Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2017; 23(28): 5158-5166
Published online Jul 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5158
Published online Jul 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5158
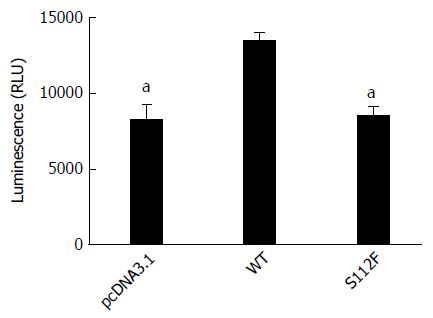
Figure 1 Effect of the class B scavenger receptor I single amino acid mutant on hepatitis C virus entry.
Huh7-siSR-BI cells were seeded on a 96-well plate, cultured overnight, and transfected with pcDNA3.1 (NC), pcDNA-SR-BI, or pcDNA-SR-BI/S112F. Three days after transfection, HCVpp were added to the cell culture. Cells were harvested 72 h post infection and cell lysates were analyzed using a fluorescence assay. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments (aP < 0.05). WT: Wild type.
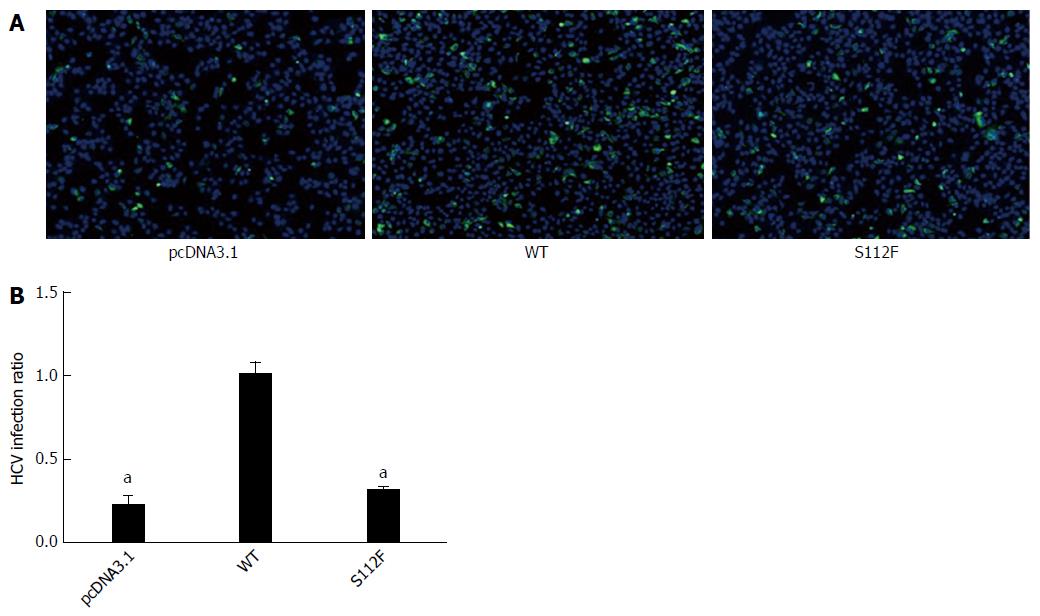
Figure 2 Effect of the class B scavenger receptor I single amino acid mutant on hepatitis C virus infectivity.
A: Immunofluorescence assay (IFA) of the effects of the SR-BI single amino acid mutant on hepatitis C virus (HCV) infectivity. Huh7-siSR-BI cells were seeded in 96-well plates, cultured overnight, and then transfected with pcDNA3.1 (NC), pcDNA-SR-BI (WT), or pcDNA- SR-BI/S112F. HCVcc (103 FFU/mL) was added 24 h after transfection, and the IFA was performed 48 h later. B: Effect of the SR-BI single amino acid mutant on the HCV viral RNA. Huh7-siSR-BI cells were seeded in 24-well plates, cultured overnight, and then transfected with pcDNA3.1 (NC), pcDNA-SR-BI, or pcDNA-SR-BI/S112F. HCVcc (104 FFU/mL) was added 24 h after transfection, and cells were harvested 72 h later to prepare RNA for the qRT-PCR analysis (aP < 0.05). SR-BI: Class B scavenger receptor I; WT: Wild type.
