Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2017; 23(33): 6088-6099
Published online Sep 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i33.6088
Published online Sep 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i33.6088
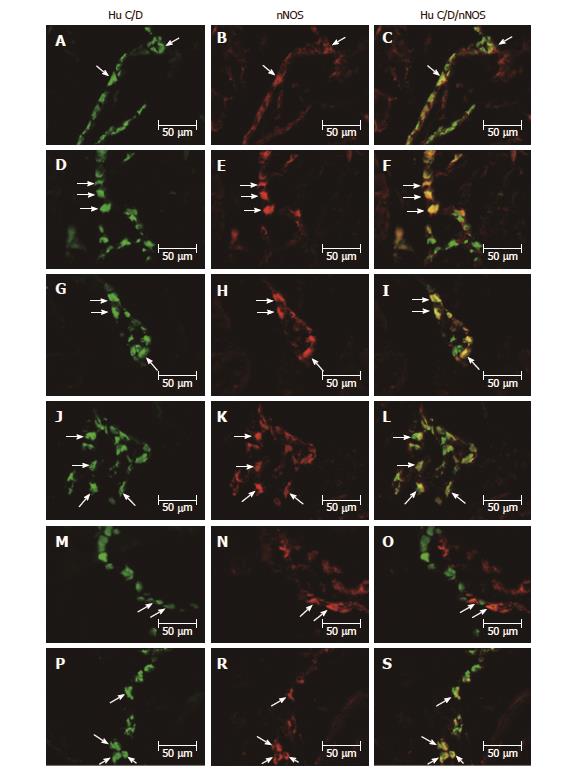
Figure 1 Myenteric ganglion of the porcine stomach under physiological condition and after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to nNOS.
A: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D; B: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum under physiological condition immunoreactive to nNOS; C: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D and n NOS; D: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D; E: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to nNOS; F: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D and nNOS; G: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D; H: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to nNOS; I: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D and nNOS; J: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D; K: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to nNOS; L: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D and nNOS; M: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine pylorus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D; N: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine pylorus under physiological condition immunoreactive to nNOS; O: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine pylorus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D and nNOS; P: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine pylorus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D; R: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine pylorus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to nNOS; S: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D and nNOS. The right column of the pictures shows the overlap of both stainings. Colocalization of both antigens in the studied cell bodies are indicated with arrows. nNOS: Neuronal isoform of nitric oxide synthase; Hu C/D: Pan-neuronal marker.
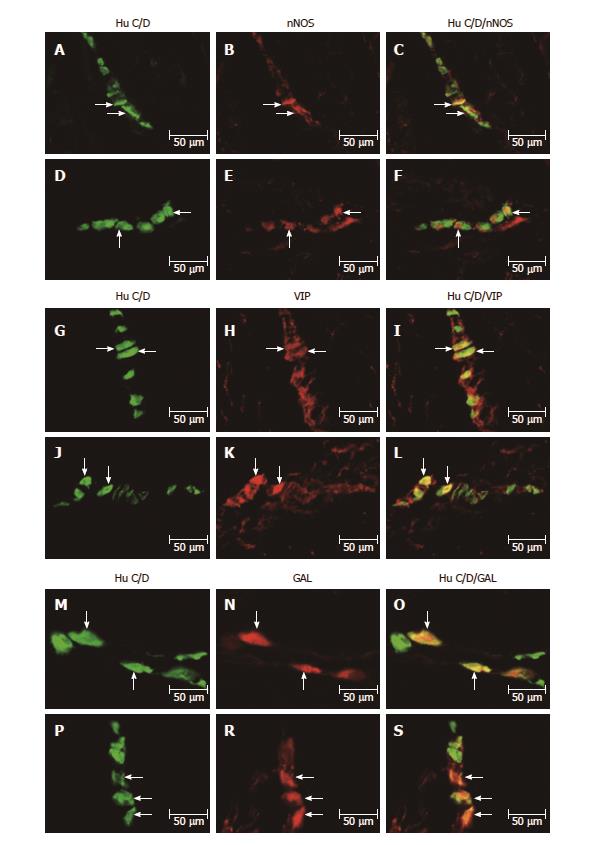
Figure 2 Submucosal ganglion of the porcine stomach under physiological condition and after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to nNOS, VIP and GAL.
