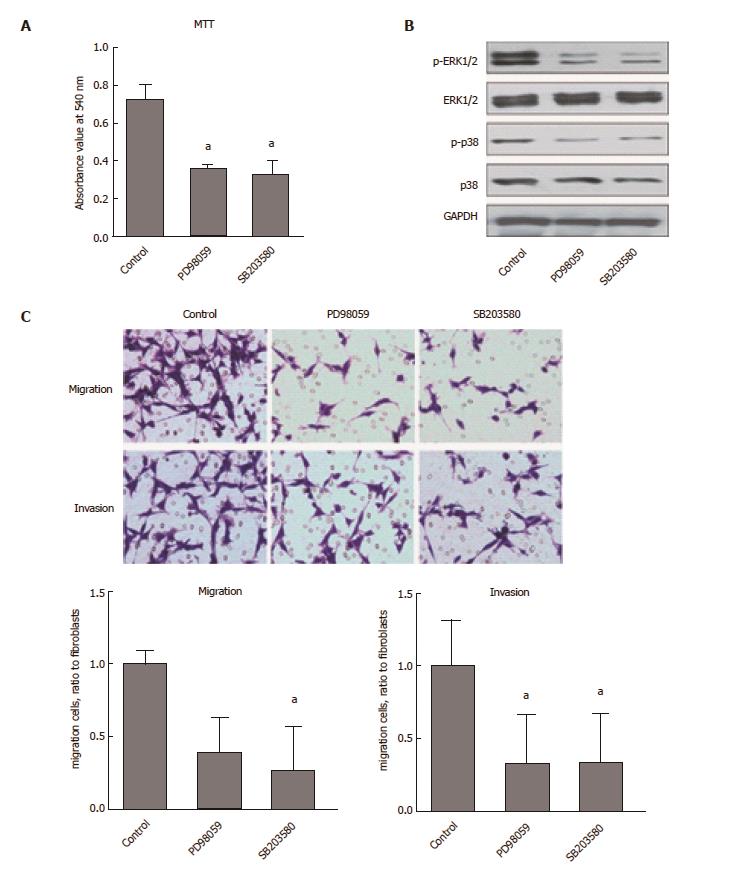
Figure 3 CaMKII regulates colon cancer cells proliferation and migration via ERK1/2- and p38-dependent pathways.
Human colon cancer cells HCT116 were treated with or without PD98059 (50 μmol/L) or SB203580 (10 μmol/L) for 24 h. A: MTT assay for cell proliferation; B: Western blot analysis of ERK1/2, phosphor-ERK1/2, p38 and phosphor-p38; C: Immigration and invasion analysis by T transwell assay. All data are presented as the mean ± standard error SE of at least three independent experiments. aP < 0.05, vs control group.
- Citation: Chen W, An P, Quan XJ, Zhang J, Zhou ZY, Zou LP, Luo HS. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II regulates colon cancer proliferation and migration via ERK1/2 and p38 pathways. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(33): 6111-6118
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i33/6111.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i33.6111