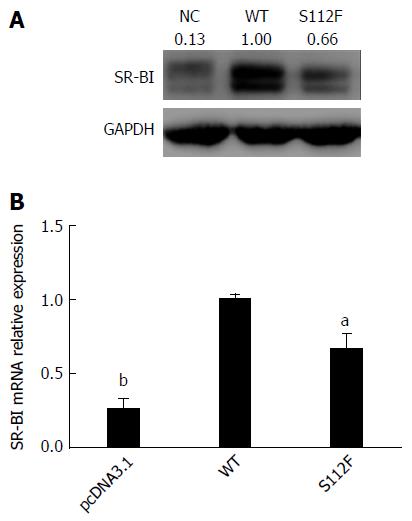
Figure 3 Effects of the single amino acid mutant on class B scavenger receptor I mRNA and protein expression.
A: Effect of the single amino acid mutant on SR-BI protein expression. Huh7-siSR-BI cells were seeded in 24-well plates, cultured overnight, and transfected with pcDNA3.1 (NC), pcDNA-SR-BI, or pcDNA-SR-BI/S112F. Cells were harvested 72 h after transfection and lysed with RIPA cell lysis buffer; Western blot was performed to analyze the expression of the SR-BI protein. B: Effect of the single amino acid mutant on the SR-BI mRNA level. Huh7-siSR-BI cells were seeded in 24-well plates, cultured overnight, and then transfected with pcDNA3.1 (NC), pcDNA-SR-BI (WT), or pcDNA-SR-BI/S112F (S112F). Cells were harvested 72 h after transfection and RNA was isolated and the level of the SR-BI mRNA was analyzed using qRT-PCR (aP < 0.05; bP < 0.001). SR-BI: Class B scavenger receptor I; WT: Wild type.
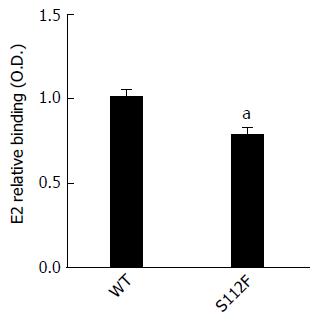
Figure 4 Ability of the class B scavenger receptor I single amino acid mutant to bind to the hepatitis C virus E2 protein.
CHO cells expressing the wild type (WT) and mutant SR-BI protein were incubated with equivalent amounts of hepatitis C virus E2 protein that had been expressed in HEK 293T cells for 1 h at RT, washed twice, and incubated with an anti-E2 mAb for 1 h at RT. After labeling with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (Invitrogen), the mean fluorescence intensity was quantified by flow cytometry (aP < 0.05). SR-BI: Class B scavenger receptor I.
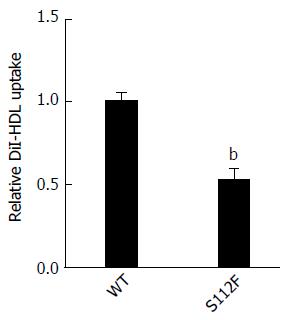
Figure 5 Effect of the single amino acid mutant on high-density lipoprotein absorption by class B scavenger receptor I.
Huh7-siSR-BI cells were seeded in a 96-well plate and cultured overnight prior to transfection. Cells were transfected with the SR-BI wild type (WT) and mutant S112F plasmids using LipofectamineTM. Complete culture medium was replaced 6 h after transfection and cells were cultured for 48 h before DiI-HDL (200 μg/mL) was added, and the cells were cultured for an additional 4 h. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst for 10 min, and cells were observed and images captured using a microscope (bP < 0.01). SR-BI: Class B scavenger receptor I.
- Citation: Gao R, Gao W, Xu G, Xu J, Ren H. Single amino acid mutation of SR-BI decreases infectivity of hepatitis C virus derived from cell culture in a cell culture model. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(28): 5158-5166
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i28/5158.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5158