A: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D; B: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to nNOS; C: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D and n NOS; D: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D; E: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to nNOS; F: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D and nNOS; G: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D; H: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to VIP; I: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D and VIP; J: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D; K: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to VIP; L: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D and VIP; M: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D; N: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to GAL; O: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D and GAL; P: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D; R: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to GAL; S: Submucosal ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D and GAL. The right column of the pictures shows the overlap of both stainings. Colocalization of both antigens in the studied cell bodies are indicated with arrows. nNOS: Neuronal isoform of nitric oxide synthase; VIP: Vasoactive intestinal peptide; GAL: Galanin; Hu C/D: Pan-neuronal marker.
Figure 3 Myenteric ganglion of the porcine stomach under physiological condition and after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to VIP.
A: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D; B: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum under physiological condition immunoreactive to VIP; C: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D and VIP; D: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D; E: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to VIP; F: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D and VIP; G: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D; H: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to VIP; I: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D and VIP; J: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D; K: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to VIP; L: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D and VIP; M: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine pylorus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D; N: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine pylorus under physiological condition immunoreactive to VIP; O: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine pylorus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D and VIP; P: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine pylorus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D; R: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine pylorus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to VIP; S: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D and VIP. The right column of the pictures shows the overlap of both stainings. Colocalization of both antigens in the studied cell bodies are indicated with arrows. VIP: Vasoactive intestinal peptide; Hu C/D: Pan-neuronal marker.
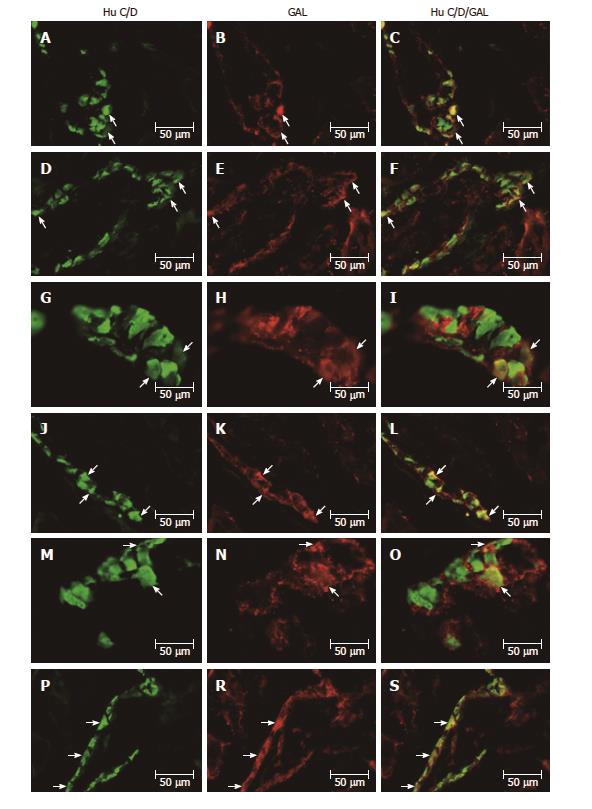
Figure 4 Myenteric ganglion of the porcine stomach under physiological condition and after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to GAL.
A: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D; B: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum under physiological condition immunoreactive to GAL; C: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D and GAL; D: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D; E: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to GAL; F: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine antrum after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D and GAL; G: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D; H: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to GAL; I: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D and GAL; J: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D; K: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to GAL; L: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D and GAL; M: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine pylorus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D; N: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine pylorus under physiological condition immunoreactive to GAL; O: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine pylorus under physiological condition immunoreactive to Hu C/D and GAL; P: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine pylorus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D; R: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine pylorus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to GAL; S: Myenteric ganglion of the porcine corpus after streptozotocine treatment immunoreactive to Hu C/D and GAL. The right column of the pictures shows the overlap of both stainings. Colocalization of both antigens in the studied cell bodies are indicated with arrows. GAL: Galanin; Hu C/D: Pan-neuronal marker.
- Citation: Bulc M, Palus K, Zielonka Ł, Gajęcka M, Całka J. Changes in expression of inhibitory substances in the intramural neurons of the stomach following streptozotocin- induced diabetes in the pig. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(33): 6088-6099
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i33/6088.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i33.6088